Home>How-To Guides>Tips and Tricks>What Is A Subtitle In An Essay

Tips and Tricks
What Is A Subtitle In An Essay
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn the tips and tricks for using subtitles in an essay effectively. Discover how to make your writing more organized and engaging with subtitles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When writing an essay, the title is often the first thing readers encounter. It serves as a gateway to the content, providing a concise and informative summary of the essay's main theme or argument. This article explores the world of titles and subtitles, examining their significance, conventions, and best practices across various academic disciplines.
The Importance of Titles
A well-crafted title is crucial for several reasons:
- Sets the Tone: Indicates the essay's focus and influences reader expectations.
- Reflects Expertise: Demonstrates the author's creativity and preparation.
- Engages Readers: Must be engaging and informative without being overly simplistic or misleading.
As Ryan Wepler notes in "Composing an Effective Title," the title "conveys what a piece of writing is or what it is about," and it "will begin to make assumptions about your creativity, preparation, and expertise" among readers.
Types of Titles
Academic Titles
Academic titles vary significantly depending on the discipline:
- Humanities: Often identify both the subject area and the text(s) the paper will analyze. Example: "Representing ‘Other’ Diasporas in Recent Global Canadian Fiction."
- Social Sciences: Aim to present the subject of the paper as simply and directly as possible. According to the APA style guide, the title should be a concise statement of the main topic, identifying the actual variables or theoretical issues under investigation and their relationship.
Non-Academic Titles
Non-academic titles, such as those found in journalism, creative nonfiction, and web writing, must account for the audience's purpose in reading:
- Informative: Direct and informative titles for readers seeking information. Example: "Inland Oil Spill Raises Detection Concerns."
- Experiential: Titles that enhance the way readers experience the subject. These titles work in conversation with the text, expanding and developing as the essay progresses.
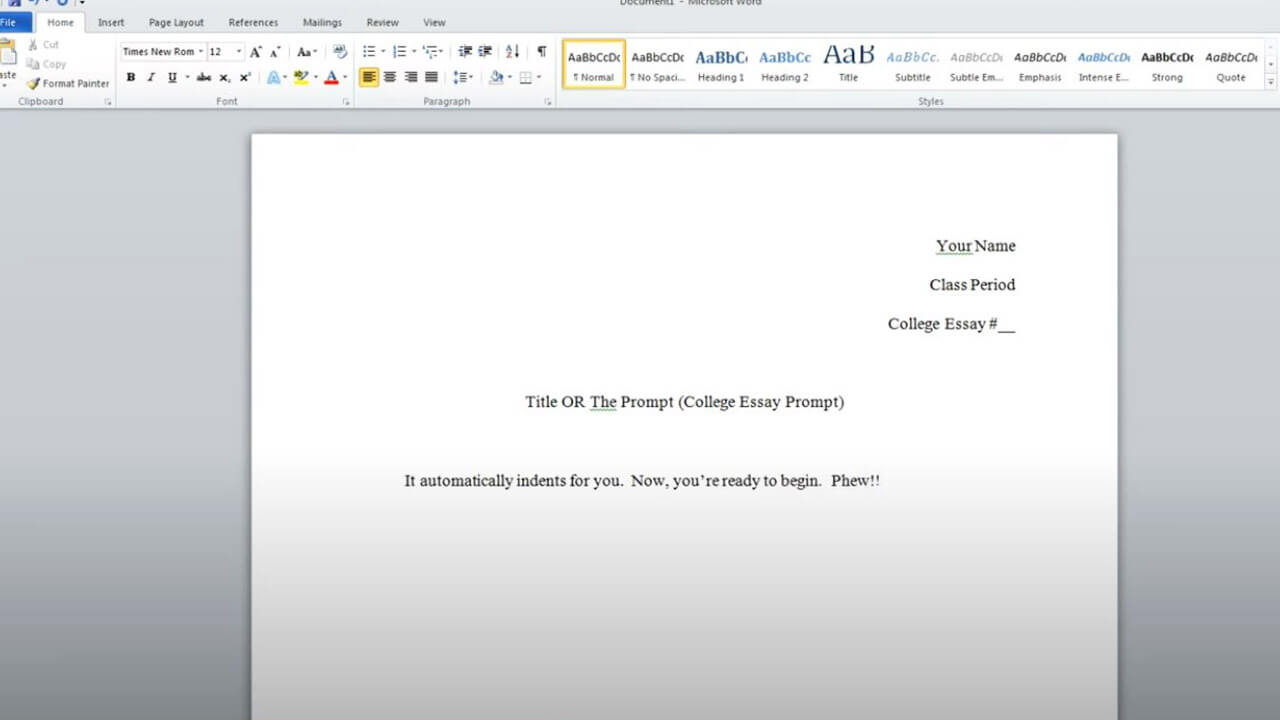
The Role of Subtitles
Subtitles provide additional context or specificity. The "title: subtitle" format is prevalent in academic writing because it allows for a greater range of possibilities than using a title alone. For instance, "Nixonland: The Rise of a President and the Fracturing of a Nation" uses a subtitle to provide more detail about the subject matter. In humanities papers, subtitles can be more suggestive, with their meaning becoming fully clear only after reading the paper. However, they should not be so economical that they limit specificity.
Conventions for Titles and Subtitles
APA Style
- Titles of academic works should be italicized in the body of the paper. This includes books, reports, webpages, and other stand-alone works.
- Periodicals (journals, magazines, newspapers) should also be italicized.
- Titles of parts within a complete work, such as chapters or articles, should be placed in quotation marks.
MLA Style
- Titles of sources should not be capitalized unless they are proper nouns.
- Subtitles should be separated from the main title by a colon and a space. Example: "The title of source is the second core element in the Works Cited entry. In general, the title of a work is taken from the title page of the publication."
HTML Titles and Subtitles
- Titles and subtitles are structured using the
<h1>tag for the main title and<h2>to<h6>tags for subtitles. - The
<h1>tag is used to determine the title of the page and should be placed at the beginning of the text. Each page should have only one<h1>tag. - Subtitles can be used more than once on a page but should be used judiciously.
Best Practices for Crafting Titles
- Conciseness: Titles should be concise yet informative. Avoid using nonquantitative, meaningless words such as "rapid" and "new." Instead, choose specific terms that accurately reflect the content of your essay.
- Clarity: Ensure that your title is clear and free of ambiguity. Avoid using phrases like "on the," "a study of," "research on," "regarding," and "use of." These phrases can make your title less specific and less engaging.
- Specificity: Use specific language in your title. For example, "a vanadium-iron alloy" is more specific than "a magnetic alloy."
- Engagement: Your title should be engaging and capture the reader's attention. Use vibrant, vivid language in humanities papers to make your title more suggestive and intriguing.
- Discipline-Specific Conventions: Adhere to the conventions of your discipline. For instance, social science titles should be concise statements of the main topic, while humanities titles may include more elaborate descriptions.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Avoid Quantitative Information: Titles should not provide quantitative or semi-quantitative information. This information is best left to the abstract or the full text of the article.
- Avoid Study Names: In medical journals, study names are rarely used in titles. Instead, focus on providing a clear and concise summary of the study's main theme or argument.
- Use of Subtitles: While subtitles can be useful, avoid using them if they do not add significant context to your title. Subtitles should be used judiciously to avoid cluttering the title.
Final Thoughts
Crafting an effective title is a critical aspect of writing an essay. It sets the tone for the reader, reflects the author's expertise, and influences the reader's expectations. By understanding the conventions and best practices for titles and subtitles in various academic disciplines, authors can create titles that are both informative and engaging. Whether writing in humanities, social sciences, or non-academic fields, a well-crafted title is essential for capturing the reader's attention and guiding them through the essay.

