Home>Latest News>Technology Trends>How Does Mixed Reality Expand On Augmented Reality?


Technology Trends
How Does Mixed Reality Expand On Augmented Reality?
Modified: May 29, 2024
Discover how mixed reality takes technology trends to the next level, expanding on augmented reality to create immersive experiences and innovative applications. Explore the future of digital interaction.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the realms of augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) have garnered significant attention and intrigue. These immersive technologies have revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with the digital world, blurring the lines between the physical and virtual realms. As we delve into the intricacies of mixed reality, it's essential to first comprehend the foundations of augmented reality and how mixed reality expands upon it.
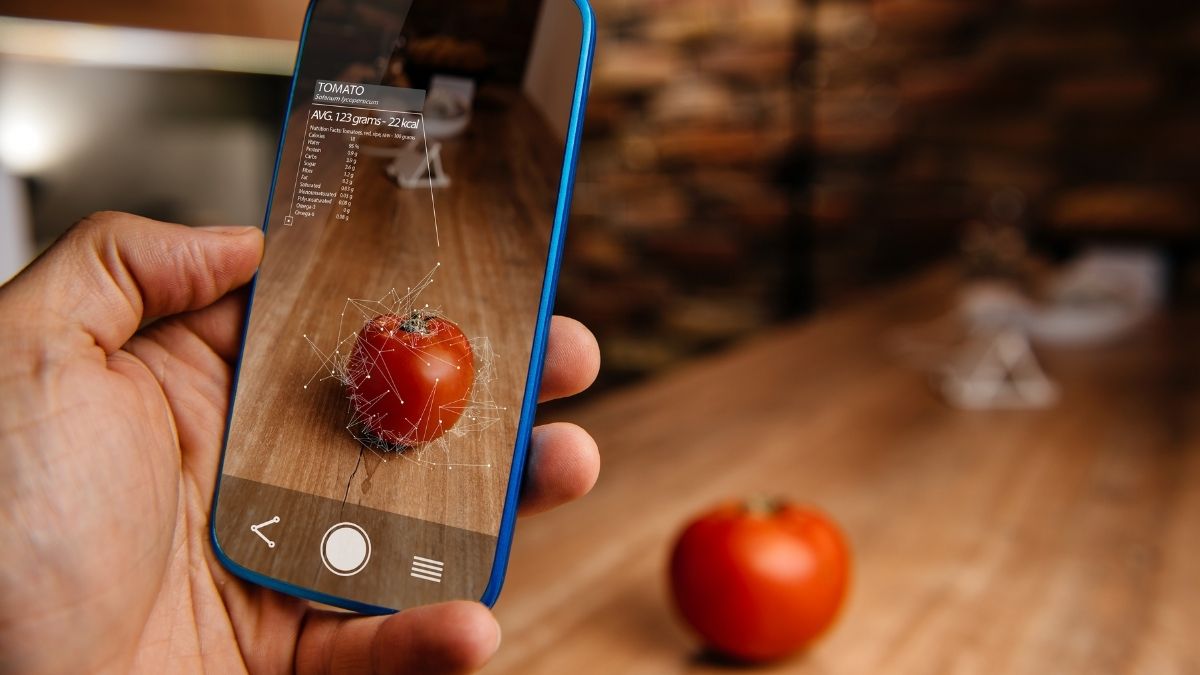
Augmented reality, often abbreviated as AR, integrates digital information and virtual elements into the user's real-world environment. This technology overlays computer-generated content, such as images, videos, or 3D models, onto the physical surroundings, thereby enhancing the user's perception and interaction with the environment. AR has found widespread applications across various industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, and retail, offering immersive experiences and innovative solutions to real-world challenges.
On the other hand, mixed reality represents a significant advancement in the fusion of digital and physical worlds. Unlike AR, which superimposes virtual elements onto the real world, mixed reality seamlessly integrates virtual objects into the user's environment, allowing for interactive and dynamic experiences. This technology enables users to interact with and manipulate virtual objects as if they were part of the physical space, blurring the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds in a more cohesive manner.
As we embark on this exploration of mixed reality, it's crucial to recognize the transformative potential of this technology and its capacity to redefine human-computer interaction. By bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms, mixed reality opens up a myriad of possibilities, ranging from immersive entertainment experiences to innovative solutions in fields such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the nuances of augmented reality and delve into the intricacies of mixed reality, shedding light on its advantages, applications, and the challenges it presents. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these immersive technologies, we can grasp the profound impact they have on reshaping our digital experiences and redefining the boundaries of reality itself.
Read more: How Does Augmented Reality Work
Understanding Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) represents a groundbreaking technological paradigm that seamlessly integrates virtual elements into the user's real-world environment. This transformative technology enhances the user's perception of reality by overlaying computer-generated content onto the physical surroundings, thereby creating a composite view that blends the virtual and physical realms.
At the core of augmented reality lies the concept of enhancing the user's sensory experience through the integration of digital information. By leveraging advanced computer vision, spatial mapping, and sensory input technologies, AR applications can precisely identify and track the user's physical environment, enabling the seamless integration of virtual content in real time. This real-time overlay of digital information onto the physical world empowers users to interact with and manipulate virtual elements within their immediate surroundings, fostering immersive and interactive experiences.
The applications of augmented reality span across diverse domains, ranging from entertainment and gaming to education, healthcare, and retail. In the realm of gaming, AR has redefined the traditional gaming experience by superimposing virtual elements onto the real world, thereby enabling users to engage in captivating and interactive gameplay within their physical environment. Moreover, AR has revolutionized the educational landscape by offering immersive learning experiences, where digital content is seamlessly integrated into the physical classroom, augmenting traditional teaching methods and enhancing student engagement.
In the healthcare sector, augmented reality has demonstrated its potential in surgical planning, medical training, and patient care. By overlaying medical imaging data onto the patient's anatomy in real time, AR enables surgeons to visualize intricate anatomical structures during surgical procedures, thereby enhancing precision and reducing the risk of complications. Additionally, AR-based medical training simulations provide healthcare professionals with realistic scenarios to hone their skills and expertise, ultimately improving patient care outcomes.
Furthermore, AR has reshaped the retail industry by introducing interactive and personalized shopping experiences. Through AR-powered applications, customers can virtually try on clothing and accessories, visualize furniture and home decor within their living spaces, and engage with immersive product demonstrations, thereby enhancing their purchasing decisions and overall shopping experience.
In essence, augmented reality represents a transformative technological frontier that transcends traditional boundaries, offering immersive, interactive, and innovative experiences across various domains. By seamlessly integrating digital content into the physical world, AR has redefined human-computer interaction, paving the way for a new era of experiential computing and digital engagement.
Exploring Mixed Reality
Exploring Mixed Reality
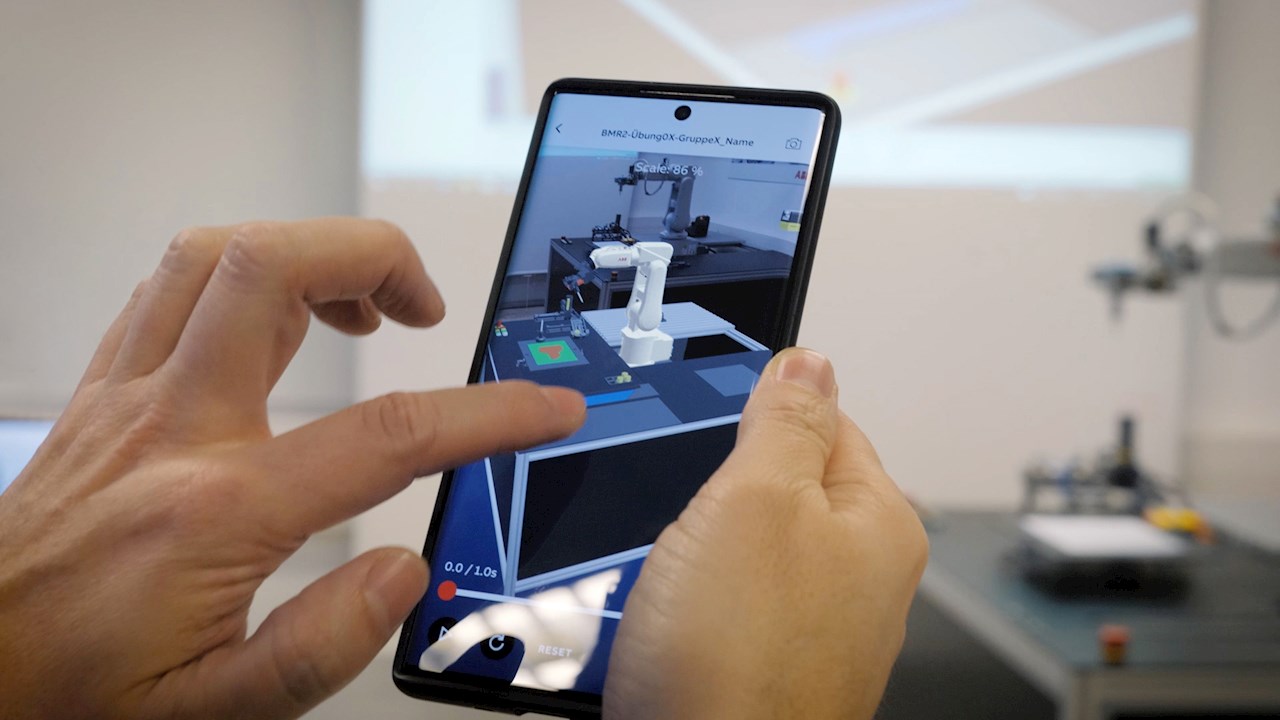
Mixed reality (MR) represents a revolutionary amalgamation of the physical and digital worlds, transcending the boundaries of traditional reality and virtual environments. At the heart of mixed reality lies the seamless integration of virtual content into the user's physical surroundings, creating an immersive and interactive experience that blurs the lines between the real and virtual realms.
Unlike augmented reality, which overlays virtual elements onto the physical environment, mixed reality goes a step further by enabling virtual objects to interact with the real world and vice versa. This dynamic interaction between the physical and digital elements fosters a sense of spatial continuity, allowing users to engage with and manipulate virtual objects as if they were part of their immediate surroundings.
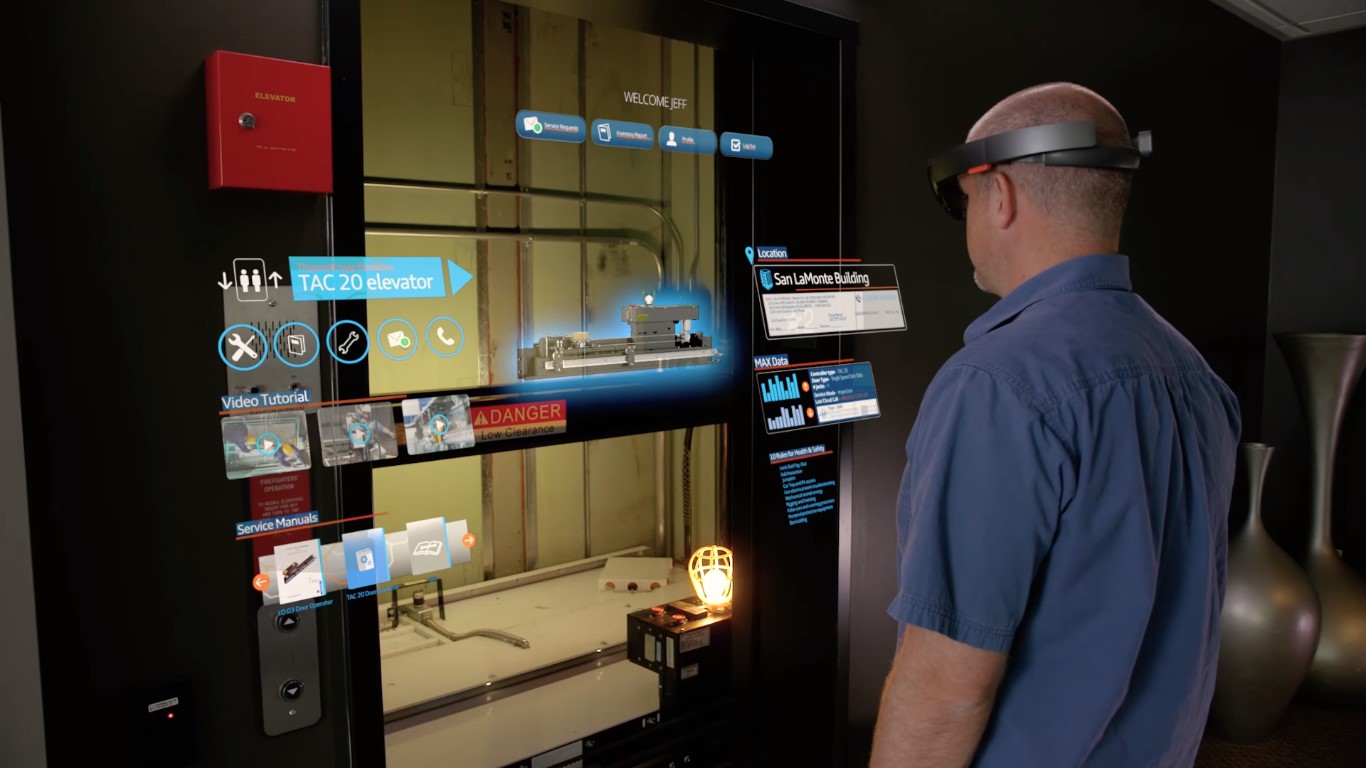
The key distinguishing factor of mixed reality is its ability to anchor virtual content to specific locations in the physical environment, thereby creating a cohesive and integrated experience. This spatial anchoring enables virtual objects to maintain their position and orientation relative to the user's surroundings, facilitating realistic interactions and immersive experiences.
One of the hallmark features of mixed reality is its spectrum, which encompasses a continuum ranging from the purely physical environment to the entirely virtual world. This spectrum enables users to seamlessly transition between the physical, augmented, and virtual realities, offering a spectrum of experiences that cater to diverse needs and preferences.
Mixed reality experiences are facilitated through advanced technologies such as spatial mapping, depth sensing, and environmental understanding, which enable the precise integration of virtual content into the user's environment. By leveraging these technologies, mixed reality devices can accurately perceive and interpret the user's surroundings, allowing for the seamless placement and interaction of virtual objects within the physical space.
The implications of mixed reality extend beyond entertainment and gaming, permeating diverse industries such as architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing. In the realm of architecture and design, mixed reality empowers professionals to visualize and interact with virtual prototypes within real-world environments, facilitating collaborative design processes and enhancing spatial comprehension.
Moreover, mixed reality has profound implications for training and simulation, enabling immersive and interactive learning experiences across various domains. From industrial maintenance simulations to medical training scenarios, mixed reality offers a compelling platform for experiential learning, allowing users to engage with realistic virtual environments and interactive content.
In essence, mixed reality represents a paradigm shift in human-computer interaction, offering a spectrum of immersive experiences that seamlessly blend the physical and digital worlds. By exploring the intricacies of mixed reality, we can grasp its transformative potential and the myriad opportunities it presents for redefining our interactions with the digital realm.
Advantages of Mixed Reality over Augmented Reality
Mixed reality (MR) presents a host of compelling advantages that distinguish it from augmented reality (AR), offering a more immersive and interactive user experience. These advantages stem from the seamless integration of virtual and physical elements, enabling dynamic interactions and spatial continuity. Here are the key advantages of mixed reality over augmented reality:
-
Enhanced Spatial Interaction: Mixed reality facilitates a deeper level of spatial interaction by allowing virtual objects to interact with the real world and vice versa. Unlike augmented reality, where virtual elements are superimposed onto the physical environment, mixed reality enables users to engage with and manipulate virtual objects within their immediate surroundings, fostering a heightened sense of spatial immersion and interactivity.
-
Seamless Integration of Virtual Content: Mixed reality seamlessly integrates virtual content into the user's physical environment, anchoring virtual objects to specific locations in the real world. This cohesive integration creates a more realistic and immersive experience, as virtual elements maintain their position and orientation relative to the user's surroundings, enhancing the sense of presence and spatial coherence.
-
Dynamic Spectrum of Experiences: Mixed reality offers a dynamic spectrum of experiences that encompass the entire continuum from the physical environment to the virtual world. This spectrum enables users to seamlessly transition between augmented reality and virtual reality, providing a diverse range of immersive experiences that cater to individual preferences and contextual requirements.
-
Realistic Spatial Mapping and Environmental Understanding: Mixed reality devices leverage advanced technologies such as spatial mapping and environmental understanding to accurately perceive and interpret the user's surroundings. This capability enables precise placement and interaction of virtual objects within the physical space, fostering realistic and context-aware experiences.
-
Immersive Applications across Diverse Industries: The advantages of mixed reality extend beyond entertainment and gaming, permeating diverse industries such as architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing. From collaborative design processes in architecture to immersive training simulations in healthcare and industrial sectors, mixed reality offers a compelling platform for experiential learning and interactive visualization.
In essence, the advantages of mixed reality over augmented reality lie in its ability to offer a more cohesive, interactive, and immersive user experience. By seamlessly integrating virtual content into the physical environment and enabling dynamic spatial interactions, mixed reality redefines the boundaries of human-computer interaction, opening up new frontiers for immersive experiences and innovative applications across various domains.
Applications of Mixed Reality
Mixed reality (MR) transcends traditional boundaries, offering a diverse array of applications across various industries and domains. The seamless integration of virtual and physical elements, coupled with dynamic spatial interactions, has paved the way for innovative and immersive experiences. Here are some compelling applications of mixed reality:
1. Architecture and Design:
Mixed reality has revolutionized the architectural and design processes by enabling professionals to visualize and interact with virtual prototypes within real-world environments. Architects and designers can leverage MR to collaboratively explore and refine design concepts, visualize spatial layouts, and conduct virtual walkthroughs of architectural models. This immersive approach enhances spatial comprehension and facilitates informed decision-making in the design and construction phases.
2. Engineering and Manufacturing:
In the realm of engineering and manufacturing, mixed reality offers invaluable applications for prototyping, assembly processes, and maintenance procedures. By overlaying virtual schematics and 3D models onto physical machinery and production environments, MR facilitates interactive visualization and training, streamlining the design iteration process and enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, mixed reality enables real-time monitoring and visualization of manufacturing processes, empowering engineers and operators with contextual insights for informed decision-making.
3. Healthcare and Medical Training:
Mixed reality has made significant inroads in the healthcare sector, particularly in medical training, surgical planning, and patient care. Medical professionals can utilize MR to visualize complex anatomical structures in 3D, facilitating enhanced understanding and precision in surgical procedures. Moreover, mixed reality-based medical simulations provide immersive training scenarios for healthcare professionals, offering realistic and interactive experiences to hone clinical skills and improve patient care outcomes.
4. Education and Training:
The educational landscape has been enriched by the immersive capabilities of mixed reality, offering interactive and experiential learning experiences. From virtual field trips and historical reconstructions to interactive science experiments, MR empowers educators to engage students in dynamic and immersive learning environments. Furthermore, mixed reality-based training simulations extend beyond traditional education, providing realistic scenarios for workforce training and skill development across diverse industries.
Read more: The Advantages of Augmented Reality
5. Entertainment and Gaming:
Mixed reality has redefined the gaming and entertainment experiences by blending virtual content with the physical environment, offering captivating and interactive gameplay. MR-based gaming experiences enable users to engage in immersive and interactive adventures, where virtual elements seamlessly integrate with the real world, creating compelling and dynamic gaming environments.
In essence, the applications of mixed reality span across a wide spectrum of industries, offering transformative solutions and immersive experiences that redefine human-computer interaction and pave the way for innovative advancements in various domains. As mixed reality continues to evolve, its potential for reshaping our interactions with the digital realm and physical world remains boundless.
Challenges and Limitations of Mixed Reality
While mixed reality (MR) holds immense potential for transforming human-computer interaction and redefining immersive experiences, it also presents a set of challenges and limitations that warrant careful consideration. These factors encompass technical constraints, user adoption barriers, and ethical implications, shaping the landscape of mixed reality deployment and development.
Technical Complexity and Infrastructure Requirements
One of the primary challenges of mixed reality lies in the technical complexity and infrastructure requirements associated with deploying MR systems. The seamless integration of virtual and physical elements demands advanced spatial mapping, environmental understanding, and real-time rendering capabilities, necessitating robust hardware and software frameworks. Furthermore, ensuring compatibility and interoperability across diverse MR devices and platforms poses a significant technical hurdle, requiring standardized protocols and frameworks for cohesive experiences.
User Experience and Interaction Design
Designing intuitive and immersive user experiences within mixed reality environments presents a nuanced challenge, as it entails reimagining interaction paradigms and spatial interfaces. The spatial continuity and dynamic interactions inherent to MR necessitate thoughtful design considerations to ensure user comfort, minimize cognitive load, and optimize engagement. Balancing the integration of virtual content with the user's physical environment while maintaining usability and accessibility remains a pivotal challenge in MR experience design.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
As mixed reality blurs the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds, ethical and privacy considerations come to the forefront. The potential for intrusive data collection, augmented surveillance, and the blurring of personal and digital spaces raises ethical concerns regarding user privacy and consent. Safeguarding user data, mitigating augmented privacy risks, and establishing ethical guidelines for mixed reality applications are critical challenges that demand proactive measures and industry-wide standards.
Adoption and Acceptance
The widespread adoption and acceptance of mixed reality technologies pose a significant challenge, particularly in domains where traditional practices and workflows prevail. Overcoming user skepticism, addressing learning curves, and demonstrating tangible value propositions are essential for fostering widespread acceptance of MR solutions across industries. Moreover, addressing concerns related to cost, accessibility, and integration with existing workflows is crucial for driving mainstream adoption of mixed reality technologies.
Content Creation and Development
The creation and curation of compelling and contextually relevant content within mixed reality environments present inherent challenges. From 3D asset creation and spatial storytelling to interactive experiences, content development for MR necessitates specialized skills and tools. Bridging the gap between traditional content creation pipelines and mixed reality experiences requires innovative approaches and streamlined workflows to empower creators and developers.
In navigating these challenges and limitations, the mixed reality ecosystem stands poised to evolve through collaborative innovation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and user-centric design principles. By addressing these complexities and embracing iterative advancements, the potential of mixed reality to redefine human-computer interaction and immersive experiences can be realized, paving the way for transformative applications across diverse domains.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of mixed reality (MR) represents a pivotal juncture in the realm of immersive technologies, heralding a new era of human-computer interaction and redefining the boundaries of reality itself. As we traverse the landscape of augmented reality (AR) and delve into the intricacies of mixed reality, it becomes evident that MR expands upon the foundational principles of AR, offering a more cohesive and interactive fusion of the physical and digital worlds.
The transformative potential of mixed reality is underscored by its seamless integration of virtual content into the user's physical environment, enabling dynamic spatial interactions and immersive experiences that transcend traditional paradigms. By anchoring virtual objects to specific locations in the real world and facilitating realistic interactions, MR engenders a heightened sense of presence and spatial continuity, fostering compelling applications across diverse industries.
From architecture and engineering to healthcare and education, the applications of mixed reality permeate various domains, offering innovative solutions and immersive experiences that redefine human-computer interaction. The advantages of MR over AR, including enhanced spatial interaction, seamless integration of virtual content, and a dynamic spectrum of experiences, underscore its potential for reshaping digital experiences and driving transformative advancements.
However, the deployment and development of mixed reality also present a set of challenges and limitations, ranging from technical complexities and user experience design to ethical considerations and adoption barriers. Addressing these complexities necessitates collaborative innovation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and user-centric design principles to realize the full potential of mixed reality technologies.
As we navigate the complexities and opportunities inherent to mixed reality, it becomes imperative to embrace iterative advancements, ethical considerations, and user-centric design principles to foster widespread acceptance and drive mainstream adoption. By doing so, we can unlock the transformative potential of mixed reality, paving the way for immersive experiences and innovative applications that redefine our interactions with the digital realm and physical world.
In essence, mixed reality represents a paradigm shift that transcends traditional boundaries, offering a spectrum of immersive experiences that seamlessly blend the physical and digital worlds. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of mixed reality and its transformative potential, we can chart a course toward a future where the lines between reality and virtual environments are blurred, opening up new frontiers for experiential computing and digital engagement.