Home>Latest News>Technology Trends>What Does The “Mesh” Do In Augmented Reality?

Technology Trends
What Does The “Mesh” Do In Augmented Reality?
Modified: September 5, 2024
Discover how the "mesh" enhances augmented reality and stay updated on the latest technology trends. Explore the impact of mesh technology in AR.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction to Augmented Reality
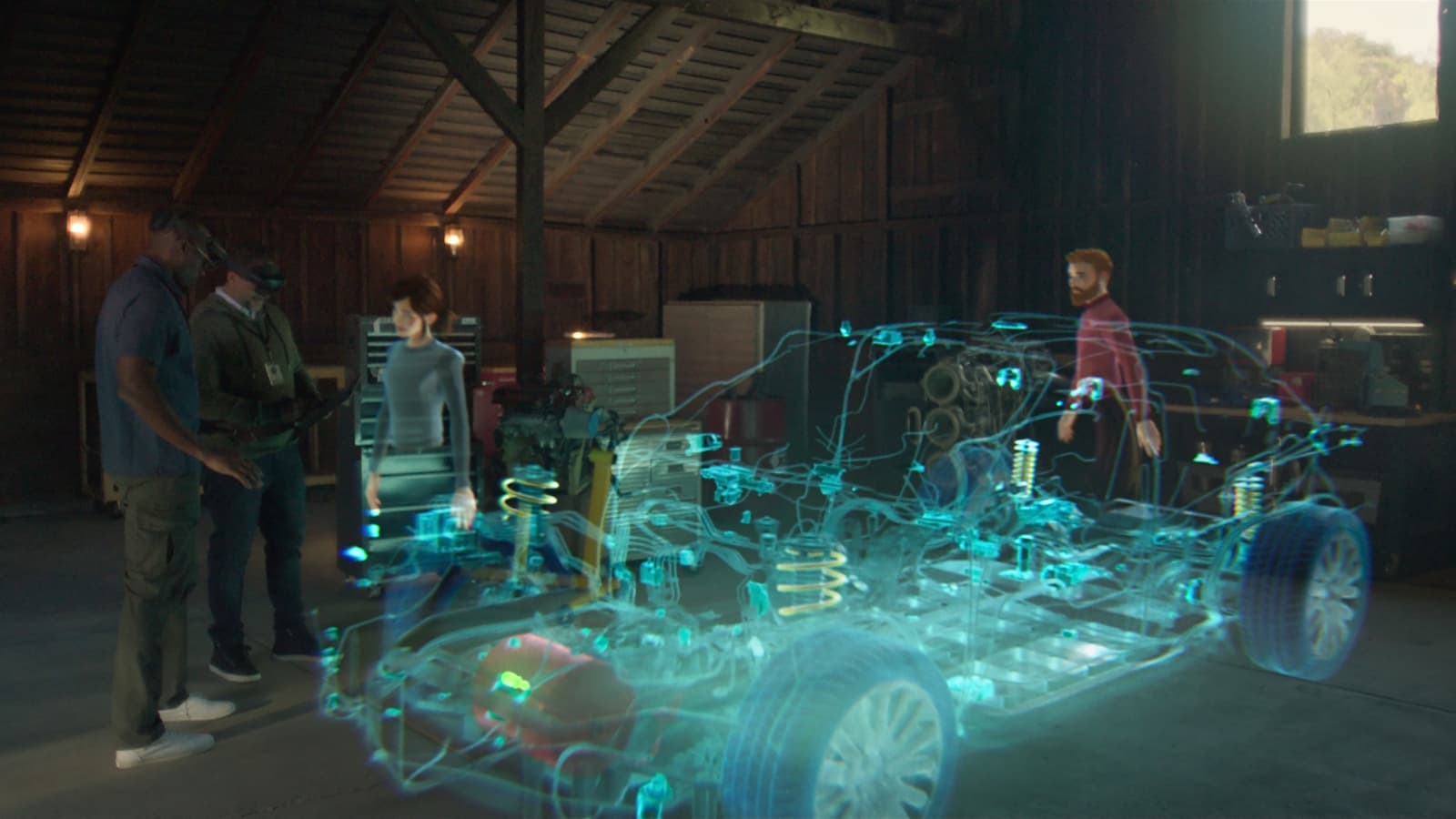
Augmented reality (AR) technology brings digital elements into the real world by overlaying virtual objects onto physical environments. Increasingly used in gaming, education, healthcare, and marketing, AR creates immersive and interactive experiences by accurately placing and manipulating virtual objects within the real world. This is where the mesh comes into play.
The Role of the Mesh in Augmented Reality
Detailed Map of Surroundings
The mesh serves as a detailed map or model of the user's surroundings. It captures and analyzes data from sensors and cameras integrated into AR devices like smart glasses, smartphones, or tablets. This data includes depth information, crucial for understanding the three-dimensional structure of the environment. By creating a precise digital representation of the physical space, the mesh enables AR applications to accurately place virtual objects within that space.
Precise Object Placement
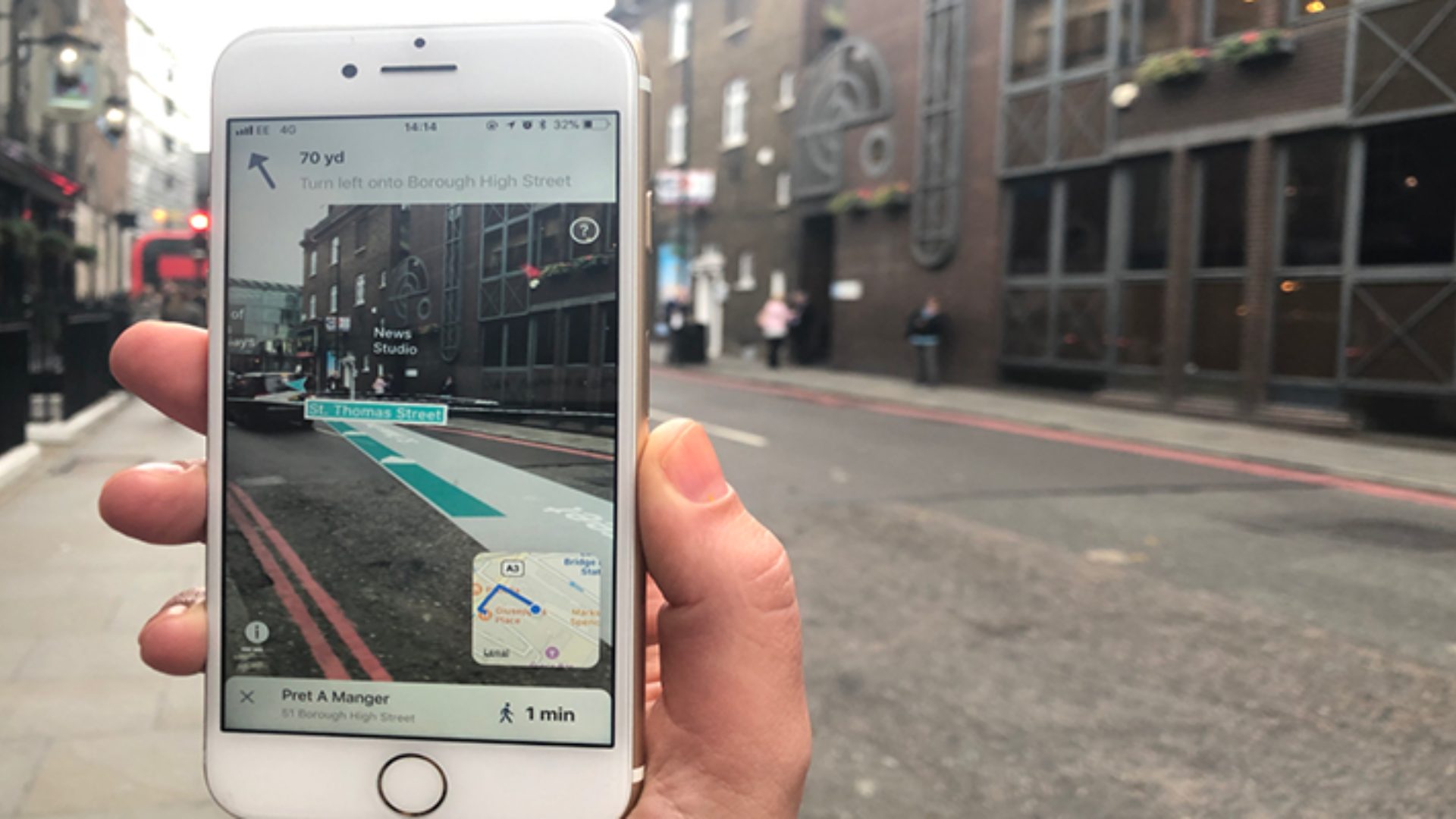
One primary function of the mesh is facilitating precise object placement. By aligning virtual objects with corresponding features of the mesh, AR applications create immersive and context-aware experiences. For instance, in an AR gaming scenario, a virtual character can be placed accurately on a table or chair based on mesh data. This ensures that the virtual object blends seamlessly into the real world, enhancing the overall experience.
Spatial Registration
Spatial registration involves aligning virtual objects with their corresponding physical counterparts in the real world. The mesh data helps achieve this alignment by providing a detailed map of the environment. This ensures that virtual objects are not only placed accurately but also interact with their surroundings in a realistic manner.
Read more: The Advantages of Augmented Reality
Environmental Understanding
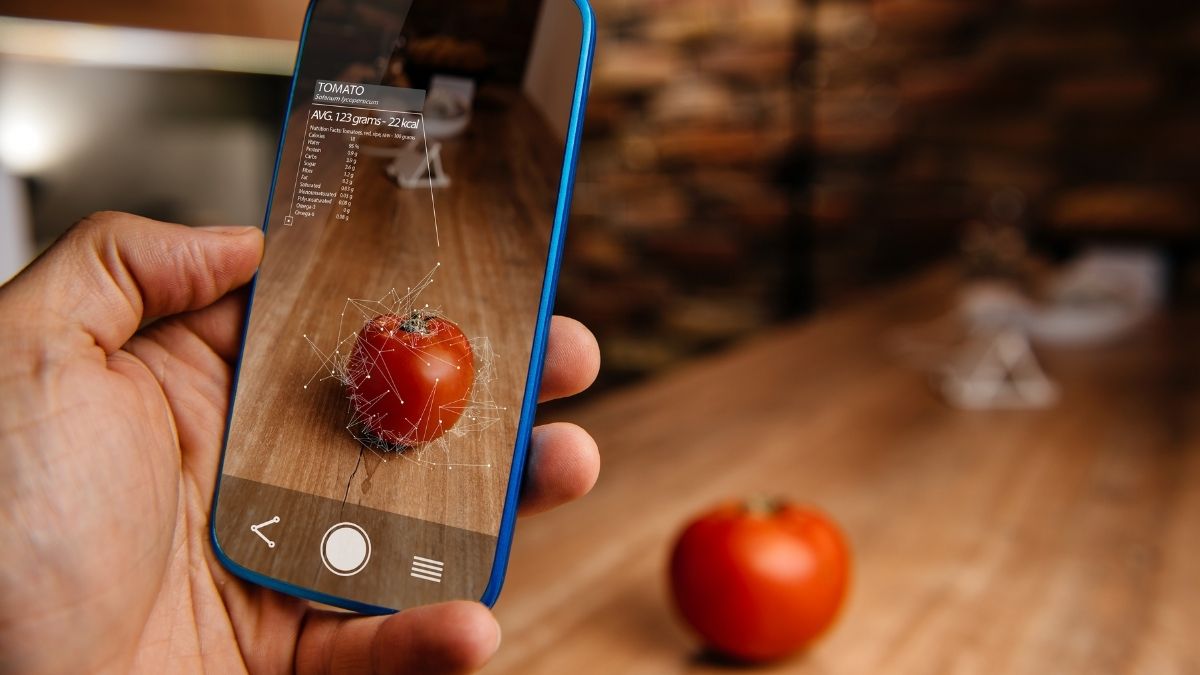
The mesh significantly contributes to environmental understanding by leveraging the data it captures. AR applications offer contextual interactions and experiences that intelligently respond to the user’s surroundings. For example, an AR application might recognize a specific object in the room and provide additional information about it, such as its name, description, or usage. This level of contextual awareness is made possible by the detailed map provided by the mesh.
Interaction Detection
The mesh enables AR systems to detect and respond to user interactions, such as hand gestures or physical objects. By tracking the movement and position of these interactions within the mesh, AR applications create more intuitive and interactive experiences. For instance, in an AR cooking tutorial, the system might recognize the user’s hand gestures to guide them through the recipe steps.
Visual Quality Enhancement
The mesh plays a significant role in enhancing the visual quality of an AR experience. By dividing a surface into numerous small triangles or polygons, the mesh adds detail and complexity to the 3D scene. This results in a more realistic virtual environment, making it easier for users to distinguish between real and virtual objects. A well-crafted mesh contributes to the immersiveness of an AR application by providing a rich and detailed digital representation of the physical space.
Fundamentals of Augmented Reality Mesh
Read more: What Are AR Apps
3D Digital Representation
The mesh consists of interconnected vertices, edges, and faces, forming a grid-like structure. This structure is essential for creating a stable foundation for virtual items to anchor and interact with their surroundings. Vertices represent points in 3D space, while edges connect these points to form lines. Faces, typically composed of triangles or other polygons, enclose these vertices and edges, creating a three-dimensional shape.
Data Capture and Tracking
Mesh creation relies on data gathered from sensors and cameras present in AR devices. These components capture the structure and appearance of the physical environment, enabling the generation of an accurate digital representation. This process involves tracking the geometry and textures of real-world objects, which is critical for ensuring that virtual objects can be placed and manipulated effectively within an augmented scene.
Importance in AR Systems
The mesh is a crucial element in augmented reality systems. It allows for the accurate placement and interaction of virtual objects within the real world, enabling users to enjoy a seamless and realistic AR experience. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of AR systems and the intricacies of the mesh will undoubtedly evolve and improve, further enhancing the magic of augmented reality.
Design and Modelling in AR
Read more: What Are AR Games
3D Modelling Techniques
In augmented reality, the design and modelling process is crucial for creating realistic and immersive experiences. This process involves the creation of 3D models representing objects and environments to be displayed in the virtual world. These models are comprised of vertices, faces, and polygons, which form the basic structure of any 3D object.
AR designers utilize tools, such as computer software, to generate 3D models with multiple vertices connected by edges, creating faces. Faces are typically composed of triangles, as they are the simplest polygons that can form a three-dimensional shape. Triangles and other polygons can be combined in various ways to create complex, detailed models.
Colour and Texture Considerations
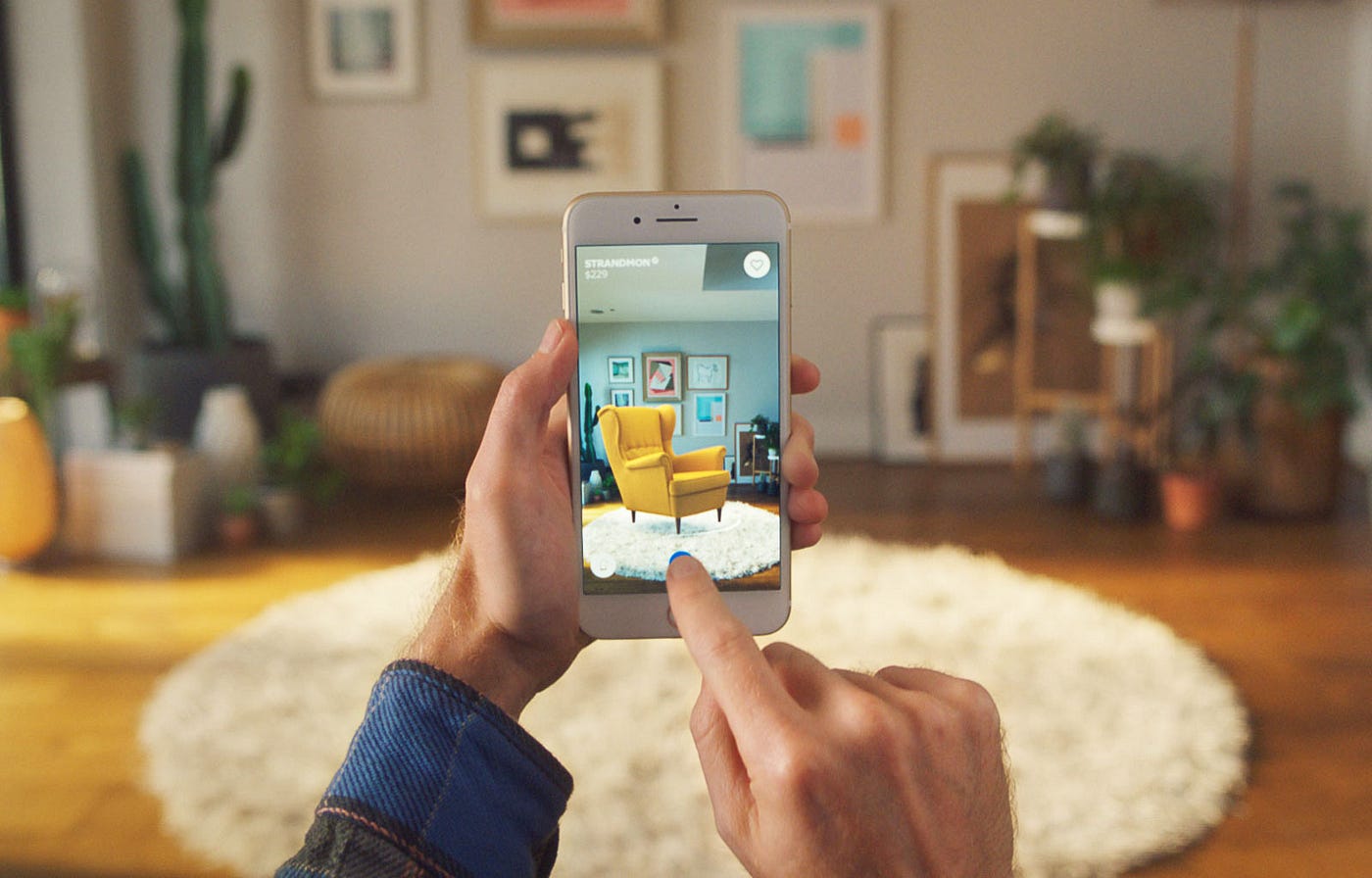
When creating a 3D model for augmented reality, designers must consider factors such as colour, texture, and level of detail. Colour and texture contribute significantly to the realism of the virtual environment. For instance, a virtual chair might be modelled with realistic wood grain texture and colour to blend seamlessly into a real-world setting. The level of detail also plays a crucial role; a highly detailed model will provide a more immersive experience compared to a less detailed one.
Real-World Applications
The applications of AR technology are vast and diverse. In gaming, AR enhances the interactive experience by allowing players to manipulate virtual objects within their real-world environment. In education, AR can create interactive lessons where students can explore virtual models of historical sites or complex biological systems. In healthcare, AR can assist surgeons during operations by providing real-time visual guidance. In marketing, AR can enhance product demonstrations by allowing customers to see how products would look in their own homes.
Final Thoughts
The mesh is an essential component in augmented reality systems. It provides a detailed map of the user’s surroundings, enabling precise object placement and accurate spatial registration. The mesh also enhances environmental understanding by offering contextual interactions and experiences that intelligently respond to the user’s surroundings. Additionally, it detects and responds to user interactions such as hand gestures or physical objects, creating more intuitive and interactive experiences. By enhancing visual quality through detailed digital representation, the mesh contributes significantly to the immersiveness of AR applications.
As technology continues to advance, expect even more sophisticated uses of the mesh in various fields. The evolution of AR technology will undoubtedly be driven by improvements in mesh creation and tracking capabilities, leading to more realistic and engaging experiences. The mesh is not just a technical component; it is the backbone of what makes augmented reality so magical and immersive.