Home>Latest News>Technology Trends>How Does Augmented Reality Work


Technology Trends
How Does Augmented Reality Work
Modified: September 5, 2024
Discover how augmented reality works and its impact on technology trends. Explore the latest advancements and applications in this exciting field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
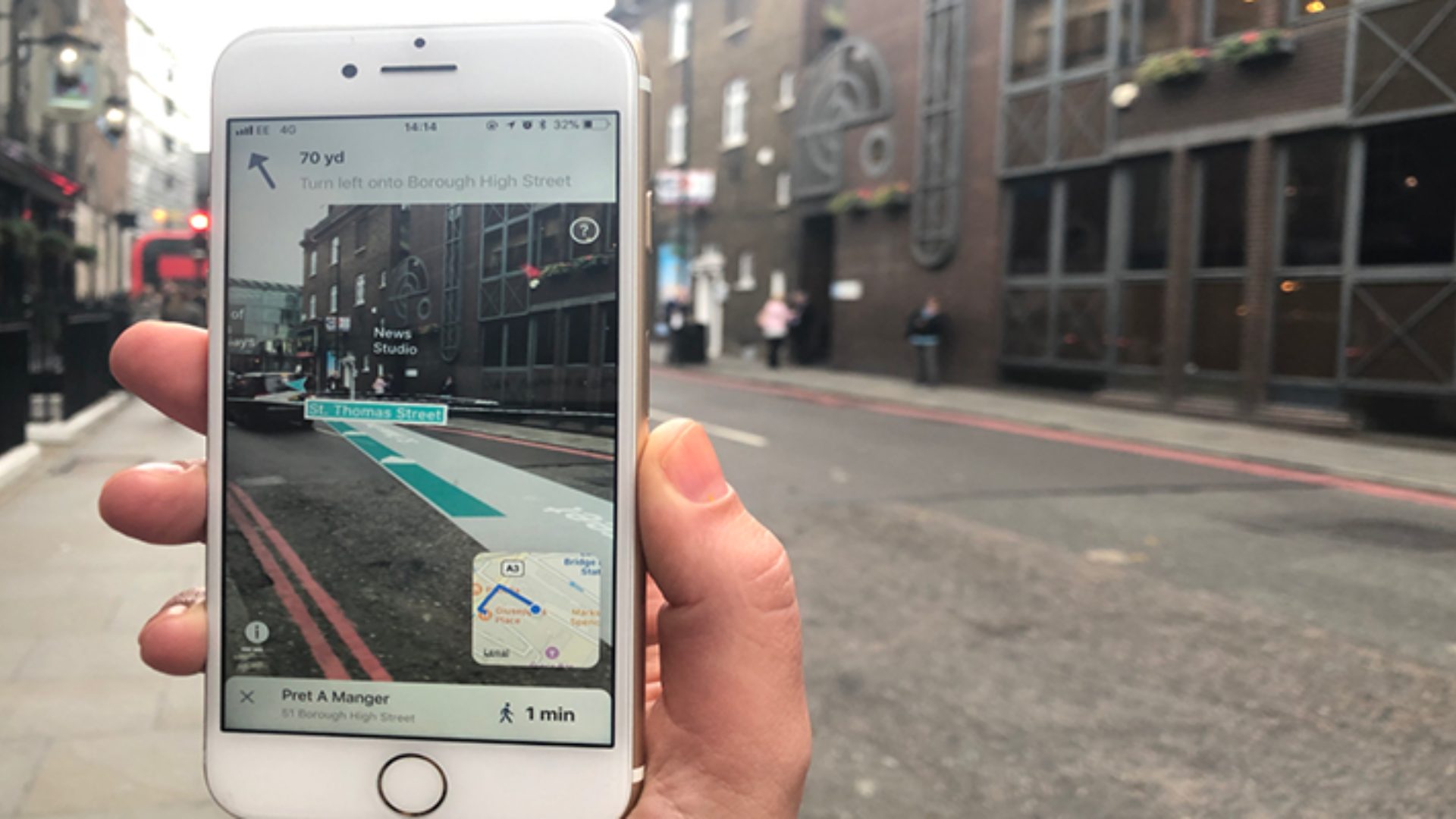
What is Augmented Reality?
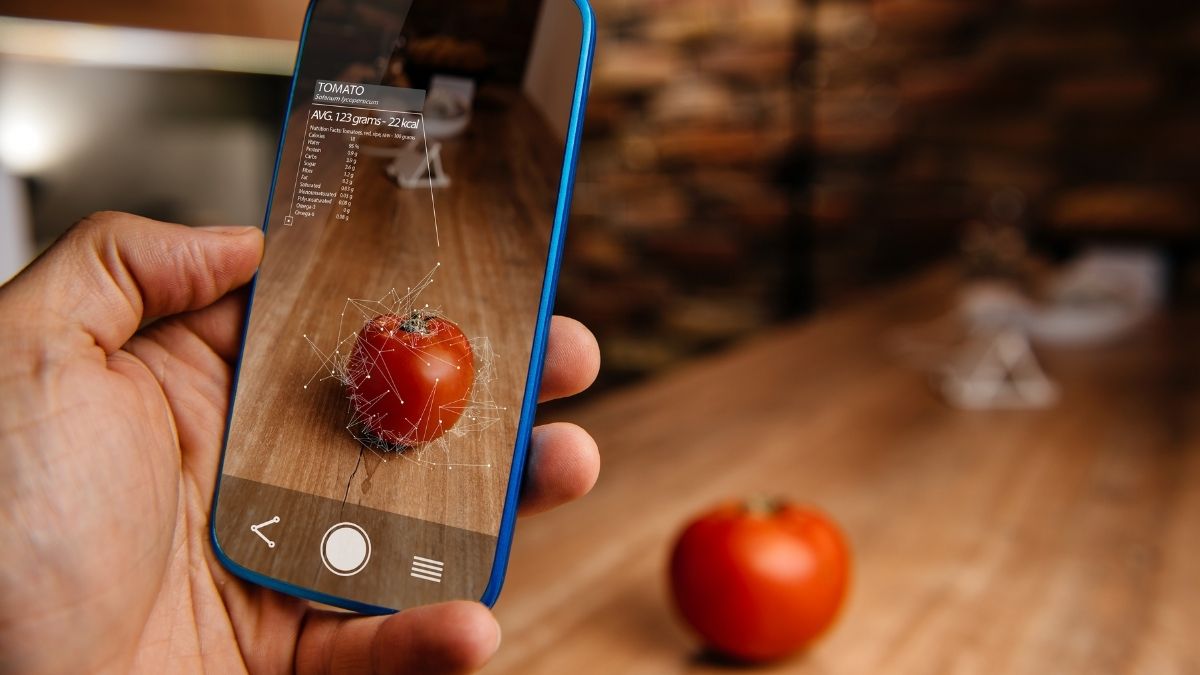
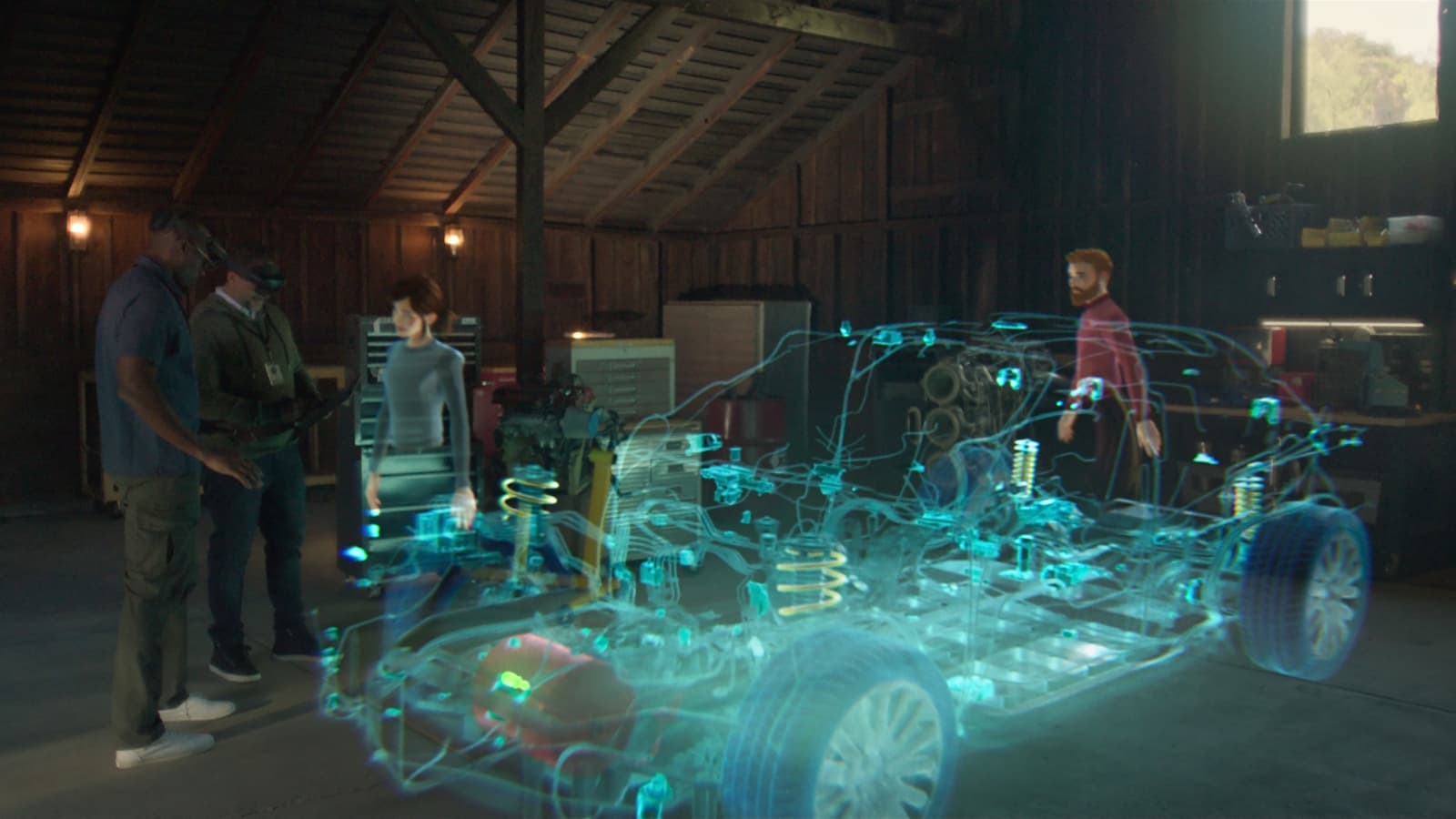
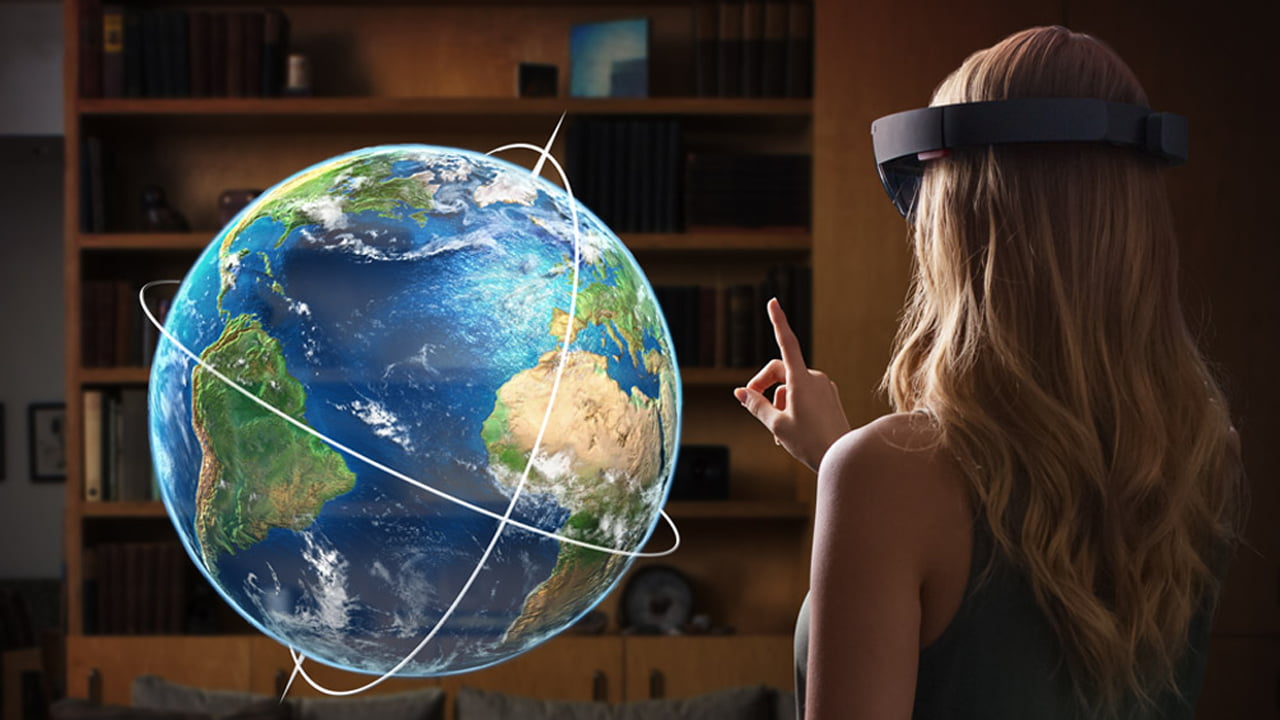
Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the real world. Unlike virtual reality, which creates a completely virtual environment, AR enhances the real world by adding virtual objects, sounds, or other sensory inputs. This can be achieved through various devices such as smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and head-mounted displays.
Read more: How Does Chromecast Work
Historical Background
The concept of AR dates back to the 1960s when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland created the first head-mounted display. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that the term "augmented reality" was coined by Tom Caudell, a Boeing engineer. Caudell used AR to help workers assemble aircraft parts more efficiently by providing them with virtual instructions.
Key Components of AR
For AR to function effectively, several key components are necessary:
- Hardware: This includes the device on which the AR experience is displayed. Common devices include smartphones, tablets, smart glasses like Google Glass, and head-mounted displays like Microsoft HoloLens.
- Software: The software is responsible for generating and rendering the virtual content. It uses various algorithms to track the user's environment and superimpose digital information onto it.
- Tracking Technology: This is crucial for aligning virtual objects with real-world objects. Common tracking methods include marker-based tracking (using QR codes or markers), markerless tracking (using cameras and machine learning algorithms), and spatial mapping.
- Display Technology: The display technology determines how the virtual information is presented to the user. This can range from simple screens on smartphones to more advanced displays like those found in smart glasses.
- User Interface: An intuitive user interface is essential for a seamless AR experience. This includes gestures, voice commands, or other interaction methods that allow users to control the AR environment.
How AR Works
The Process
- Initialization: The AR application initializes by setting up the necessary hardware and software configurations. This includes calibrating the camera, setting up tracking systems, and loading relevant data.
- Tracking: The application begins tracking the user's environment using various methods such as marker-based or markerless tracking. This involves capturing images or videos of the real world and processing them in real-time to identify features and objects.
- Rendering: Once the environment is tracked, the application renders virtual objects onto the real-world scene. This involves complex calculations to ensure that the virtual objects are correctly positioned and scaled relative to their real-world counterparts.
- Displaying Content: The rendered content is then displayed on the device's screen or directly into the user's field of view through a head-mounted display.
- User Interaction: Users interact with the AR environment using various methods such as gestures, voice commands, or other input devices. The application responds accordingly by updating the virtual content in real-time.
Read more: How Does Bitdefender VPN Work
Tracking Technologies
Tracking technologies are essential for aligning virtual objects with real-world objects. Here are some common methods:
Marker-Based Tracking
Marker-based tracking uses physical markers like QR codes or specific patterns to track the environment. The application captures images of these markers and uses them as reference points to position virtual objects accurately. This method is simple but limited by the need for physical markers.
Markerless Tracking
Markerless tracking uses machine learning algorithms and computer vision techniques to track features in the environment without any physical markers. This method is more sophisticated but requires powerful processing capabilities to handle complex calculations in real-time.
Spatial Mapping
Spatial mapping involves creating a 3D map of the environment using data from cameras and sensors. This map is then used to track changes in the environment and position virtual objects accordingly. Spatial mapping is particularly useful in applications like interior design or architecture where precise spatial awareness is crucial.
Display Technologies
Display technologies play a critical role in how AR content is presented to users. Here are some common display technologies used in AR:
Screens
Smartphones and tablets are the most common devices used for AR experiences. These devices use LCD or OLED screens to display virtual information overlaid onto real-world scenes.
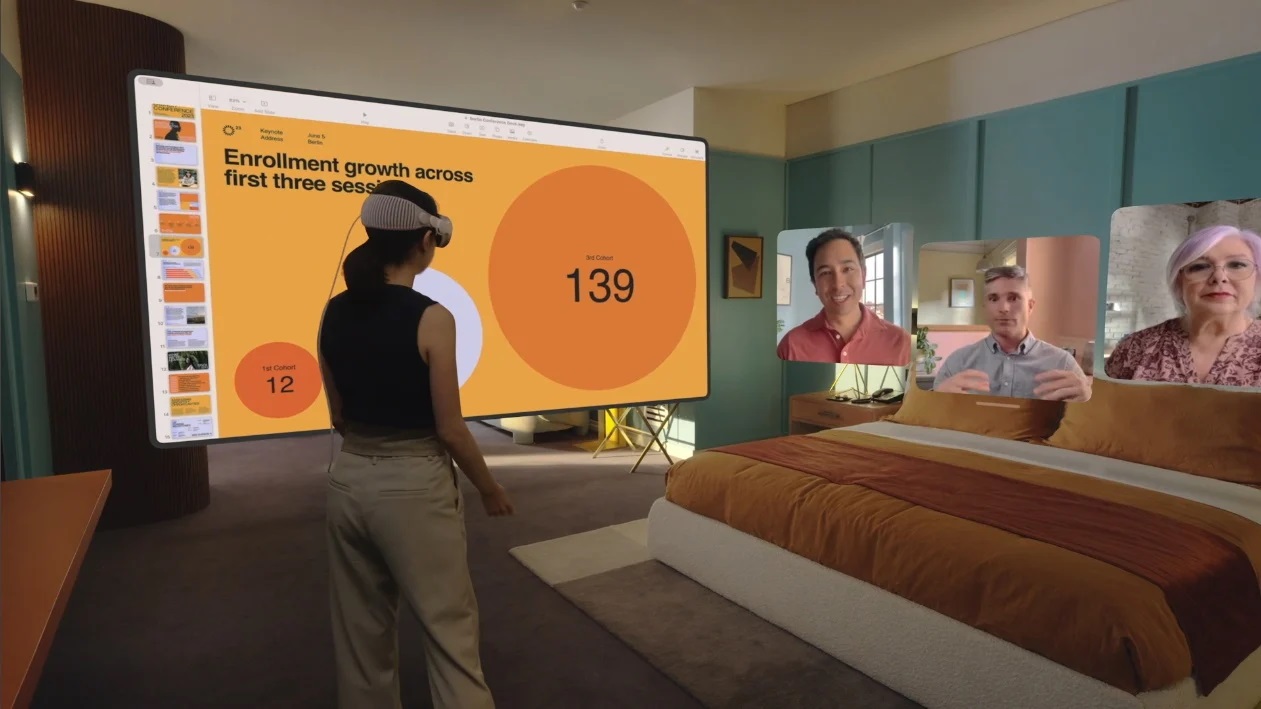
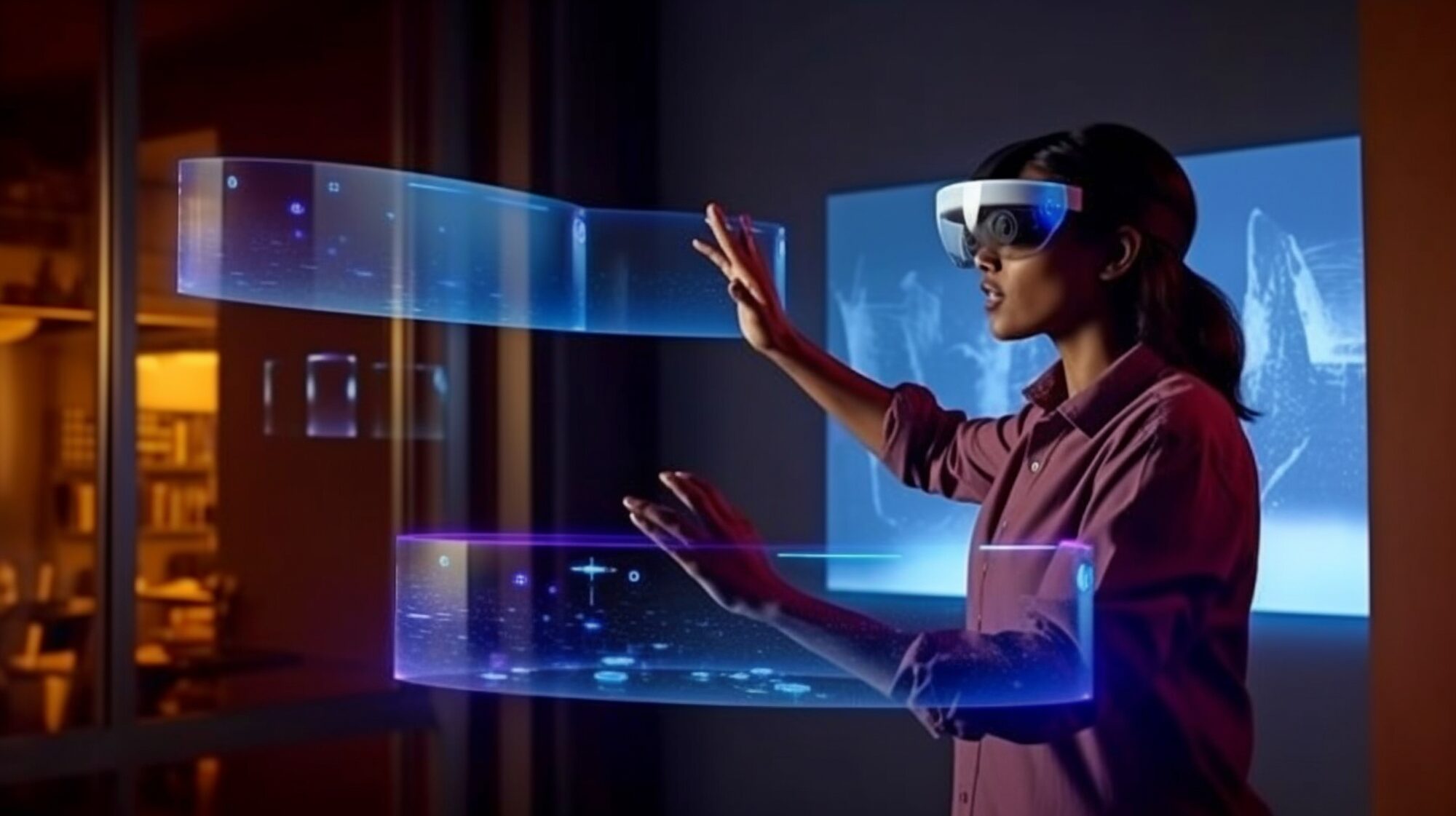
Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs)
HMDs like Microsoft HoloLens provide a more immersive experience by displaying virtual content directly into the user's field of view. These devices use advanced display technologies such as waveguides and micro-LEDs to achieve high-resolution images with minimal latency.
Read more: How Does Norton VPN Work
Smart Glasses
Smart glasses like Google Glass offer a more subtle AR experience compared to HMDs. They use small displays that show information in the user's peripheral vision, allowing them to interact with their environment without being fully immersed.
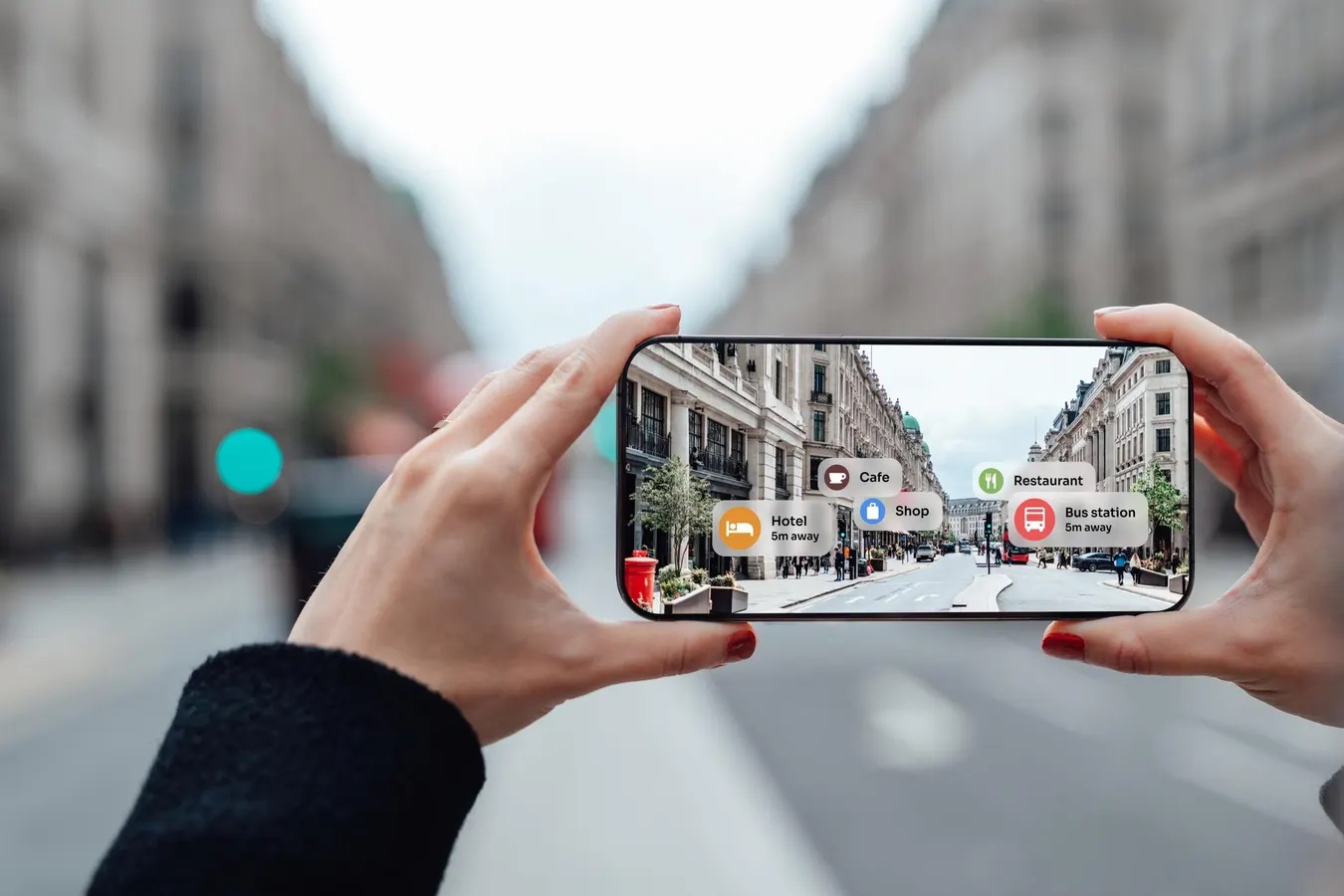
Applications of AR
AR has a wide range of applications across various industries:
Education
AR can enhance educational experiences by providing interactive 3D models and simulations that help students understand complex concepts better. For example, students can use AR apps to visualize anatomical structures or historical events.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AR is used for surgical training and patient care. Surgeons can practice procedures using AR simulations before performing actual surgeries, reducing the risk of complications. AR also helps doctors communicate more effectively with patients by providing them with detailed information about their conditions.
Read more: How Does Google Authenticator Work
Retail
Retailers use AR to enhance customer experiences by providing virtual try-ons for clothing and makeup. Customers can see how products look on them without having to physically try them on. This not only saves time but also reduces returns due to incorrect sizing or color matching.
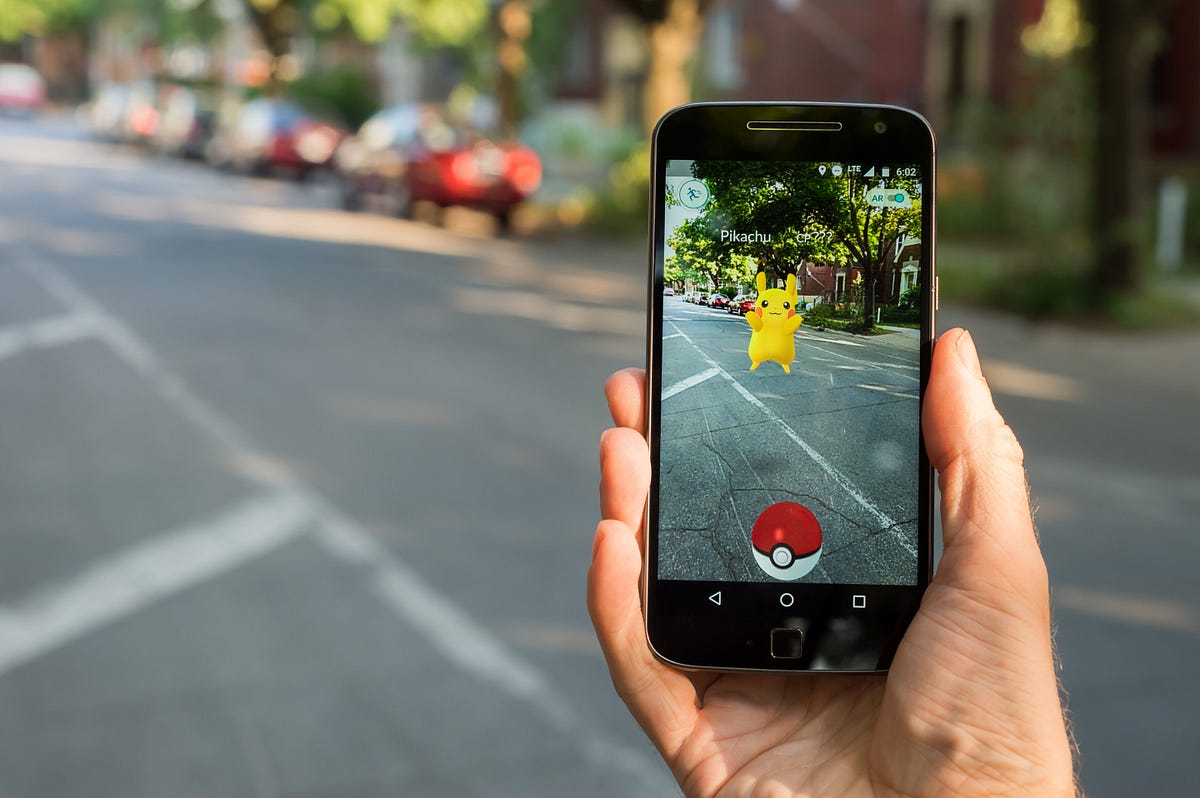
Gaming
Gaming is another significant application of AR. Games like Pokémon Go have revolutionized the gaming industry by bringing players into the real world. Players use their smartphones to capture virtual creatures that appear in their surroundings, creating an immersive experience that blurs the line between reality and fantasy.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use AR for assembly instructions and quality control. Workers can receive step-by-step instructions on how to assemble complex machinery using AR overlays that highlight specific parts and provide detailed instructions.
Real Estate
Real estate agents use AR to give potential buyers a virtual tour of properties. Buyers can see how furniture fits into rooms or visualize different design options without having to physically visit each property.
Read more: How Does Opera VPN Work
Challenges and Limitations
While AR has made significant strides in recent years, there are still several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed:
Technical Challenges
One of the primary technical challenges is achieving high-resolution displays with minimal latency. This is particularly important for applications like gaming where smooth performance is crucial.
Another challenge is ensuring accurate tracking in various lighting conditions. AR applications often struggle with tracking objects in low-light environments or when there are multiple reflective surfaces involved.
Cost and Accessibility
Currently, high-end AR devices like HMDs are expensive and not widely accessible. This limits the adoption rate among consumers who may not be willing or able to invest in such technology.
Privacy Concerns
There are also privacy concerns associated with AR technology. For instance, some AR applications may require access to location data or camera permissions which raises ethical questions about data privacy.
Read more: Does VPN Work On Data
Future of AR
The future of AR looks promising with advancements in technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and display technologies. Here are some potential trends that could shape the future of AR:
Advancements in Display Technologies
Future AR devices are likely to feature more advanced display technologies such as micro-LEDs or even holographic displays which will provide higher resolution images with better contrast ratios.
Integration with IoT Devices
AR will increasingly integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create more seamless experiences. For example, smart home devices could use AR to provide users with interactive instructions on how to use them.
Increased Adoption in Everyday Life
As prices drop and technology improves, we can expect AR to become more integrated into everyday life. From virtual try-ons in retail stores to interactive educational materials in classrooms, AR will continue to transform various industries by enhancing user experiences.