Home>Software and Apps>How Does Google Authenticator Work


Software and Apps
How Does Google Authenticator Work
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how Google Authenticator, a popular software and app, works to provide two-factor authentication for enhanced security. Understand the process and benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
What is Google Authenticator?
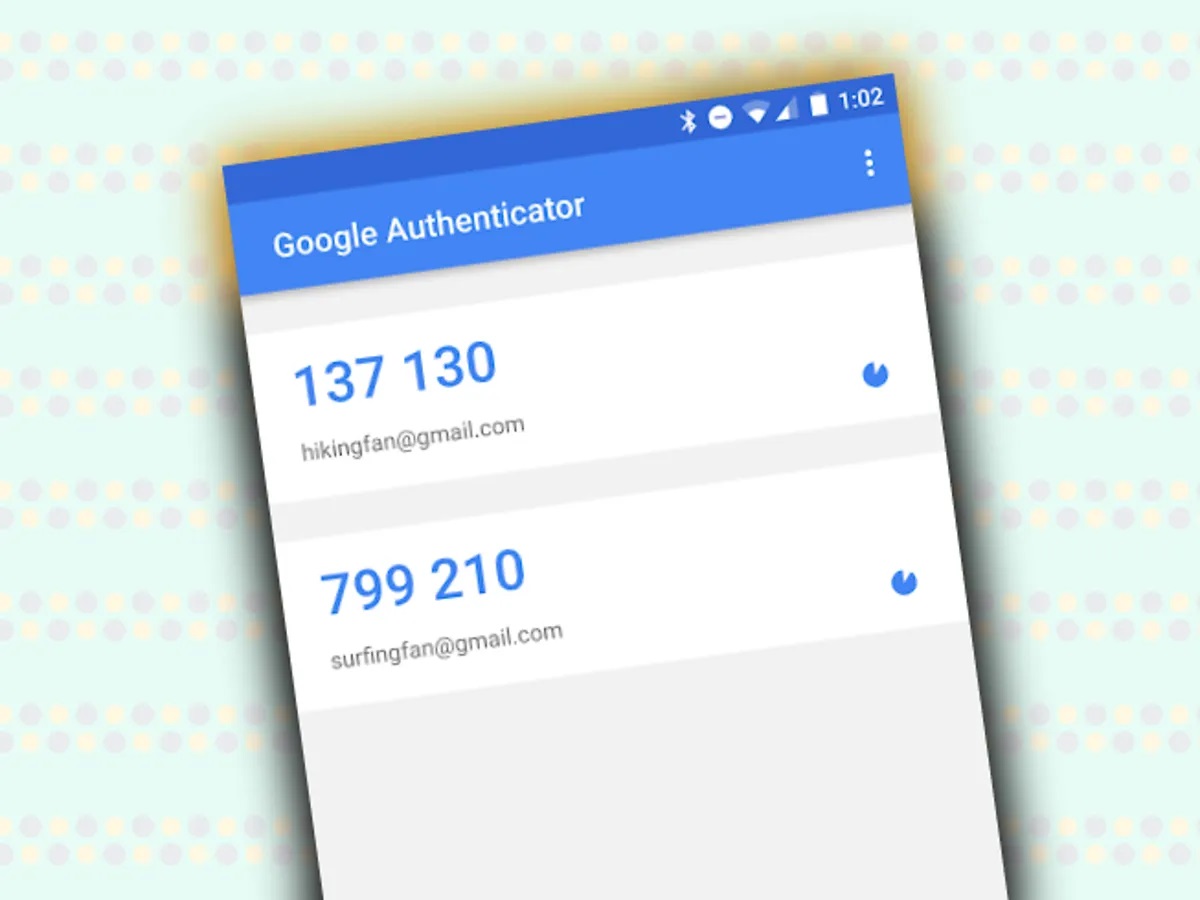
Google Authenticator is a free app available for both iOS and Android devices. It generates time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) used as a second factor in the authentication process. These passwords are unique and change every 30 seconds, making them highly secure and resistant to phishing attacks and other forms of unauthorized access.
Read more: How Does Chromecast Work
How Does Google Authenticator Work?
Setup Process
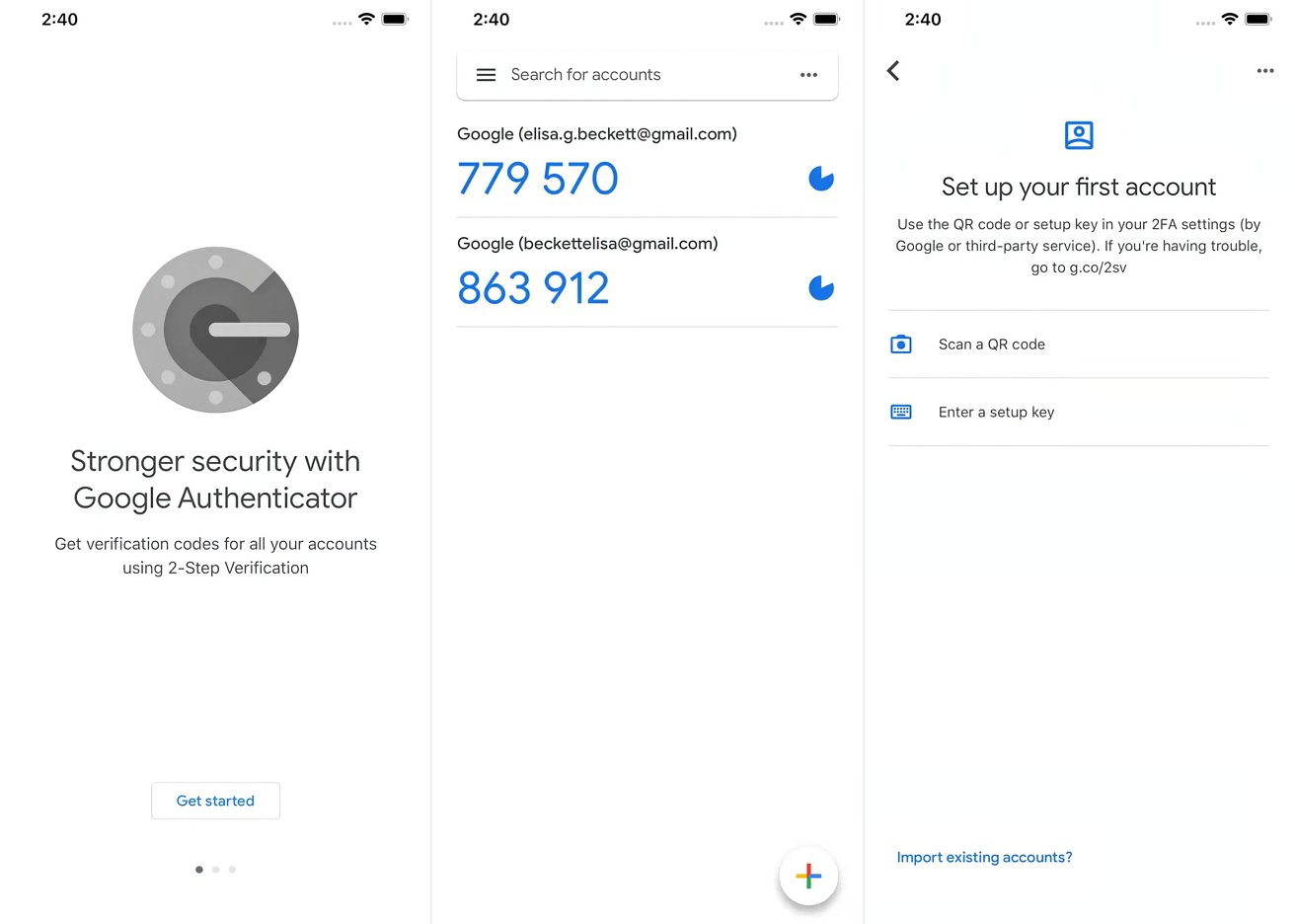
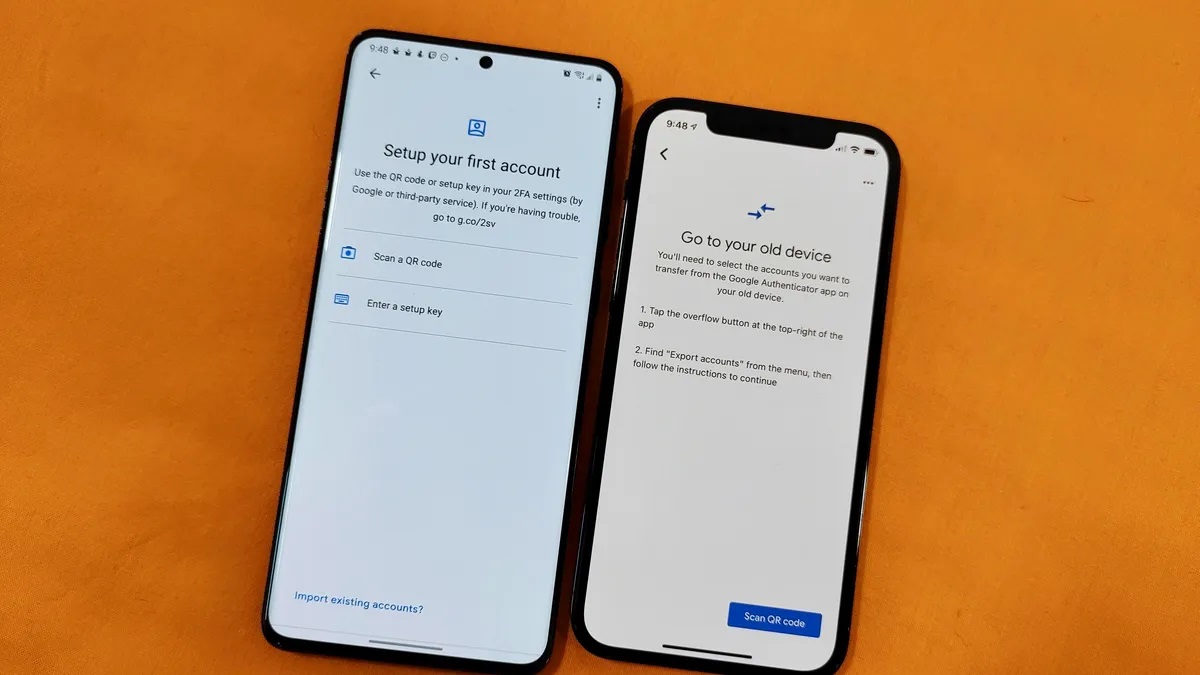
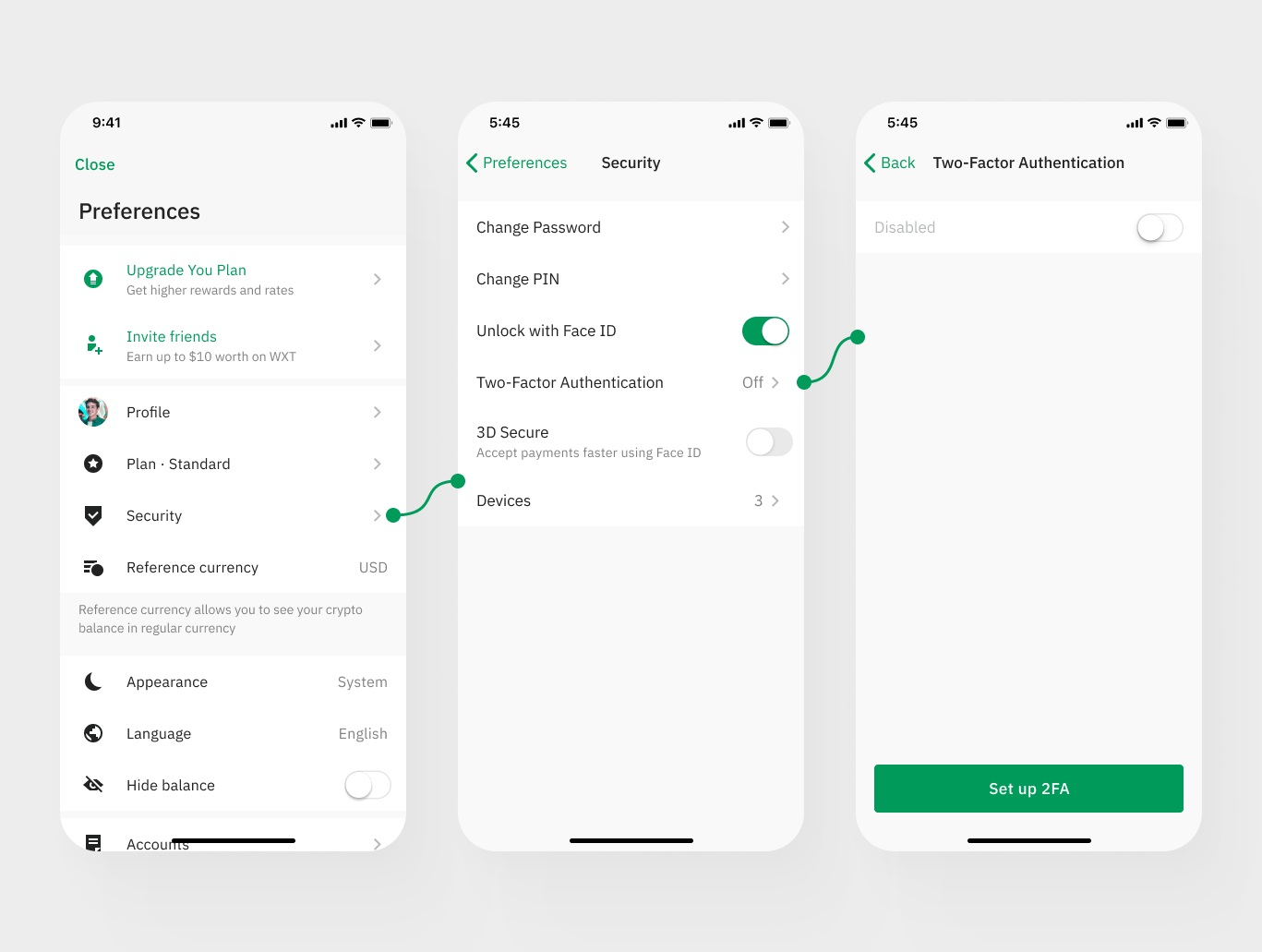
To set up Google Authenticator, users need to follow these steps:
- Download and Install the App: Download and install the Google Authenticator app from the Google Play Store for Android or the App Store for iOS.
- Enable 2FA on the Service: Enable two-factor authentication on the website or service you want to secure. This typically involves generating a QR code or entering a setup key provided by the service.
- Add the Account to Google Authenticator: Open Google Authenticator and add the account by scanning the QR code or entering the setup key. The app will then display a six-digit verification code.
- Complete Setup: Return to the service and complete the setup process by entering the verification code displayed in Google Authenticator. This code is used in conjunction with your password to verify your identity.
Technical Overview
Google Authenticator uses algorithms like TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Password) and HMAC-Based One-Time Password (HOTP) to generate verification codes. TOTP relies on the current time and a shared secret key to create unique codes valid for a short period, typically 30 seconds. This makes it difficult for hackers to guess or steal the codes, as they are time-sensitive and change frequently.
TOTP Algorithm
The TOTP algorithm is specified in the Internet Engineering Task Force's (IETF) RFC 6238. It works by combining the current time with a shared secret key to generate a six-digit code. This process repeats every 30 seconds, resulting in a new code that must be entered each time the user logs in.
HOTP Algorithm
HOTP uses a counter-based approach. It increments a counter each time a new code is generated and combines this counter with the shared secret key to produce the verification code. While HOTP is also used in some 2FA systems, TOTP is more commonly employed due to its time-based nature, which adds an extra layer of security.
Usage and Functionality
Once set up, Google Authenticator provides a seamless experience for users. Here’s how it works:
- Generating Codes: When logging in to a service with 2FA enabled, users are prompted to enter a verification code generated by Google Authenticator.
- Entering Codes: Enter the six-digit code displayed in the app along with your usual password to complete the login process.
- Offline Functionality: One key benefit of Google Authenticator is its offline functionality. The app can generate codes even without an internet connection, making it useful for users in areas with poor reception or when traveling.
- Multiple Account Support: Manage 2FA codes for multiple online accounts within the same app, making it convenient for managing multiple services.
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
Benefits of Using Google Authenticator
- Enhanced Security: Adds a second layer of defense against unauthorized access, even if someone has your password. This makes it much harder for hackers to gain access to your accounts.
- Free and Easy to Use: Available for free on both iOS and Android devices and simple to set up and use. Users can easily scan QR codes or enter setup keys to link their accounts.
- Offline Functionality: Generates codes even without an internet connection, which is particularly useful when traveling or in areas with poor reception.
- Multiple Account Support: Manage 2FA codes for multiple online accounts within the same app, making it convenient for managing multiple services.
- Protects Against Phishing: Prevents hackers from gaining access even if they trick you into revealing your password. The time-sensitive nature of the codes makes them resistant to phishing attacks.
Additional Features
- Dark Mode: For easier viewing in low-light conditions, Google Authenticator offers a dark mode option.
- Cloud Backup (Android Only): Android users can back up their 2FA codes to their Google account for easy restoration. This feature ensures that users do not lose access to their accounts even if they lose their phone.
- Time Correction for Codes: The app allows users to adjust for slight time discrepancies between their device and the authentication server, ensuring that the codes remain valid.
Security Considerations
While Google Authenticator significantly enhances security, it also requires users to protect their phones. Here are some security considerations:
- Phone Security: Make sure your phone is secured with a strong PIN, password, or biometric lock. Losing your phone without a backup of your shared secret keys can result in losing access to your accounts.
- Backup Recovery: Always follow the recovery instructions provided by each service when setting up 2FA. This ensures that you have a plan in place in case you lose access to your phone.
Google Authenticator is a powerful tool in the fight against cybercrime, providing an additional layer of security that is both free and easy to use. By generating time-based one-time passwords, it makes it much harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access to your accounts. Its offline functionality, multiple account support, and protection against phishing attacks make it an essential tool for anyone looking to enhance their digital security. Whether managing personal accounts or professional services, Google Authenticator is a reliable choice for ensuring the integrity of your online presence.