Home>Software and Apps>The Power of Google Authenticator


Software and Apps
The Power of Google Authenticator
Modified: September 5, 2024
Discover the convenience and security of Google Authenticator. Explore how this software and app enhances your online safety and protects your accounts.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction to Google Authenticator
In today's digital age, security is paramount. With the rise of online transactions, sensitive information, and personal data, protecting accounts and devices has become a top priority. One of the most effective tools in this endeavor is Google Authenticator, a two-factor authentication (2FA) app that provides an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
What is Google Authenticator?
Google Authenticator is a free app developed by Google that generates time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) for 2FA. This app works seamlessly with various services supporting 2-step verification, ensuring only authorized users can access their accounts. Available for both Android and iOS devices, it is accessible to a wide range of users.
How Google Authenticator Works
Understanding the power of Google Authenticator requires grasping how it operates. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Setup
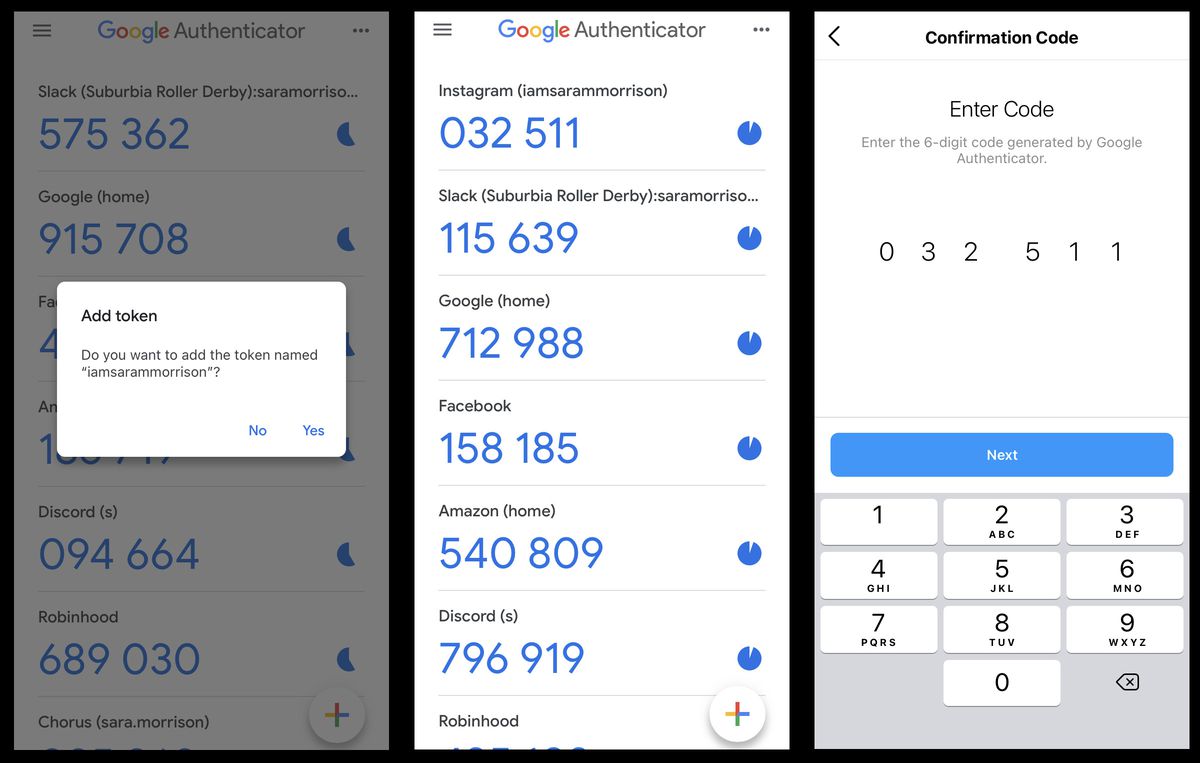
When enabling 2-step verification for your Google Account or any other service supporting it, you are prompted to download and install the Google Authenticator app. The app generates a unique QR code that you scan using the app.
QR Code Scanning
Once you scan the QR code, the app automatically sets up the account and generates a six-digit code every 30 seconds. This code is unique and valid for a short period, making it virtually impossible to guess or reuse.
Verification
When attempting to log in to your account, you are prompted to enter the six-digit code generated by the Google Authenticator app. If the code is correct, access is granted.
Code Generation
Codes are generated based on the current time, ensuring each code is unique and valid only for a short period. This makes it extremely difficult for hackers to intercept and reuse the codes.
Synchronization
One of the most significant features of Google Authenticator is its ability to synchronize codes across all your devices. This means that if you have the app installed on multiple devices, you can access the same account using any of them, as long as you have the latest code.
Benefits of Using Google Authenticator
The benefits of using Google Authenticator are numerous and significant:
Read more: Resetting Google Authenticator
Enhanced Security
The primary benefit is the additional layer of security it provides. By requiring a second form of verification, it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts.
Ease of Use
The app is incredibly user-friendly. Setting up an account is straightforward, and the interface is intuitive, making it easy for anyone to use.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Available on both Android and iOS, Google Authenticator ensures you can use it regardless of the device you prefer.
Offline Access
One of the most impressive features is its ability to generate codes even without an internet connection. This means you can still access your accounts securely even in areas with poor network coverage.
Read more: Lost Phone? Use Google Authenticator
Synchronization Across Devices
As mentioned earlier, the app allows you to synchronize your codes across all your devices. This feature is particularly useful if you have multiple devices and want to ensure you can always access your accounts securely.
Encryption
Google encrypts the codes both in transit and at rest, ensuring your verification codes remain protected from any potential bad actors.
Compatibility with Various Services
Google Authenticator is compatible with a wide range of services that support 2-step verification, including Google Accounts, Dropbox, Facebook, and many more.
Setting Up Google Authenticator
Setting up Google Authenticator is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps:
Read more: How To Use Google Authenticator On PC
Download and Install
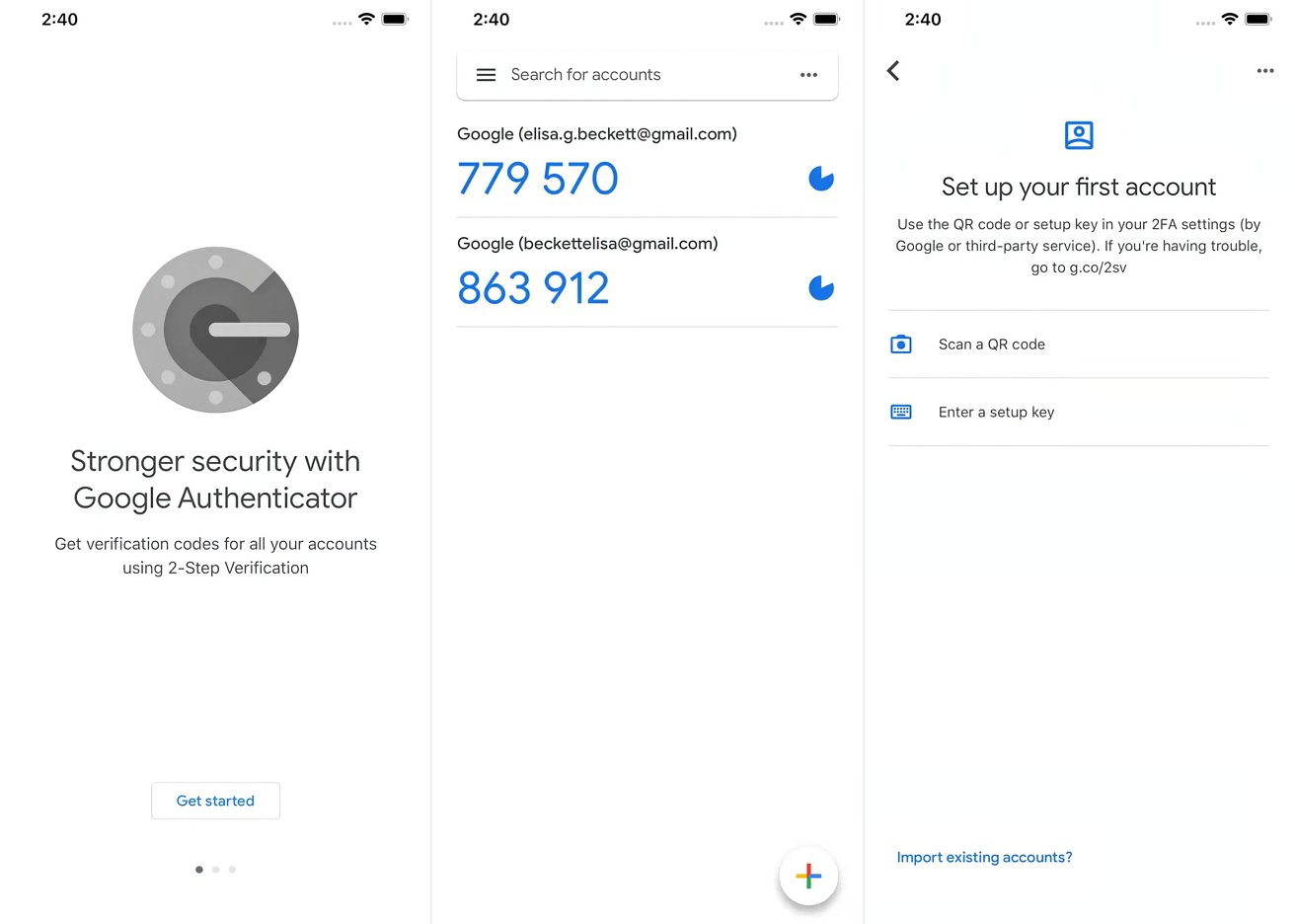
First, download and install the Google Authenticator app from the Google Play Store (for Android) or the App Store (for iOS).
Enable 2-Step Verification
Once installed, go to your account settings (e.g., Google Account settings) and enable 2-step verification. You will be prompted to download the Google Authenticator app.
Scan the QR Code
Open the Google Authenticator app and scan the QR code provided by your account service. This will automatically set up the account and generate a six-digit code.
Add Accounts Manually
If you prefer not to use the QR code, you can add accounts manually by entering the secret key provided by your service.
Read more: Google Authenticator: Is it Free?
Synchronize Codes
Once you have set up multiple accounts, you can synchronize your codes across all your devices by signing in to your Google Account.
Tips for Using Google Authenticator Effectively
To get the most out of Google Authenticator, here are some tips to keep in mind:
Keep Your Devices Updated
Ensure your devices are running the latest version of the Google Authenticator app to access all the latest features and security patches.
Backup Your Codes
While Google Authenticator synchronizes codes across devices, it's still a good idea to backup your codes manually. This can be done by taking a screenshot of the codes or writing them down in a secure location.
Read more: Restoring Google Authenticator
Use Strong Passwords
While Google Authenticator provides an additional layer of security, it's crucial to use strong passwords for your accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words.
Monitor Your Accounts
Regularly monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity. If you notice any unusual activity, immediately change your passwords and notify the service provider.
Use Multiple Authentication Methods
Consider using multiple authentication methods such as SMS or U2F keys in addition to Google Authenticator for added security.
Final Thoughts
Google Authenticator is a powerful tool in the fight against cyber threats. By providing an additional layer of security through time-based one-time passwords, it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts. Its ease of use, cross-platform compatibility, and ability to generate codes offline make it an essential tool for anyone looking to improve their online security. Whether you're protecting your personal Google Account or securing sensitive business information, Google Authenticator is an indispensable component of any robust security strategy.
The power of Google Authenticator lies in its simplicity, effectiveness, and widespread compatibility. By integrating this app into your daily routine, you can significantly bolster the security of your online presence and protect yourself against potential threats. As technology continues to evolve, tools like Google Authenticator will remain crucial in safeguarding our digital lives.