Home>Software and Apps>How To Recover Google Authenticator

Software and Apps
How To Recover Google Authenticator
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how to recover Google Authenticator for your Software and Apps. Regain access to your accounts with our step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Google Authenticator
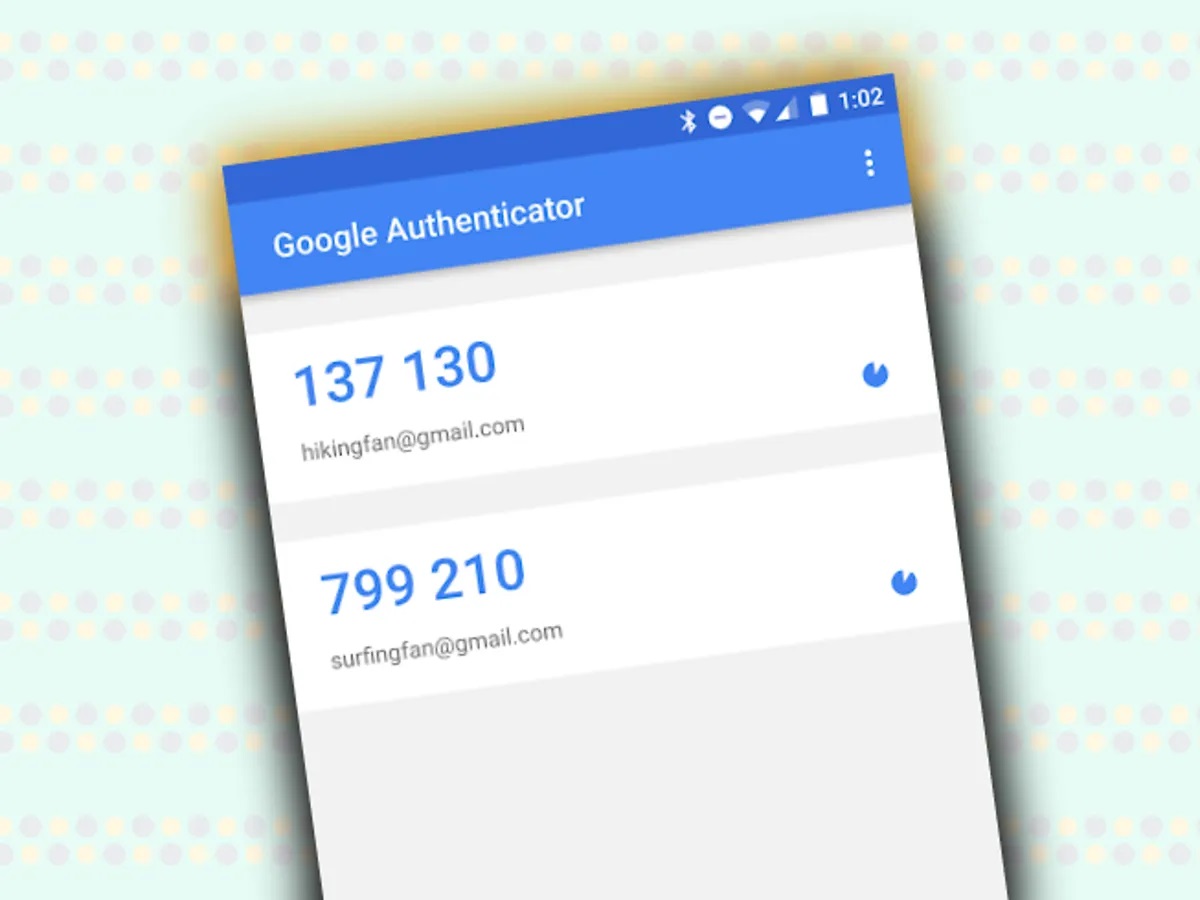
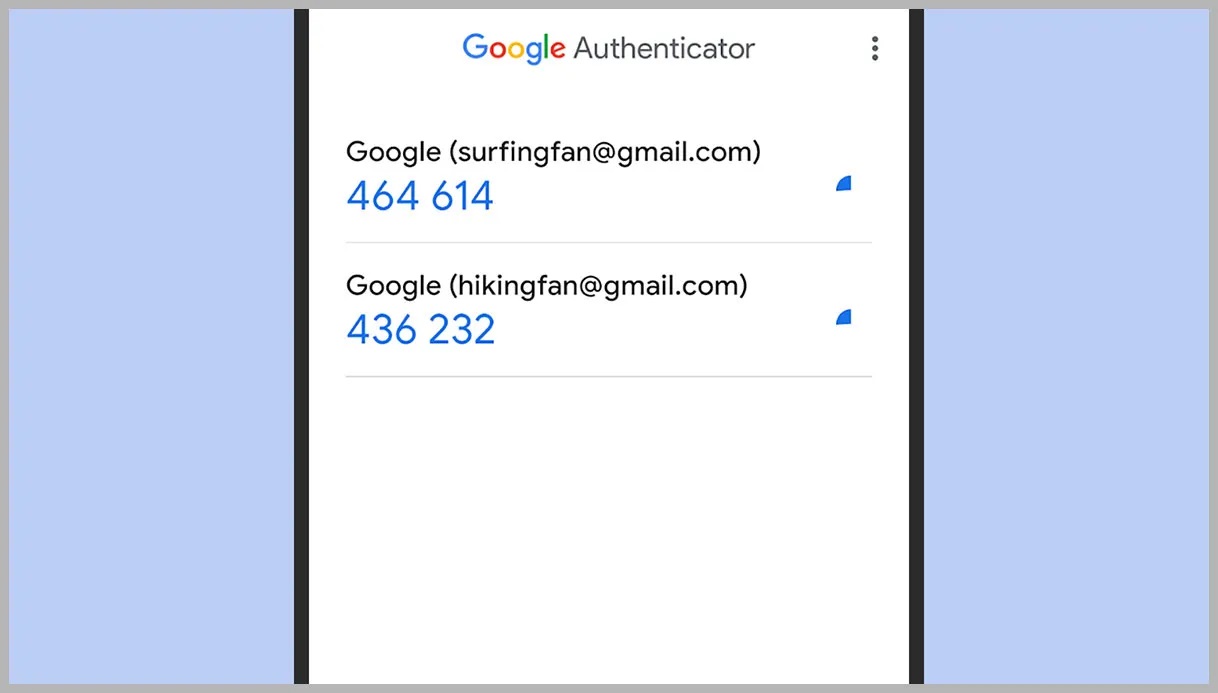
Google Authenticator is a widely-used two-factor authentication (2FA) method that adds an extra layer of security to your Google account. It generates time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) on your smartphone. These six-digit codes are valid for a short period, typically 30 seconds.
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
Preparing for Recovery
Preparation is key to ensuring a smooth recovery process. Here are some steps to take:
Generate Backup Codes
- When setting up Google Authenticator, generate backup codes. These can be used instead of SMS 2FA and are essential for recovery.
- To generate backup codes, go to Google Account settings, select "Security," then "2-Step Verification." Click on "Backup codes" and follow the instructions to generate and print the codes.
Save Backup Codes Securely
- Store backup codes in a safe place, such as a secure note-taking app or a physical document. Ensure they are not easily accessible to others.
- Consider encrypting the document containing the backup codes for added security.
Enroll Multiple Security Keys
- Administrators should enroll multiple security keys for their accounts. This ensures a spare key is available if the primary key is lost or compromised.
Read more: How To Use Google Authenticator On PC
Steps to Recover Your Google Authenticator
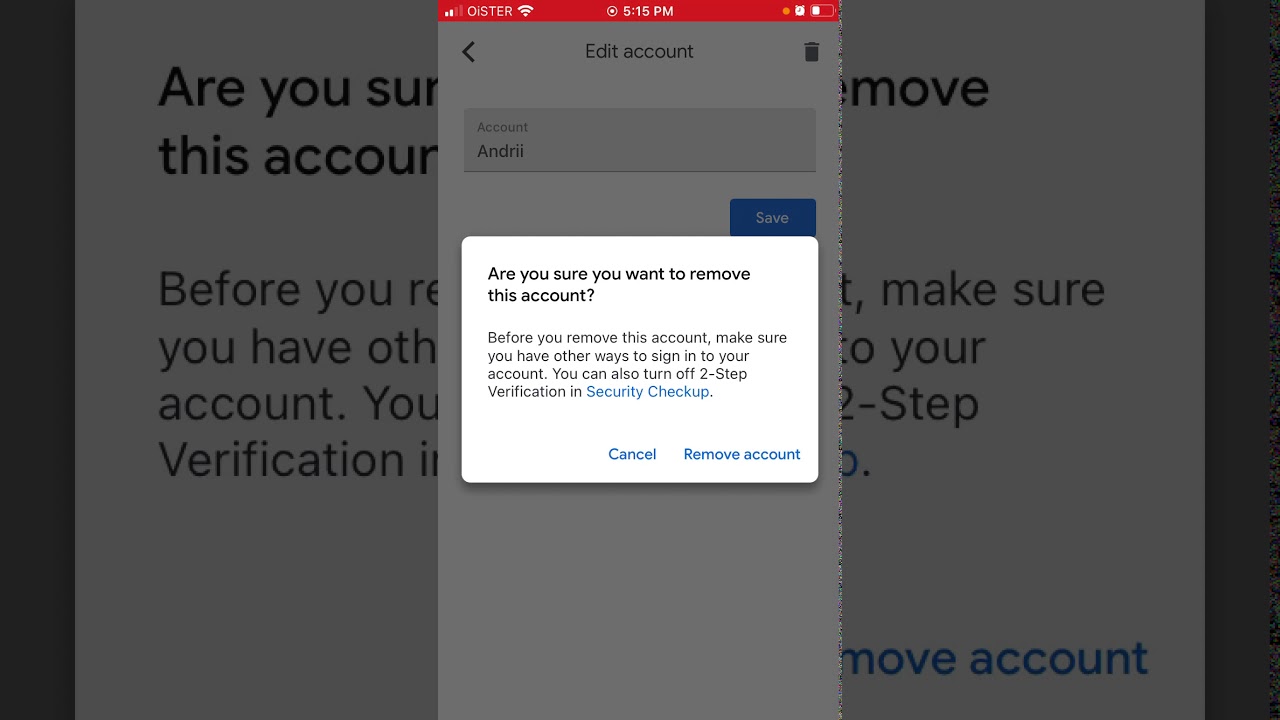
If access to your authenticator app or security key is lost, follow these steps to recover your Google account:
Step 1: Access Your Google Account
Sign In Using Your Password
- Go to the Google Account sign-in page and enter your email address and password. If 2-Step Verification is enabled, you will be prompted to enter the code from your authenticator app or security key.
Use Backup Codes
- If backup codes are available, use them to sign in. Enter one of the unused backup codes in the provided field and click "Next." This temporarily bypasses the 2-Step Verification requirement.
Step 2: Generate New Backup Codes
If all backup codes are used or new ones are needed, generate more:
Access the 2-Step Verification Settings
- Go to Google Account settings, select "Security," then "2-Step Verification."
Generate New Backup Codes
- Click on "Backup codes" and follow the instructions to generate new codes. These will be displayed on the screen and can be downloaded as a .txt file or printed directly.
Step 3: Set Up a New Authenticator App
If access to the original authenticator app is lost, set up a new one:
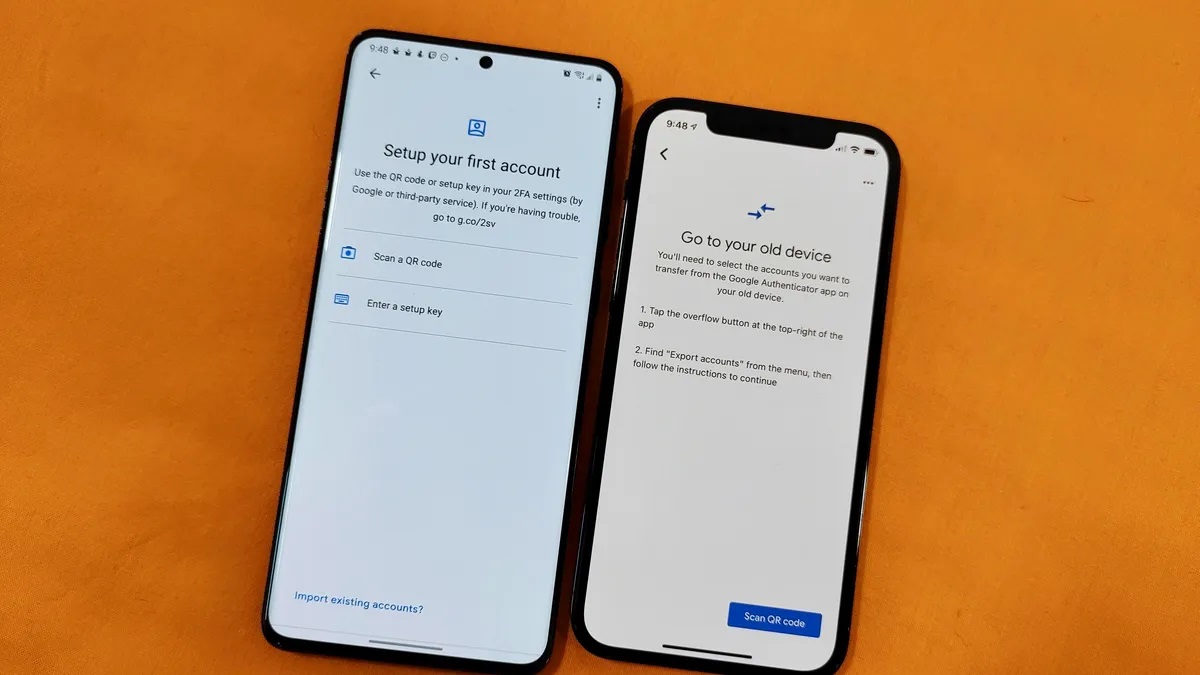
Download and Install a New Authenticator App
- Download and install an authenticator app from the Google Play Store (e.g., Google Authenticator) or Apple App Store (e.g., Google Authenticator).
Scan the QR Code
- Open the new authenticator app and scan the QR code displayed on the Google Account settings page under "2-Step Verification." This links your account to the new app.
Read more: How To Sign Into Google Authenticator
Step 4: Set Up a Security Key
If a security key is preferred over an authenticator app, set one up:
Purchase a Security Key
- Buy a security key from Google or a third-party vendor.
Add the Security Key to Your Account
- Go to Google Account settings, select "Security," then "2-Step Verification." Click on "Add security key" and follow the instructions to add the new key.
Additional Tips for Security
To avoid losing access to Google Authenticator again, follow these additional tips:
Regularly Generate New Backup Codes
- Periodically generate new backup codes to ensure a fresh set is available.
Store Backup Codes Securely
- Always store backup codes in a secure location, such as an encrypted note-taking app or a physical document.
Read more: How Does Google Authenticator Work
Use Multiple Security Measures
- Consider using both an authenticator app and a security key for added security.
Keep Your Devices Up to Date
- Regularly update devices and apps to ensure the latest security patches and features are installed.
By following these steps and tips, you can effectively recover Google Authenticator and regain access to your account. Prioritize security by generating and storing backup codes securely and using multiple security measures.