Home>Software and Apps>How to Backup Google Authenticator

Software and Apps
How to Backup Google Authenticator
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how to backup Google Authenticator easily with our step-by-step guide. Keep your software and apps secure with our expert tips. Protect your digital assets today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding the Risks of Google Authenticator
Before exploring backup methods, it's important to understand the risks associated with relying solely on Google Authenticator:
- Losing Access to Your Phone: If your phone is lost, stolen, or damaged, you might lose access to your Google Authenticator app. This can be particularly problematic if you don't have backup codes or another method to recover your accounts.
- Cloud Backup Risks: Google recently introduced the option to backup your one-time codes into the cloud. However, this feature is not end-to-end encrypted, which means that Google or anyone with access to their servers could potentially see the secret codes.
- Backup Code Vulnerabilities: Printed backup codes can be easily intercepted by an intruder if they are in physical proximity to the paper. This makes them as secure as a password written on a piece of paper.
Read more: How Does Google Authenticator Work
Official Methods for Backing Up Google Authenticator
Google provides several official methods for backing up your Google Authenticator codes. Here’s how you can do it:
Generating Backup Codes
To generate backup codes, follow these steps:
- Log in to Your Google Account: Open your web browser and sign in to your Google account.
- Access Security Settings: Click on the profile icon in the top right corner of the screen and select “Manage your Google Account.”
- Navigate to 2-Step Verification: Scroll down to the “Security” section and click on “2-Step Verification.”
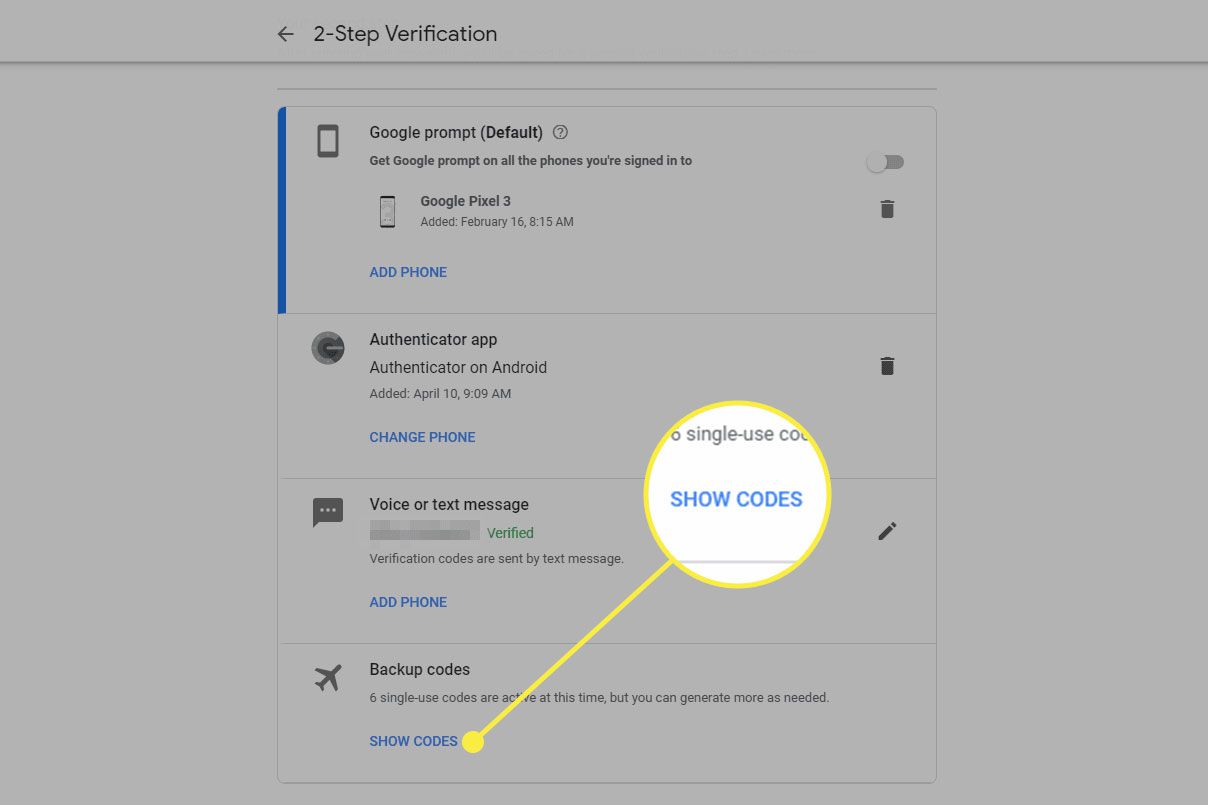
- Generate Backup Codes: If you haven’t already set up backup codes, you will see an option to generate them. Click on “Backup codes” and then “Show codes.”
- Download or Print Codes: You will see 10 single-use eight-digit codes. You can either download these codes as a .txt file or print them out. Each code can only be used once.
Using Backup Codes for Recovery
If you lose access to your Google Authenticator app, you can use these backup codes to regain access to your accounts:
- Enter 2FA Code: When prompted to enter a 2FA code and you can’t access your Google Authenticator app, use one of the backup codes.
- Restore Account: If you want to restore your Google Authenticator account on a new phone, use the backup codes as a recovery method.
Alternative Methods for Backing Up Google Authenticator
Given the risks associated with cloud backups and printed backup codes, it’s advisable to explore alternative methods for securing your 2FA codes. Here are some options:
Read more: How To Sign Into Google Authenticator
YubiKey
YubiKey is a hardware key that can be used for multiple accounts, providing a more secure alternative to cloud backups. These keys are reliable, easy to use, and offer a one-time cost. They are particularly useful if you switch phones frequently or have accounts that are targeted by attacks.
Authy
Authy is another authenticator app that offers more robust backup and recovery features compared to Google Authenticator. It allows for easy transfer of accounts to new devices and provides better security measures, making it a preferred choice for many users.
Chrome Authenticator App
The Chrome Authenticator App is a browser extension that can store and manage your 2FA codes. It allows you to backup all your codes to a plain text file, which can be downloaded and stored securely. This app also auto-fills the 2FA text box when needed and can regenerate the original QR code for transferring codes to other devices.
Best Practices for Backing Up Google Authenticator
To ensure maximum security when backing up your Google Authenticator codes, follow these best practices:
- Store Backup Codes Securely: Keep your backup codes in a secure location, such as a safe or a locked cabinet. Avoid storing them in easily accessible places like your desk drawer or wallet.
- Encrypt Backup Files: If you choose to download your backup codes as a .txt file, encrypt it immediately. This will prevent anyone from accessing the codes if the file falls into the wrong hands.
- Use Hardware Keys: Consider using hardware keys like YubiKey for added security. These keys are less likely to be compromised compared to cloud backups or printed codes.
- Regularly Update Your Backup: Regularly generate new backup codes and store them securely. This ensures that you always have a valid set of codes in case you need to recover your accounts.
- Avoid Sharing Backup Codes: Never share your backup codes with anyone, including friends or family members. This is crucial to maintaining the security of your accounts.
Backing up your Google Authenticator codes is crucial for maintaining access to your online accounts in case of an emergency. While Google provides official methods for generating backup codes, these methods come with inherent risks such as lack of end-to-end encryption. Therefore, it’s advisable to explore alternative solutions like YubiKey or Authy for added security. By following best practices and using secure methods for backing up your codes, you can ensure that your accounts remain protected even if you lose access to your primary device.
In summary, while Google Authenticator is a reliable app for generating 2FA codes, it’s essential to be proactive about securing these codes to prevent potential risks. By understanding the risks and using the right backup methods, you can significantly enhance the security of your online presence.