Home>Software and Apps>Lost Phone with Google Authenticator: A Digital Dilemma


Software and Apps
Lost Phone with Google Authenticator: A Digital Dilemma
Modified: September 5, 2024
Protect your digital assets with our guide on recovering a lost phone with Google Authenticator. Learn how to safeguard your software and apps.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Google Authenticator
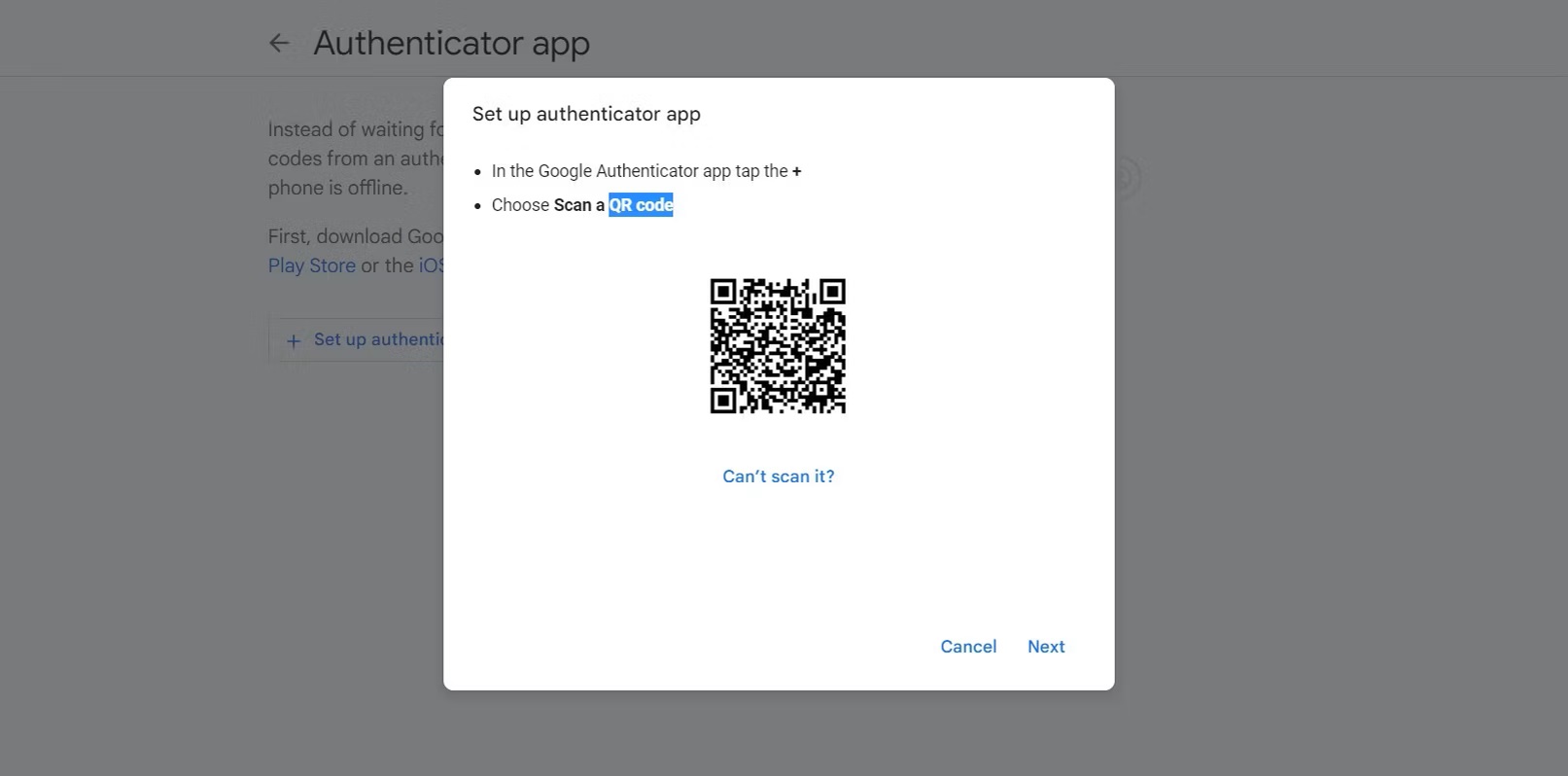
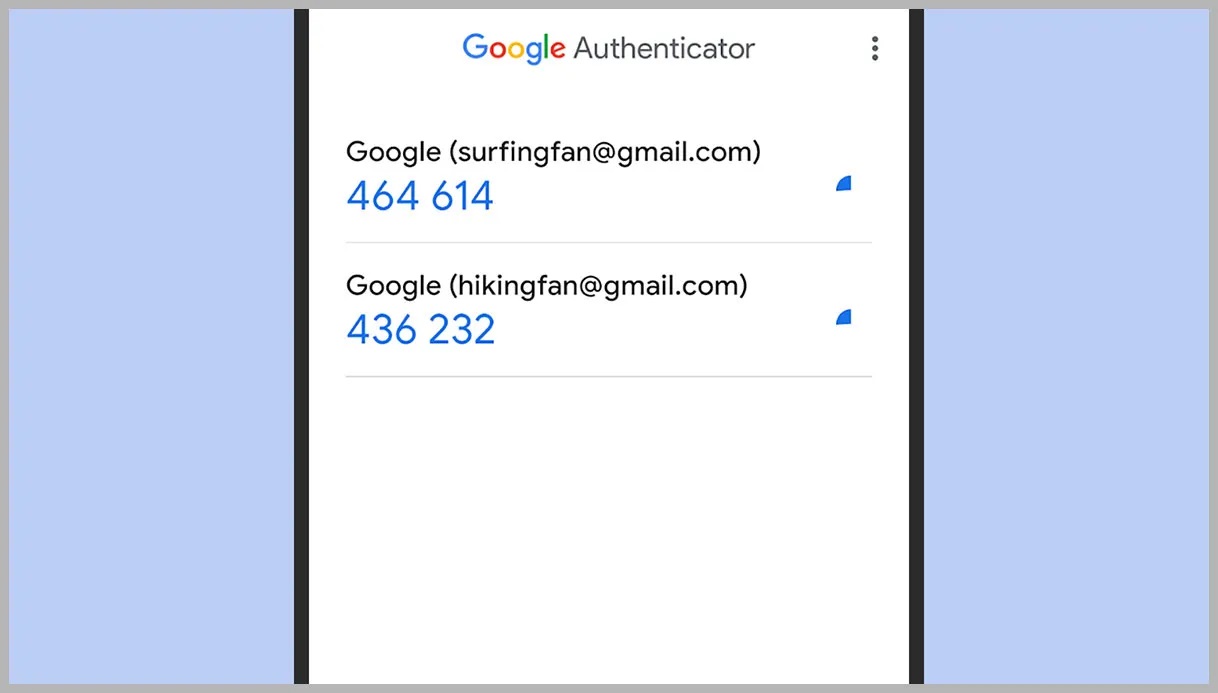
Google Authenticator serves as a time-based one-time password (TOTP) generator, adding an extra layer of security to Google accounts. It generates a unique code every 30 seconds, which must be entered along with the account password to log in. This method significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring a second form of verification.
Read more: Lost Phone? Use Google Authenticator
The Problem of a Lost Phone
Losing a phone equipped with Google Authenticator presents immediate challenges in regaining access to the associated Google account. The process can be complex and time-consuming, especially if backup options or additional security measures have not been set up.
Initial Steps
- Sign In with Password Only: Attempt to sign in using only the password. However, this will not work if 2-Step Verification is enabled, as the system will prompt for the second verification step.
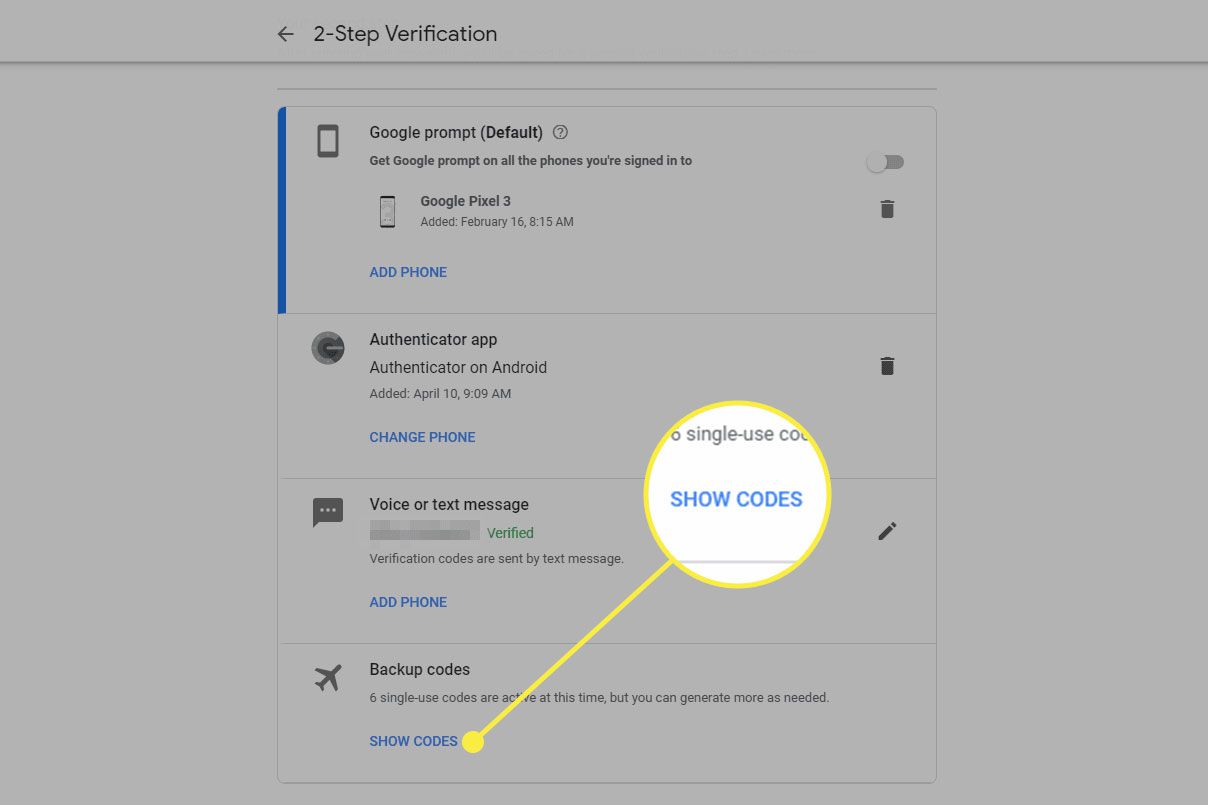
- Backup Options: Utilize backup options such as verification codes, Google prompts, or a backup security key. If these options are unavailable or compromised, the situation becomes more critical.
Recovery Process
- Verification Codes: Use stored verification codes to sign in. Only the newest code will work, and using multiple codes can lead to confusion and potential account lockout.
- Google Prompts: Google prompts offer an alternative to text message (SMS) verification codes. They provide a more secure way to verify identity by using the Google app on another device. This method requires another device with the Google app installed and an active internet connection.
- Backup Security Key: If a backup security key has been added to the account, it can be used as the second verification step. This method is particularly useful if Advanced Protection is enabled, which requires a backup security key for recovery.
- Recovering Without Backup Options: If none of the above options are available, follow the steps to recover the account. This process involves answering security questions and providing identification information, which can take up to 3-5 business days.
Complications and Challenges
Losing a phone with Google Authenticator can lead to several complications:
- Account Lockout: If unable to access the account within a certain time frame (usually 24 hours), the account may lock out, requiring further verification steps to regain access.
- Time-Sensitive Nature: The codes generated by Google Authenticator are time-sensitive, making it crucial to act quickly to avoid missing the window for verification.
- Technical Issues: Technical issues such as incorrect time settings on the Google Authenticator app can prevent codes from working correctly, adding to the frustration.
- User Experience: The recovery process can be user-unfriendly, especially for those who are not tech-savvy. Navigating through complex menus and following precise instructions can be overwhelming.
Solutions and Best Practices
To mitigate the risks associated with losing a phone equipped with Google Authenticator, consider the following best practices:
- Set Up Backup Options: Always set up backup options such as verification codes, Google prompts, or a backup security key. This ensures that even if the primary phone is lost, there are alternative methods to regain access.
- Regularly Update Devices: Ensure that all devices used for 2-Step Verification are regularly updated with the latest software to avoid technical issues.
- Sync Time Correctly: Ensure that the time on the Google Authenticator app is correctly synced to prevent code generation issues.
- Use Multiple Devices: Use multiple devices for 2-Step Verification to ensure that there is always an alternative method available in case one device is lost.
- Educate Yourself: Understand the recovery process and have all necessary information readily available to expedite the recovery process.
- Advanced Protection: Consider enabling Advanced Protection, which requires a backup security key for recovery, providing an additional layer of security.
Additional Tips
- Use a Secure Storage Method: Store backup codes and security keys in a secure location, such as a password manager or a physical safe, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly Review Account Settings: Regularly review account settings to ensure that all backup options are up-to-date and functioning correctly.
- Educate Family Members: Educate family members or colleagues who may need to access the account in case of an emergency about the recovery process and backup options.
- Consider Third-Party Solutions: Consider using third-party solutions that offer additional security features, such as password managers or security apps, to further enhance digital security.
By following these tips and understanding the recovery process, users can ensure that their digital lives remain secure even in the event of a lost phone with Google Authenticator.