Home>Latest News>Technology Trends>What Is Augmented Reality


Technology Trends
What Is Augmented Reality
Modified: September 5, 2024
Discover the latest technology trends with a comprehensive guide to augmented reality. Learn how this innovative technology is shaping the future.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
What Is Augmented Reality?
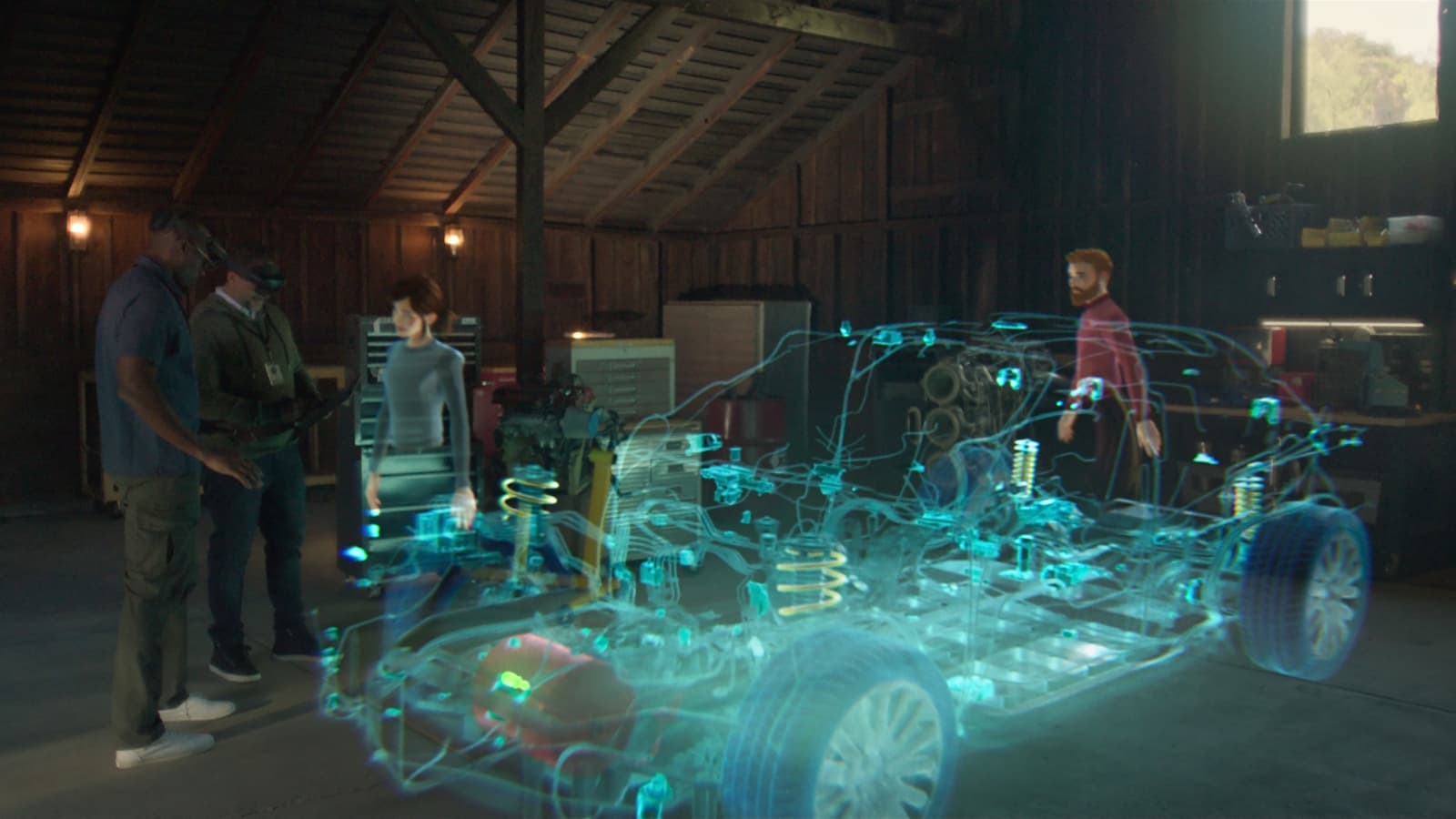
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing user experiences by providing additional context and insights. This technology has gained significant attention due to its potential applications in education, entertainment, healthcare, and business. This article explores the concept of augmented reality, its history, how it works, and its current and future applications.
Read more: What Are AR Apps
History of Augmented Reality
The concept of augmented reality dates back to the 1960s when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland created the first head-mounted display (HMD) capable of displaying virtual objects in real-time. However, the term "augmented reality" was first coined by Tom Caudell in 1990 while working at Boeing. Caudell used the term to describe a system displaying information about aircraft parts in real-time, aiding workers in assembling aircraft more efficiently.
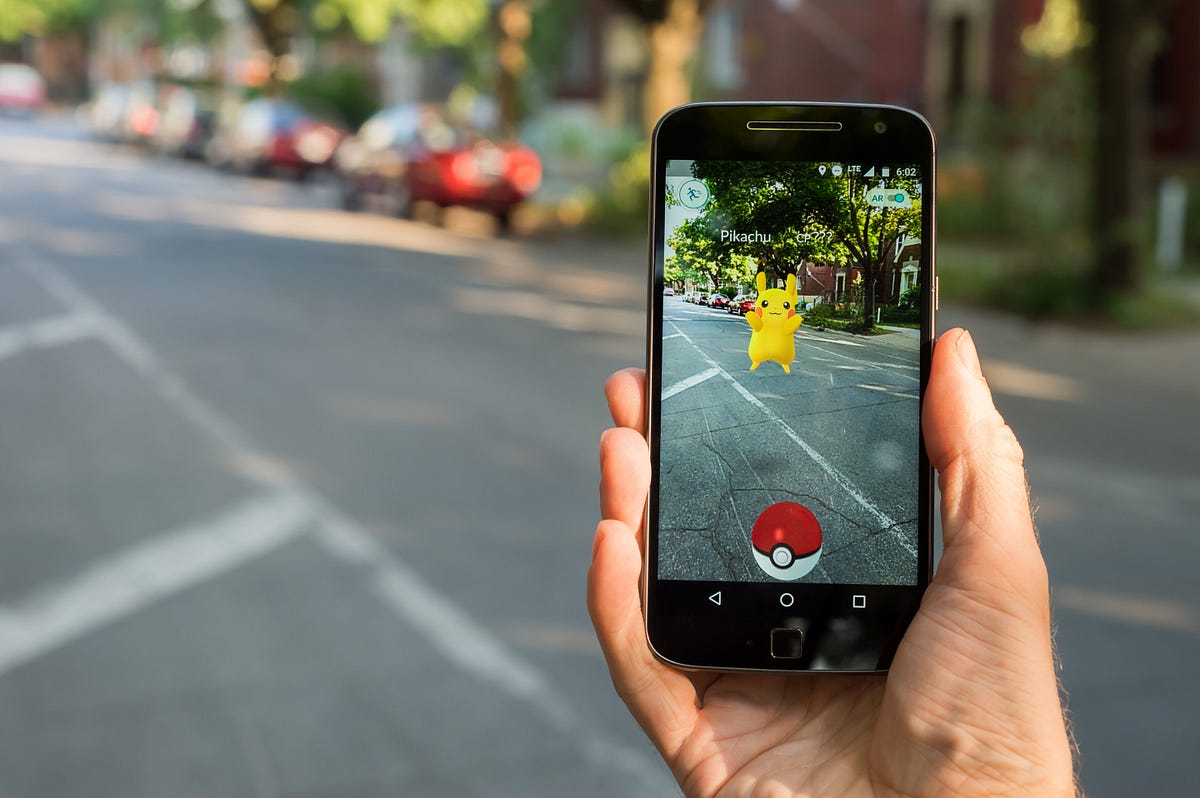
In the early 2000s, AR began gaining traction with the development of mobile devices and the introduction of AR applications like Pokémon Go. Released in 2016, Pokémon Go became a global phenomenon, showcasing AR's potential to engage users interactively. Since then, AR has continued evolving with advancements in hardware and software technologies, making it more accessible and user-friendly.
How Augmented Reality Works
Augmented reality uses a combination of hardware and software technologies to overlay digital information onto the real world. Here’s a breakdown of the key components involved:
Hardware
- Display: The most common display technology used in AR is the head-mounted display (HMD). HMDs can be either simple glasses or more advanced systems like Microsoft HoloLens. Other displays include smartphones and tablets.
- Sensors: These track the user's movements and position in space. Common sensors include GPS, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and cameras.
- Cameras: Essential for capturing the real-world environment and overlaying digital information onto it.
Software
- AR Engines: Software frameworks that manage the AR experience. Examples include ARKit (Apple) and ARCore (Google).
- Tracking Systems: Use machine learning algorithms to track the user's position and orientation in space.
- Content Creation Tools: Allow developers to create AR content, such as 3D models and interactive experiences.
Types of Augmented Reality
There are several types of augmented reality, each with unique characteristics and applications:
Marker-Based AR
Uses markers or QR codes to trigger the display of digital information. For example, a user might point their smartphone at a QR code to see additional details about a product.
Markerless AR
Does not require any markers and uses machine learning algorithms to detect the environment and overlay digital information accordingly. Examples include Pokémon Go and many other location-based games.
Superimposition AR
Superimposes digital information directly onto the real world. For instance, a user might see virtual arrows pointing to specific parts of a car while looking at it.
Read more: The Advantages of Augmented Reality
Projection-Based AR
Projects digital information onto a surface using a projector. Commonly used in interactive displays and presentations.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality has a wide range of applications across various industries:
Education
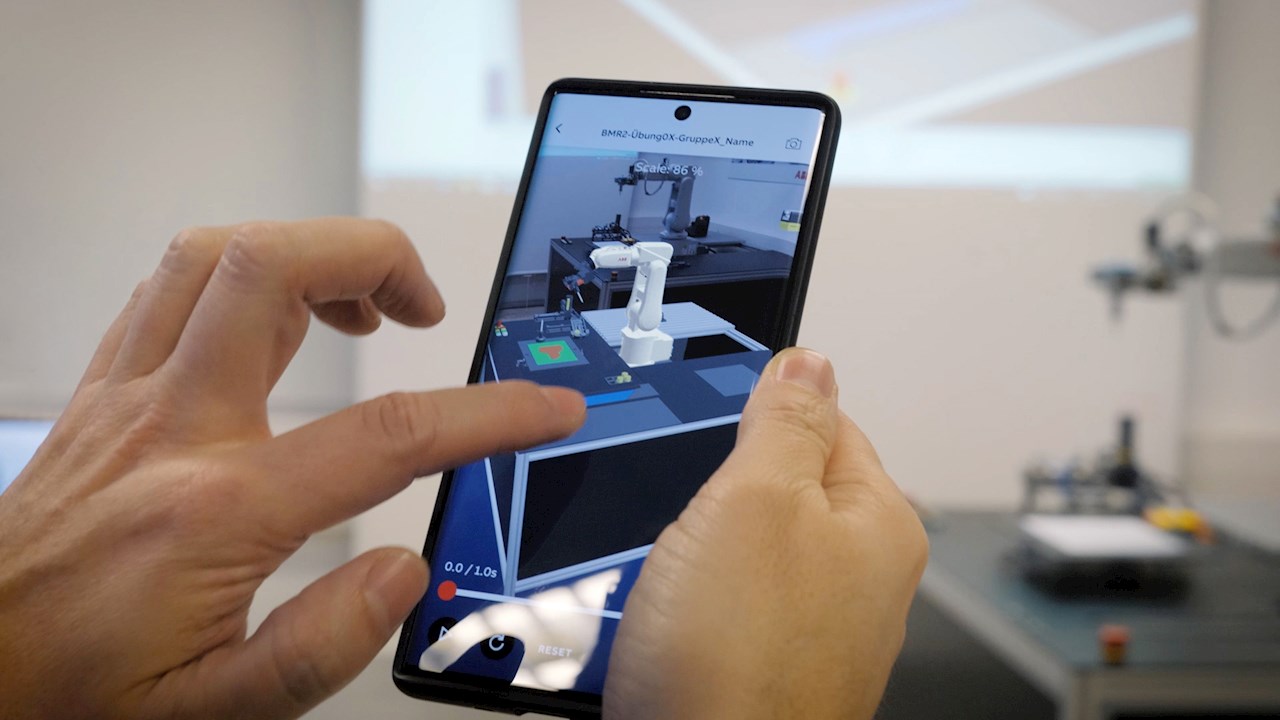
- Interactive Learning: AR can enhance learning by providing interactive and immersive experiences. For example, students can visualize complex anatomical structures or historical sites.
- Interactive Textbooks: AR can turn textbooks into interactive learning tools by overlaying videos, 3D models, and interactive quizzes onto the pages.
Healthcare
- Surgical Training: AR can train surgeons by simulating complex surgeries in a virtual environment.
- Patient Education: AR can help patients understand their conditions better by providing interactive visualizations of their anatomy and treatment options.
Read more: What Are AR Glasses
Retail
- Virtual Try-On: AR allows customers to try on clothes virtually before making a purchase.
- Product Demonstrations: Retailers can use AR to demonstrate products in a more engaging way, such as showing how furniture would look in a customer's home.
Entertainment
- Gaming: AR has revolutionized the gaming industry with location-based games like Pokémon Go.
- Interactive Experiences: AR can create immersive experiences for movies and theater performances by overlaying digital information onto the real environment.
Manufacturing
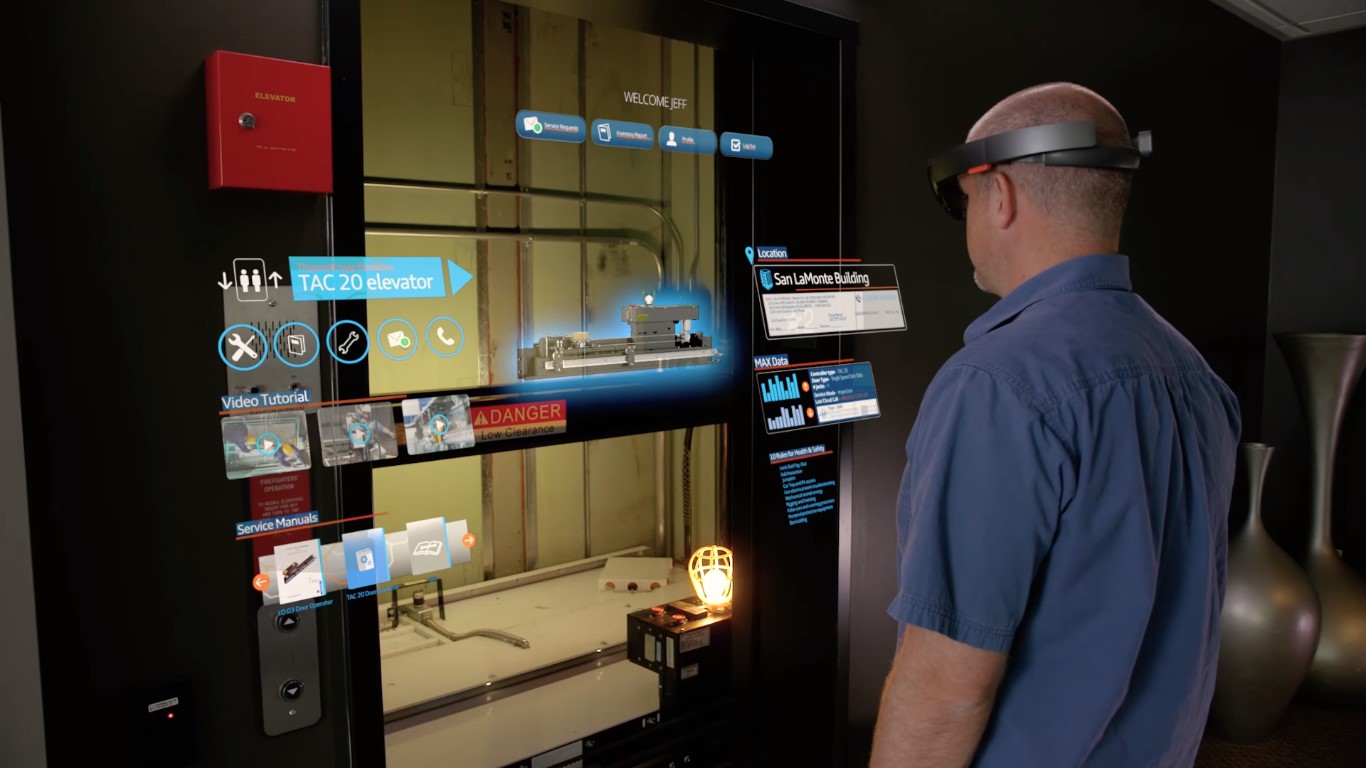
- Assembly Instructions: AR can provide workers with step-by-step assembly instructions for complex machinery, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Quality Control: AR can help inspectors identify defects more easily by highlighting them in real-time.
Real Estate
- Virtual Tours: AR can provide potential buyers with virtual tours of properties, allowing them to explore homes remotely.
- Furniture Placement: AR can help buyers visualize furniture in their desired location before making a purchase.
Read more: What Are AR Games
Challenges and Limitations
While augmented reality has shown immense potential, it also faces several challenges and limitations:
Hardware Requirements
- High-quality AR experiences often require advanced hardware, which can be expensive and not widely available.
- Battery Life: AR devices can quickly drain batteries due to the processing power required for real-time tracking and rendering.
Content Creation
- Developing high-quality AR content is time-consuming and requires specialized skills.
- User Experience: Ensuring a seamless user experience is crucial but challenging, especially in markerless AR scenarios where the environment can be unpredictable.
Privacy Concerns
- AR applications often require access to location data and camera permissions, raising privacy concerns.
- Data Security: Ensuring the security of user data is essential, especially in healthcare and financial applications.
Read more: Augmented Reality Business Card
User Adoption
- Despite its potential, AR adoption is still relatively low due to the need for specialized hardware and the learning curve associated with using AR applications.
Future of Augmented Reality
The future of augmented reality looks promising with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries. Here are some trends and predictions:
Advancements in Hardware
- Future AR devices are expected to be more compact, lightweight, and affordable.
- Improved Tracking Systems: Next-generation tracking systems will provide more accurate and robust tracking capabilities, enhancing the overall AR experience.
Increased Adoption
- As more people become familiar with AR through popular applications like Pokémon Go, the technology is expected to become more mainstream.
- Enterprise Adoption: More businesses will start integrating AR into their operations, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Integration with Other Technologies
- AR is expected to integrate seamlessly with other emerging technologies like blockchain, IoT, and 5G networks.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Future AR applications will be designed to work across multiple platforms, including smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses.
Enhanced User Experience
- Future AR experiences will be more intuitive and user-friendly, with better support for voice commands and gesture-based interactions.
- Personalization: AR applications will be able to personalize the experience based on user preferences and behavior.
Augmented reality is a rapidly evolving technology with vast potential across various industries. While it faces several challenges and limitations, ongoing advancements in hardware and software technologies are expected to overcome these hurdles. As AR continues to integrate with other emerging technologies, it is poised to change the way we interact with the world around us.