Home>Software and Apps>Google Authenticator: Is it Free?


Software and Apps
Google Authenticator: Is it Free?
Modified: September 5, 2024
Discover if Google Authenticator is a free and secure software for two-factor authentication. Learn how to use it for added security in your apps.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction to Google Authenticator
Google Authenticator is an application developed by Google that provides a simple and secure way to generate one-time verification codes. These codes verify user identity during account logins, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password. The app supports 2-Step Verification, requiring both something you know (your password) and something you have (the verification code generated by the app).
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
How Google Authenticator Works
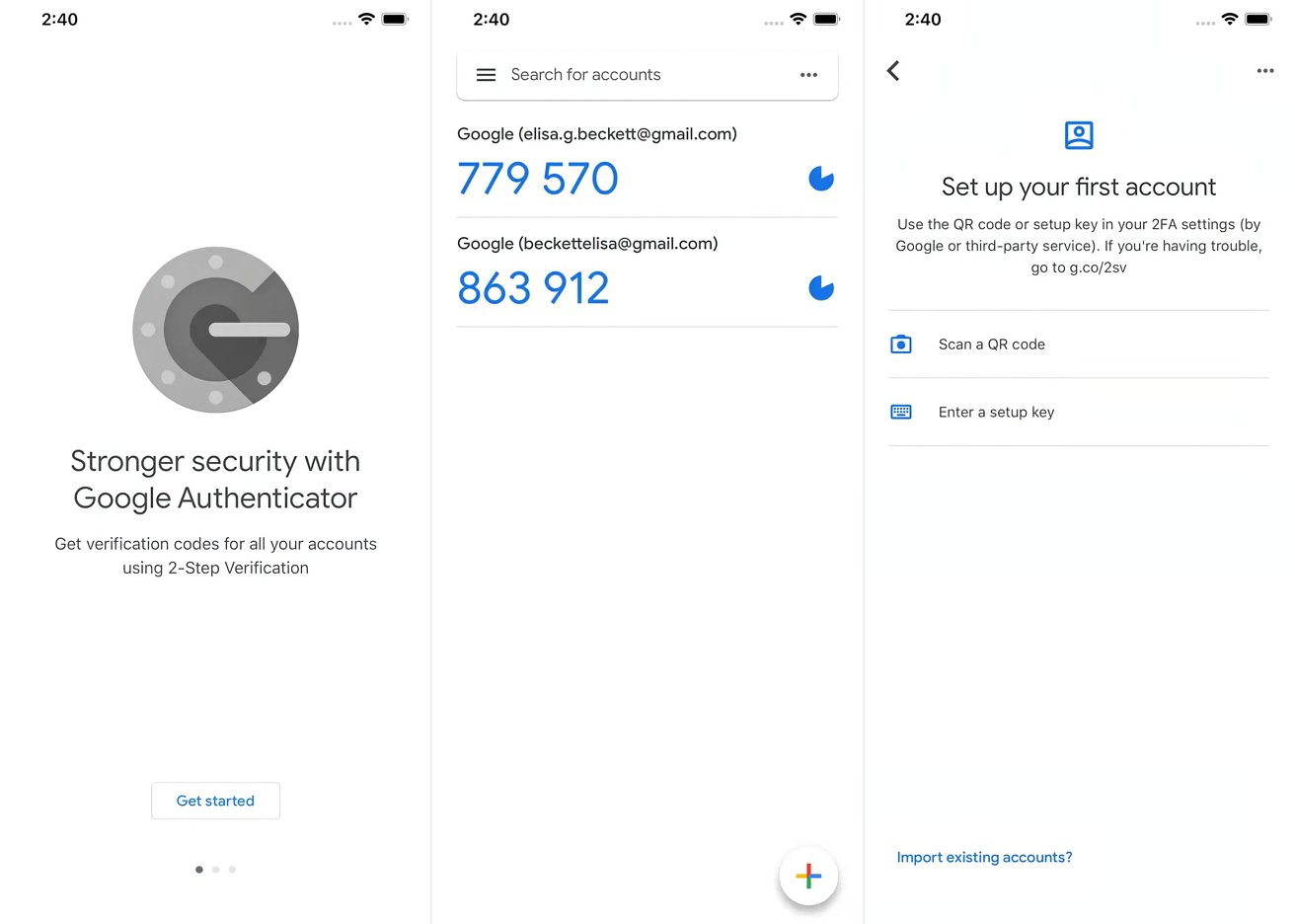
Steps to Set Up Google Authenticator
- Enable 2-Step Verification: Begin by enabling 2-Step Verification for your Google Account. Access your Google Account settings and follow the prompts to set up the feature.
- Download and Install the App: After enabling 2-Step Verification, download and install the Google Authenticator app on your device. Available for both Android and iOS devices.
- Scan the QR Code: Once installed, scan a QR code displayed on the Google Account settings page. This QR code contains the secret key needed to generate verification codes.
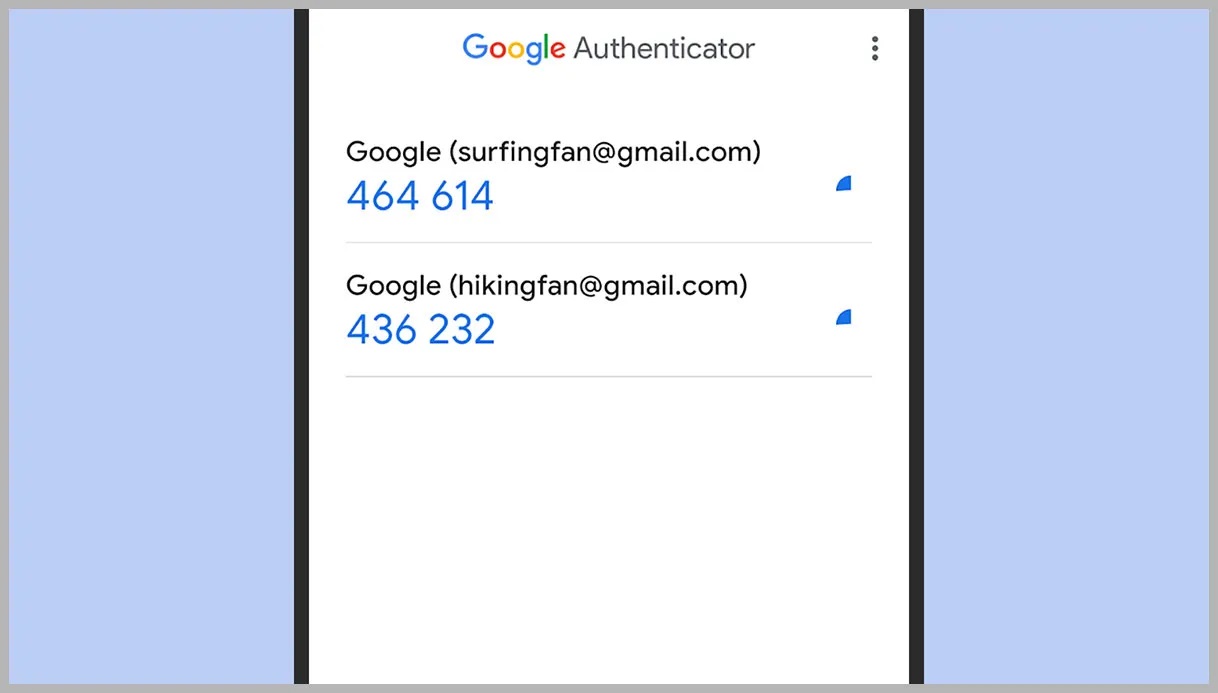
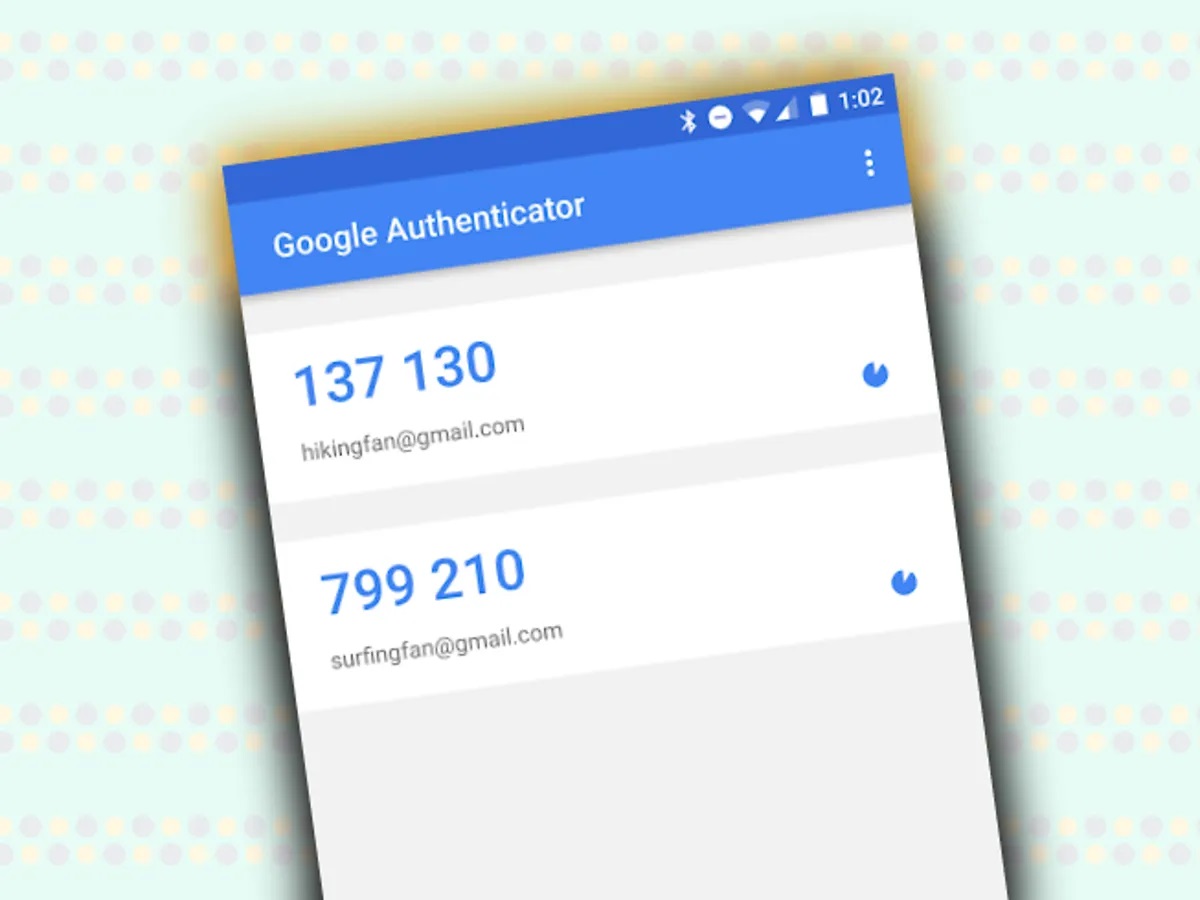
- Generate Verification Codes: After scanning the QR code, the app will start generating one-time verification codes. These codes are usually six digits long and valid for a short period (usually 30 seconds).
- Enter the Code: When logging into your Google Account, enter the verification code generated by the app. If correct, access will be granted.
Features of Google Authenticator
Key Features
- Cross-Device Synchronization: Synchronize verification codes across all devices. Access your codes from any device where the app is installed.
- Offline Capability: Generate verification codes without an internet connection. Highly reliable and secure, even in areas with poor network connectivity.
- Encryption: Verification codes are encrypted both in transit and at rest. Ensures that intercepted codes cannot be used without the corresponding secret key.
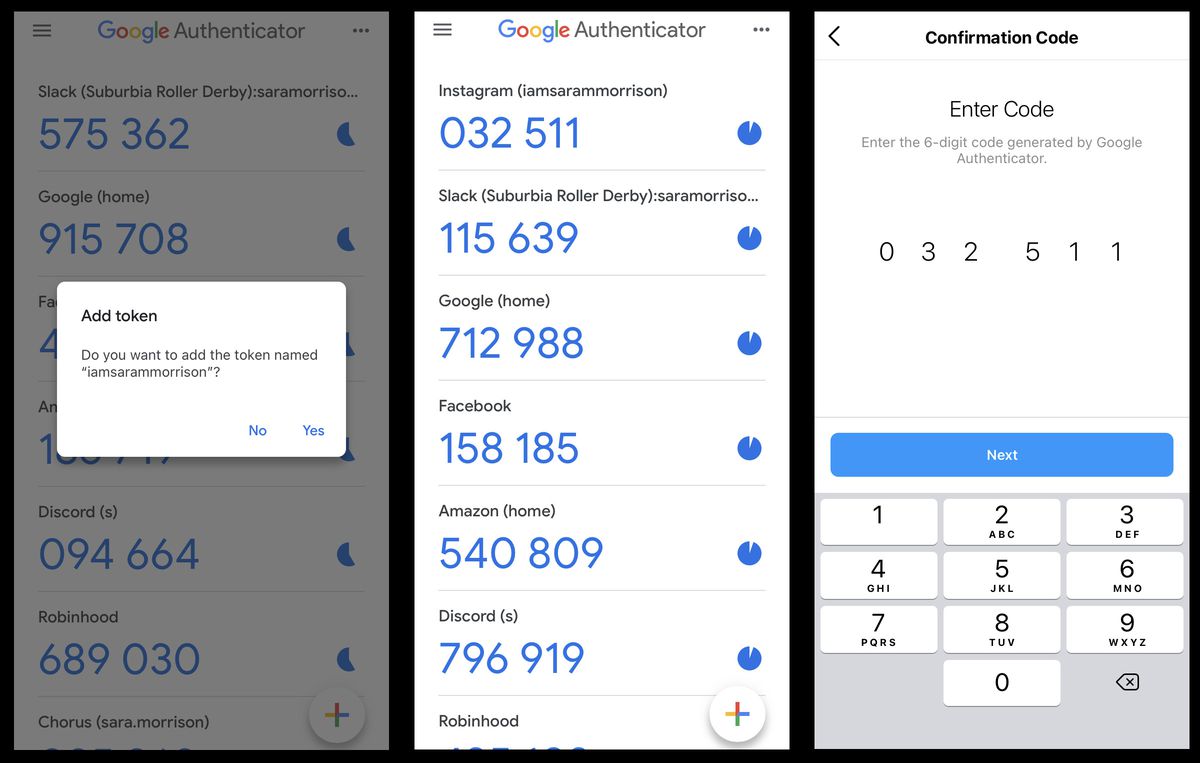
- Organizing Codes: Organize verification codes by dragging and dropping them to reorder. Use the search bar to quickly find specific codes.
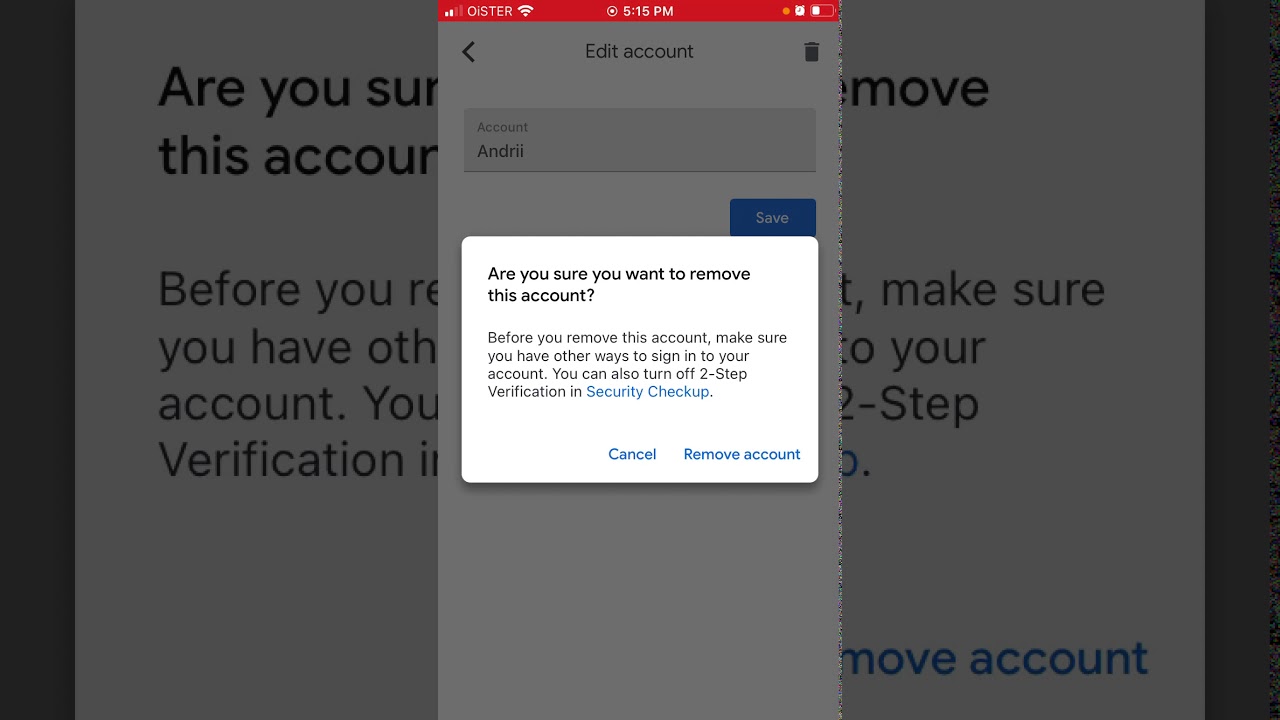
- Deleting Codes: Swipe right on a code to delete it. This action will delete the code from all devices where it is synced.
- Privacy Screen: For additional protection, the Privacy Screen feature requires verification from your device, such as a PIN, pattern, or biometric prompt, before using the app.
Using Google Authenticator Without a Google Account
Steps to Use Without a Google Account
- Initial Setup: When first opening the app, choose the option to use it without an account. This means synchronization with your Google Account will not be available, but the app can still generate verification codes.
- Removing Codes from Google Account: If codes are already saved to your Google Account and you want to use them without the account, tap your profile picture at the top right corner of the home screen and select “Use Authenticator without an account.” This action removes the codes from all Google Accounts and stores them on your device.
Is Google Authenticator Free?
Google Authenticator is free to download and use. Available for both Android and iOS devices, it does not require any subscription or payment. Google provides this service to enhance online security and protect user accounts from unauthorized access.
Common Questions and Issues
Read more: The Power of Google Authenticator
Syncing Codes
To sync verification codes across all devices, ensure you have version 6.0 or above on Android and version 4.0 or above on iOS.
Deleting Codes
Deleting a verification code from one device will also delete it from all other devices where it is synced. Deleting the entire Google Authenticator service will remove all verification codes from your Google Account.
Privacy Screen
To enable the Privacy Screen feature, go to the app’s settings and select “Privacy Screen.” Complete a verification step, such as entering a PIN or using biometric authentication.
Organizing Codes
Organize verification codes by dragging and dropping them to reorder. Use the search bar to quickly find specific codes.
Google Authenticator offers a robust and user-friendly application that plays a crucial role in protecting user identities in the digital age. Its features and functionalities make it an essential tool for anyone concerned about online security.