Home>Software and Apps>Resetting Google Authenticator

Software and Apps
Resetting Google Authenticator
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how to reset Google Authenticator easily with our step-by-step guide. Keep your software and apps secure with these simple instructions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Why Reset Google Authenticator?
Understanding the reasons for resetting Google Authenticator helps in knowing when to take action. Common reasons include:
- Lost or Stolen Device: Prevent unauthorized access by resetting the app.
- Device Change: Reconfigure the app when switching to a new device.
- App Issues: Fix malfunctions or unresponsiveness by resetting.
- Security Concerns: Enhance security if account compromise is suspected.
Read more: How To Reset Google Authenticator On IPhone
Preparing for Reset
Before starting the reset process, gather the following:
- Google Account Information: Have your username and password ready.
- Backup Codes: Keep backup codes for 2-Step Verification accessible.
- Alternative Authentication Methods: Be ready to use Google prompts or verification codes via email or SMS.
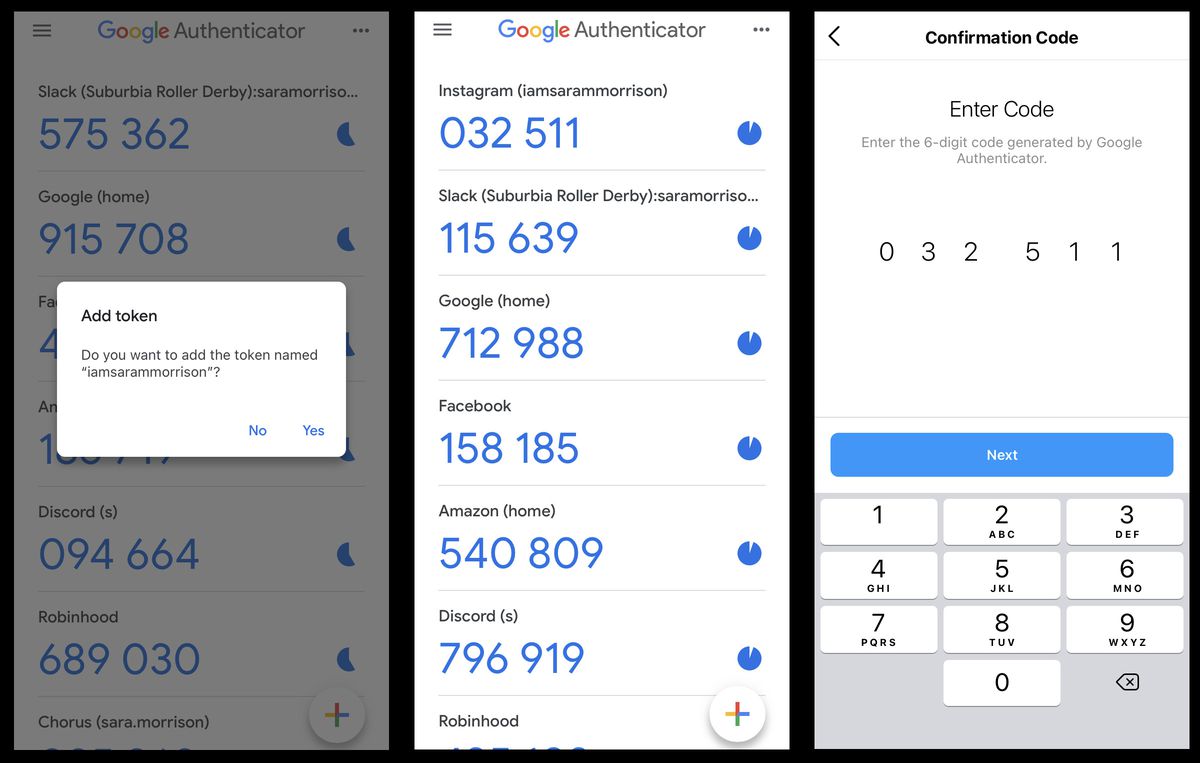
Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting Google Authenticator
Scenario 1: Resetting on a New Device
Switching to a new device? Follow these steps:
- Sign Out of Google Account: Log out on the new device.
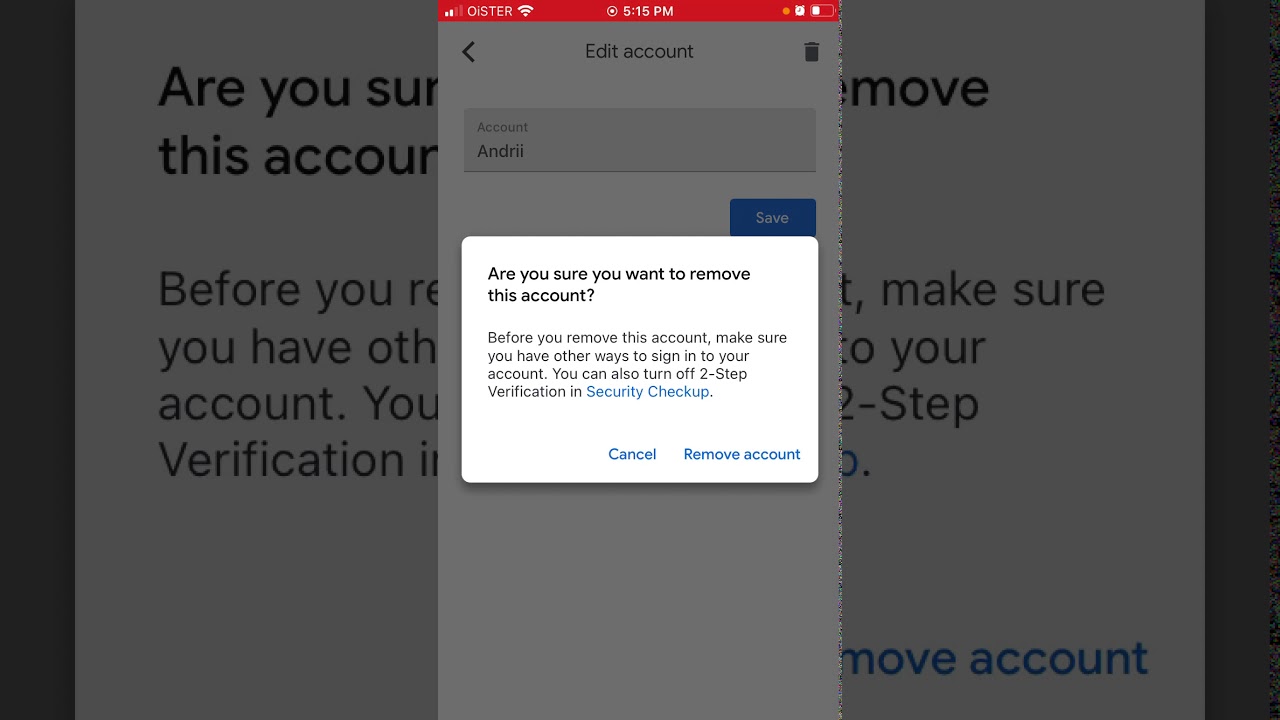
- Remove Old Device: In Google Account settings, remove the old device.
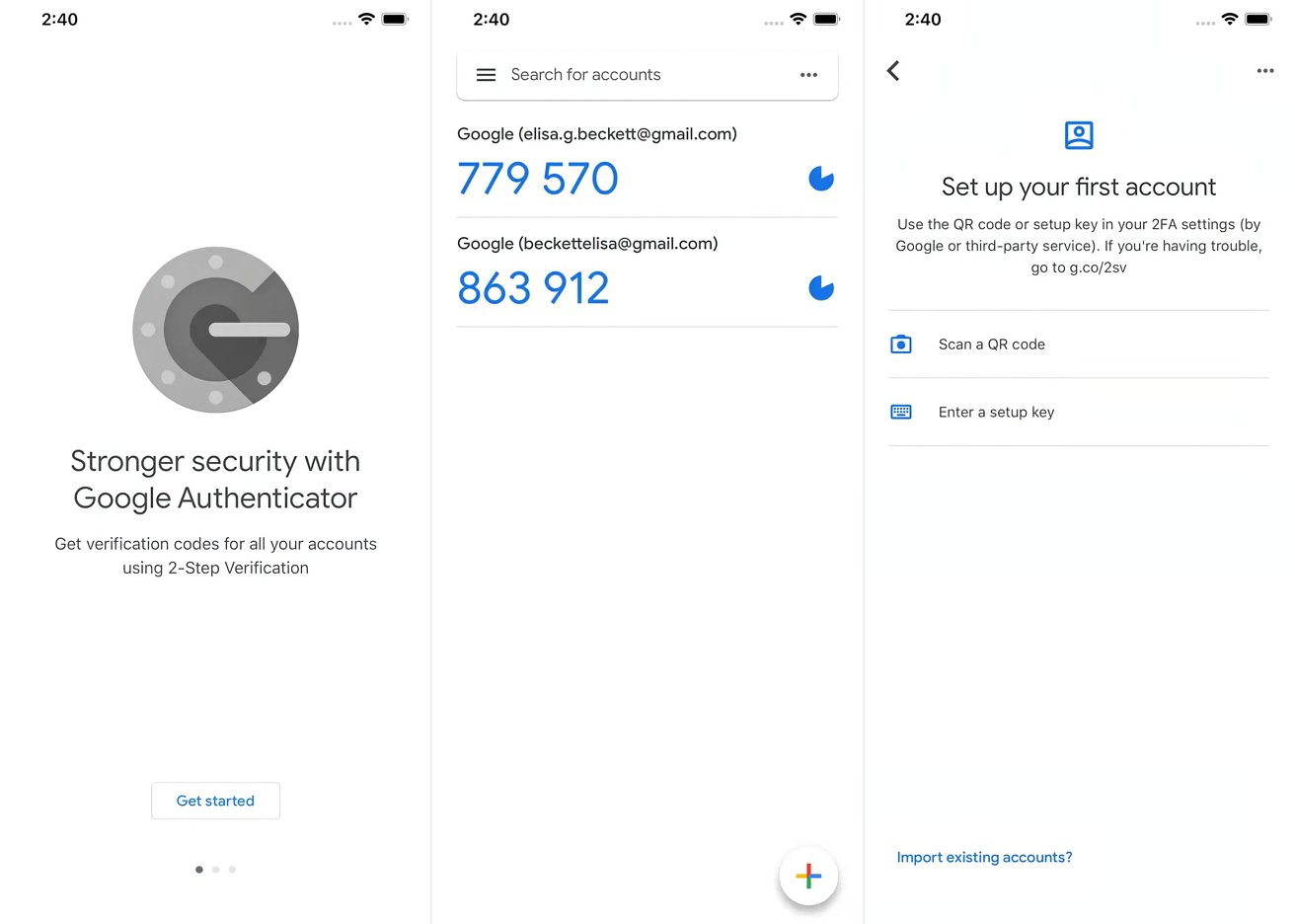
- Re-Enroll in 2-Step Verification: Sign back in and re-enroll using the new device.
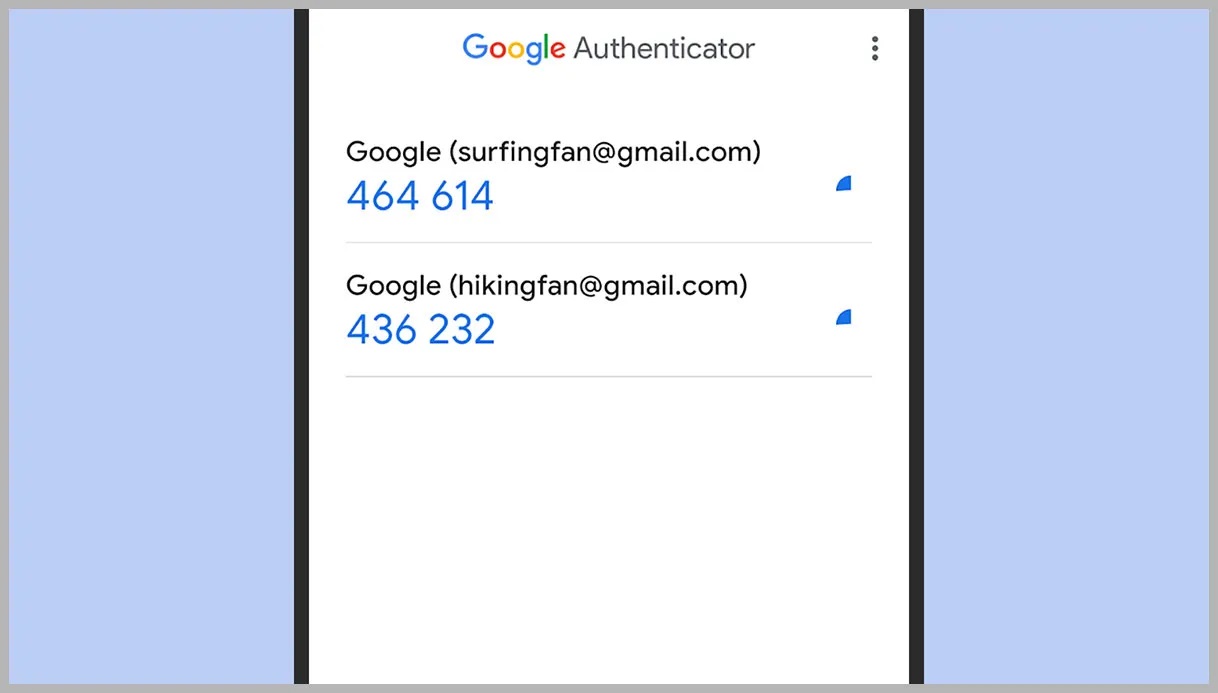
- Generate New Codes: Enter the new codes generated during setup.
Scenario 2: Resetting Due to App Issues
If the app malfunctions, try these steps:
- Uninstall and Reinstall: Remove and reinstall the app.
- Clear Cache and Data: Clear the app's cache and data.
- Reset App Settings: Restore default settings if available.
- Contact Support: Reach out to Google support if issues persist.
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
Scenario 3: Resetting Due to Lost or Stolen Device
For lost or stolen devices, follow these steps:
- Sign Out of Google Account: Log out on all devices.
- Remove Device from Account: In Google Account settings, remove the lost or stolen device.
- Use Backup Codes: Sign in using backup codes.
- Re-Enroll in 2-Step Verification: Re-enroll using a new device or method.
Troubleshooting Tips
Issue: Google Authenticator Codes Not Working
- Time Sync Issue: Ensure device time is correctly synced.
- Code Generation: Restart or reinstall the app if codes aren't generated.
- Alternative Methods: Use Google prompts or verification codes via email or SMS.
Issue: Unable to Sign In
- Backup Codes: Use backup codes if sign-in fails.
- Google Prompts: Use Google prompts as an alternative.
- Contact Support: Reach out to Google support for further help.
Advanced Protection
For accounts with Advanced Protection, follow these steps:
- Add Backup Security Key: Ensure a backup security key is added to the account.
- Remove Lost Key: Remove the lost key from the account.
- Get New Key: Add a new security key.
- Re-Enroll in 2-Step Verification: Re-enroll using the new security key.
Resetting Google Authenticator can be straightforward with the right steps. Whether switching devices, fixing app issues, or recovering from a lost device, understanding the process helps maintain account security. Always keep backup codes handy and be prepared to use alternative authentication methods if needed.