Home>Software and Apps>Restoring Google Authenticator


Software and Apps
Restoring Google Authenticator
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how to restore Google Authenticator easily with our step-by-step guide. Get back to using your favorite software and apps in no time!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Restoring Google Authenticator: A Comprehensive Guide
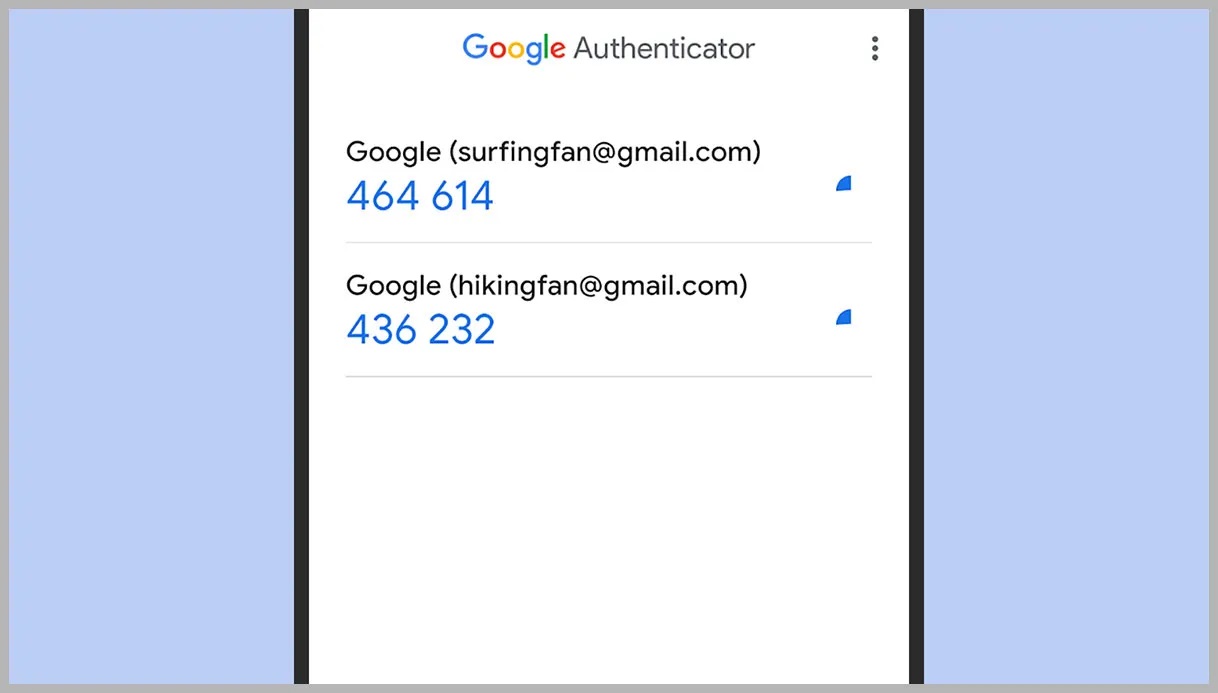
Google Authenticator is a popular two-factor authentication (2FA) app that adds an extra layer of security to your Google Account. Losing access to your Google Authenticator codes or needing to restore them can be frustrating. This guide will walk you through restoring Google Authenticator, setting it up, synchronizing codes, and troubleshooting common issues.
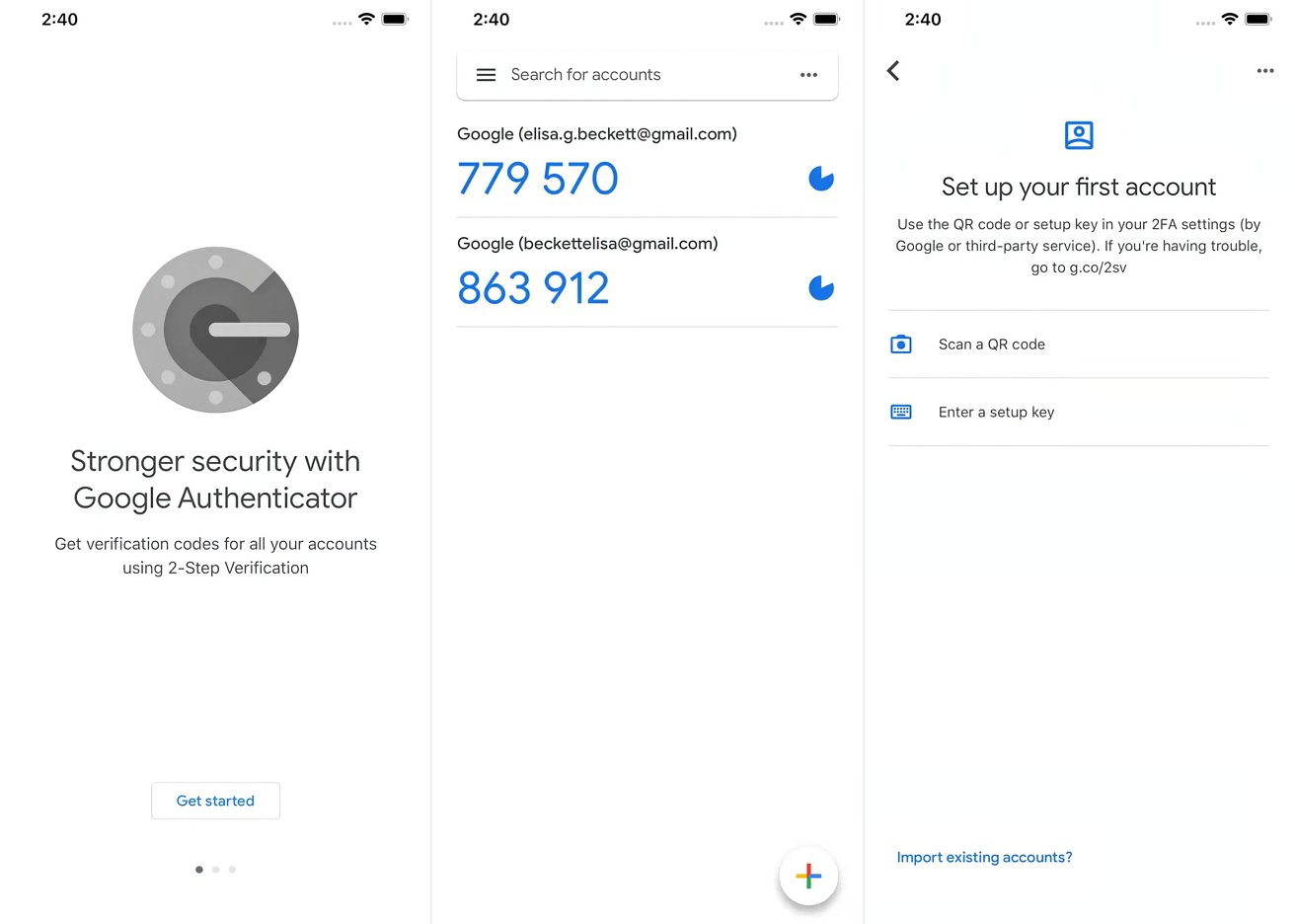
Setting Up Google Authenticator
Before diving into the restoration process, understanding the initial setup of Google Authenticator is crucial. Follow these steps:
Download and Install the App
- Android: Download from the Google Play Store.
- iOS: Download from the App Store.
Open the App
- Launch the Google Authenticator app after installation.
Set Up Authenticator
- Navigate to your 2-Step Verification settings for your Google Account.
- Sign in if prompted.
- Tap Set up authenticator.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
Read more: How to Backup Google Authenticator
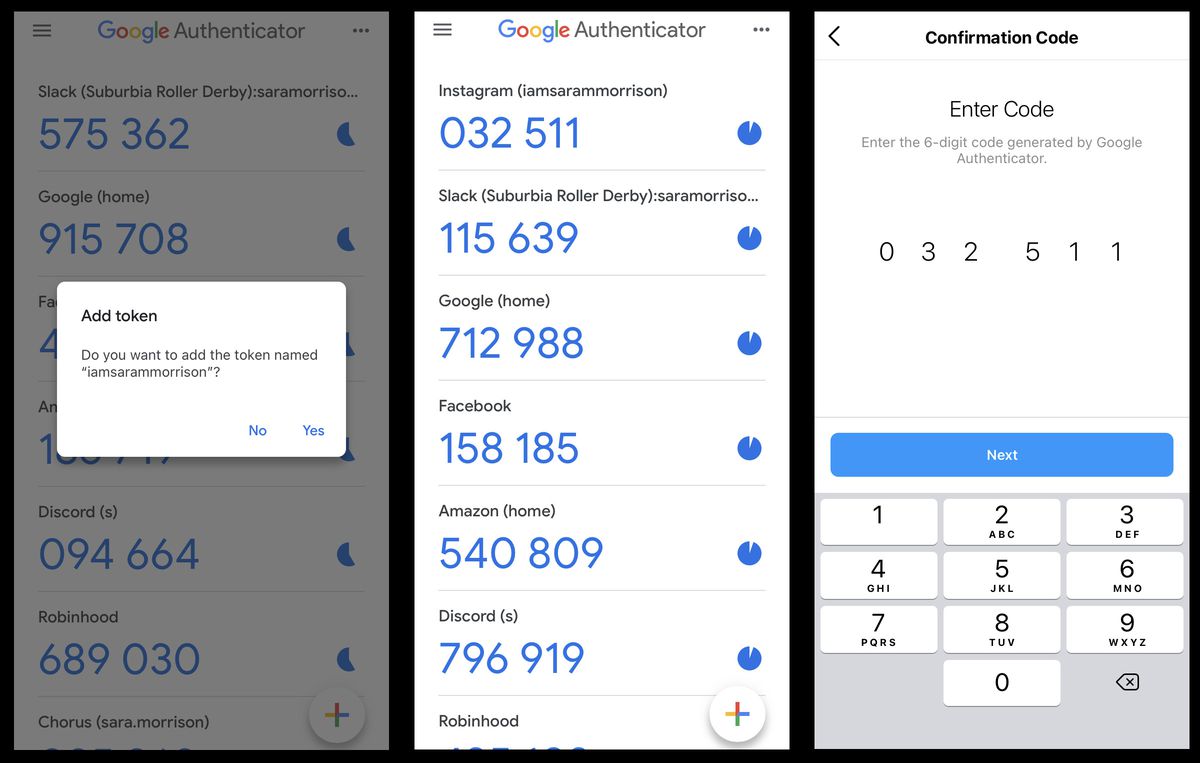
Add Accounts
- Add accounts by scanning a QR code or entering a secret key provided by the service you are using (e.g., Google Account).
Synchronizing Google Authenticator Codes
Synchronizing verification codes across all devices ensures access from any device set up with the app.
Requirements for Synchronization
- Android: Version 6.0 or above.
- iOS: Version 4.0 or above.
Steps to Synchronize Codes
-
Sign In to Your Google Account:
- Open the Google Authenticator app on any device.
- Sign in to your Google Account.
-
Sync Codes:
- The app will automatically sync verification codes with your Google Account.
- Changes made to codes on one device will reflect on all other devices with the app set up.
Restoring Google Authenticator
If access to Google Authenticator codes is lost or restoration is needed, follow these steps:
Option 1: Use Without a Google Account
-
Open the App:
- Launch the Google Authenticator app on your device.
-
Use Without an Account:
- Tap Use without an account when first opening the app.
- If codes are saved to your Google Account, tap your profile picture at the top right corner, then tap Use Authenticator without an account.
- This action removes codes from all Google Accounts and stores them on your device only.
Option 2: Transfer Codes to a New Device
-
Sign In to Your Google Account:
- Open the Google Authenticator app on your new device.
- Sign in to your Google Account.
-
Sync Codes:
- The app will automatically sync verification codes with your Google Account.
- Changes made to codes on one device will reflect on all other devices with the app set up.
Option 3: Re-Scan QR Code
- Re-Scan QR Code:
- Open the Google Authenticator app on your device.
- Tap the "+" icon to add a new account.
- Select "Scan a QR code" and re-scan the QR code provided by the service.
Read more: The Power of Google Authenticator
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issues may arise when restoring or using Google Authenticator. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Codes Not Syncing
- Ensure the latest version of the app is used.
- Verify devices meet the minimum requirements for synchronization (Android 6.0 or above, iOS 4.0 or above).
Lost Secret Key
- Re-scan the QR code provided by the service to generate a new secret key and sync it with your Google Account.
Device Not Recognized
- Ensure you have signed in to your Google Account within the app.
- Verify the device meets the minimum requirements for synchronization.
Read more: Is Google Authenticator Secure?
Organizing and Managing Codes
Proper organization and management of Google Authenticator codes are vital for maintaining security and convenience.
Organizing Codes
- Touch and hold any code, then drag it to reorder to a desired location.
- Use the search bar to find the code needed by entering any text matching the username.
Deleting Codes
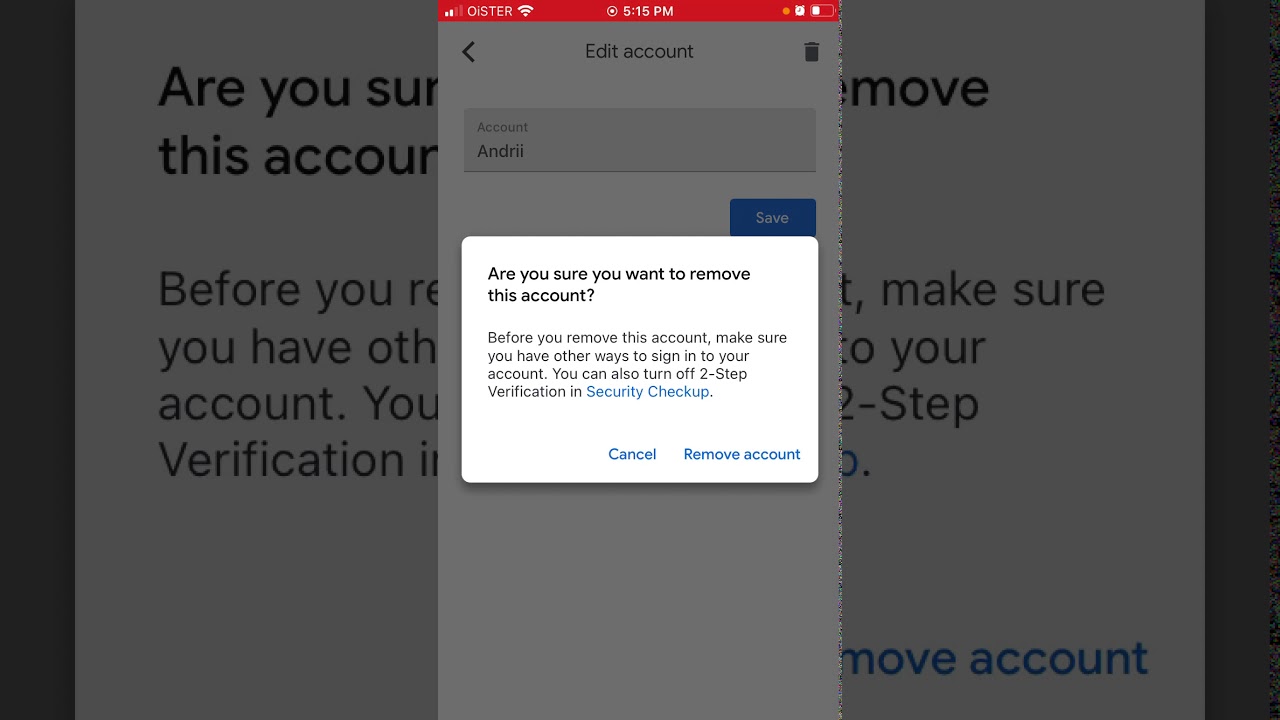
- On Android, swipe right on any code to show the delete option. Confirm deletion when prompted.
- If codes are synced to your Google Account, they will also be deleted from all devices where codes are synced.
Additional Security Measures
For added protection, turn on Privacy Screen in Google Authenticator. This requires verification from your device, like a PIN, pattern, or biometric prompt, before the app can be used.
Read more: Google Authenticator: Is it Free?
Steps to Turn On Privacy Screen
-
Open the App:
- Launch the Google Authenticator app on your device.
-
Go to Settings:
- Tap Menu > Settings > Privacy Screen.
-
Turn On Privacy Screen:
- Enable Privacy Screen.
- Complete the verification process required by your device.
Restoring Google Authenticator can be straightforward if the right steps are followed. By understanding how to set up the app, synchronize codes, and troubleshoot common issues, you can ensure that your 2FA setup remains secure and convenient. Whether using multiple devices or needing to restore codes after losing access, this guide provides the necessary information to manage Google Authenticator effectively. Always keep the app updated and follow best practices for organizing and managing codes to maintain the highest level of security for your Google Account.