Home>Software and Apps>How To Turn Off Two Factor Authentication

Software and Apps
How To Turn Off Two Factor Authentication
Modified: September 5, 2024
Learn how to disable two-factor authentication for software and apps. Follow our step-by-step guide to turn off 2FA and enhance your user experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of protection to online accounts by requiring a second form of verification in addition to a password. This can include a code sent to your phone, a fingerprint scan, or a one-time password generated by an authenticator app. While 2FA significantly enhances security, there may be situations where turning it off becomes necessary, such as experiencing issues with your authentication device or setting up a new device.
Purpose of 2FA
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: By requiring a second form of verification, 2FA significantly reduces the risk of hackers gaining access to your account even if they manage to obtain your password.
- Types of 2FA:
- Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP): Uses a time-based algorithm to generate a one-time password that changes every 30 seconds.
- SMS-Based 2FA: Sends a verification code via SMS to your phone.
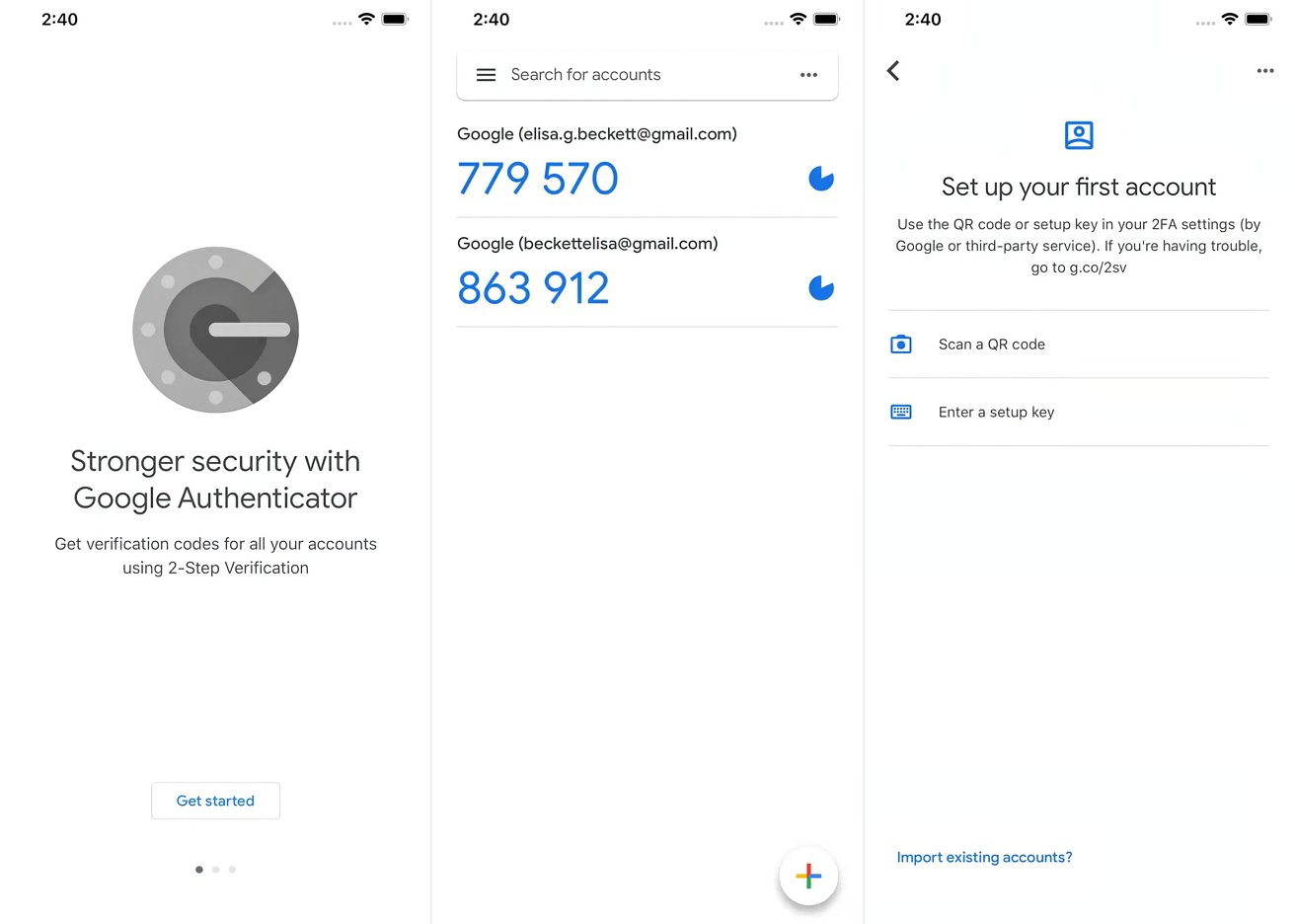
- Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator generate one-time passwords based on a secret key.
- Biometric Authentication: Includes fingerprint or facial recognition scans.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices like fobs that generate one-time passwords.
Benefits of Two-Factor Authentication
Despite the potential inconvenience, 2FA offers several significant benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password, they will still need the second factor to access your account.
- Protection Against Phishing: 2FA makes phishing attacks much less effective because hackers cannot obtain both your password and the second factor through phishing.
- Compliance with Security Policies: Many organizations, especially those in the financial sector, require employees to use 2FA as part of their security policies.
- Reduced Risk of Social Engineering: Social engineering attacks often rely on tricking users into revealing their passwords. 2FA makes these attacks much more difficult.
Challenges with Two-Factor Authentication
While 2FA is highly effective, it also presents several challenges:
- Convenience: The need to carry an additional device or use an app can be inconvenient, especially for users who are not tech-savvy.
- Technical Issues: Users may experience technical issues such as problems with their authentication devices or difficulties in setting up the second factor.
- Cost: While not always a significant issue, specialized hardware tokens can be expensive.
- User Adoption: Some users may resist using 2FA due to the perceived inconvenience or lack of understanding about its benefits.
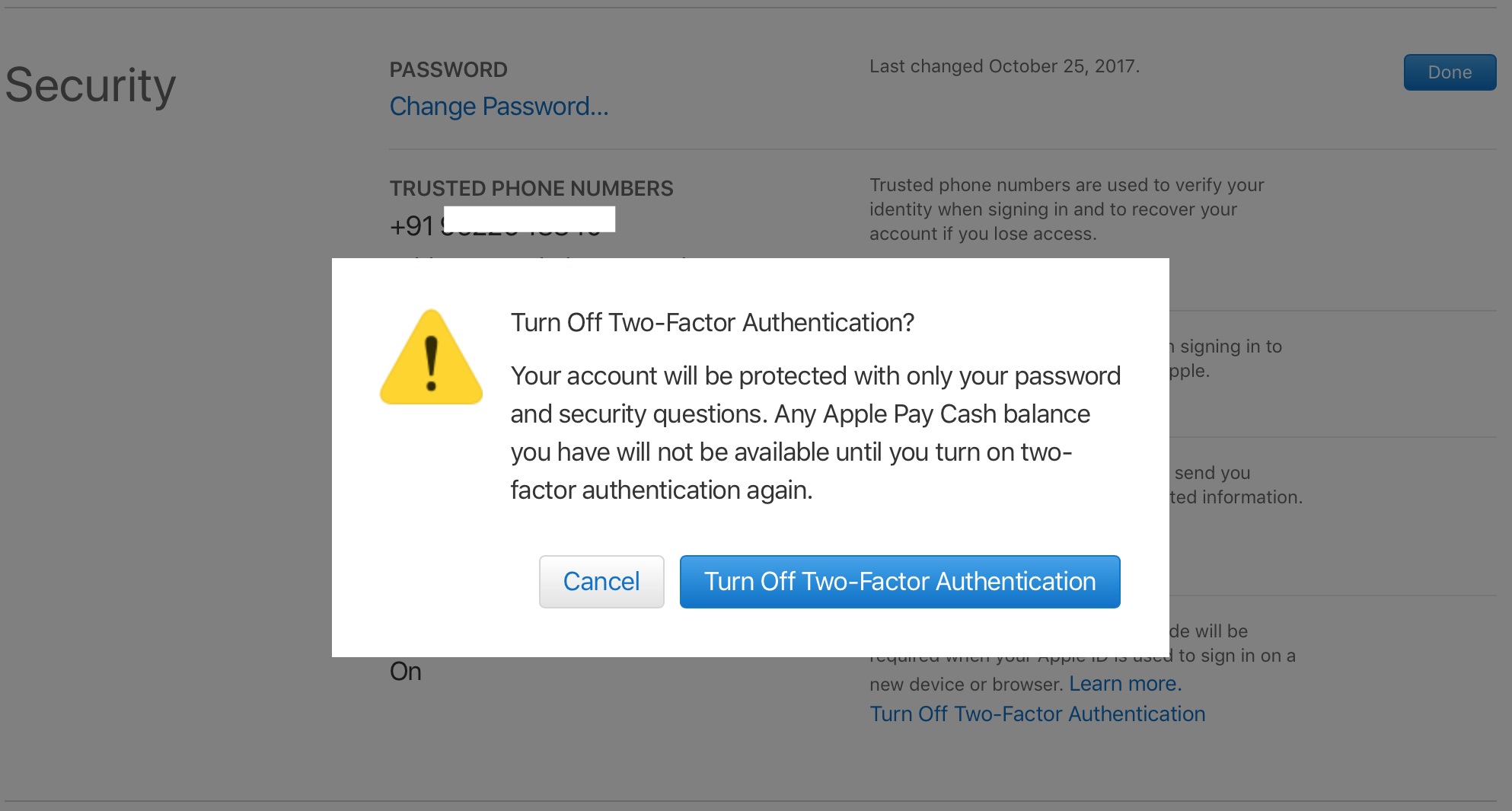
Steps to Turn Off Two-Factor Authentication
Turning off 2FA is generally a straightforward process, but it requires careful consideration to ensure that account security is not compromised. Here are the steps to turn off 2FA for various platforms:
Read more: How To Turn Chromecast Off
Turning Off 2FA on Wikipedia
Wikipedia uses a time-based one-time password (TOTP) system for its administrators. To turn off 2FA on Wikipedia, follow these steps:
- Log In with 2FA: First, log in with your current 2FA setup.
- Navigate to Preferences: Once logged in, navigate to your preferences page.
- Disable 2FA: Look for the section related to two-factor authentication and select the option to disable it.
- Confirm Disabling: You may be prompted to confirm that you want to disable 2FA. Ensure you understand the implications before proceeding.
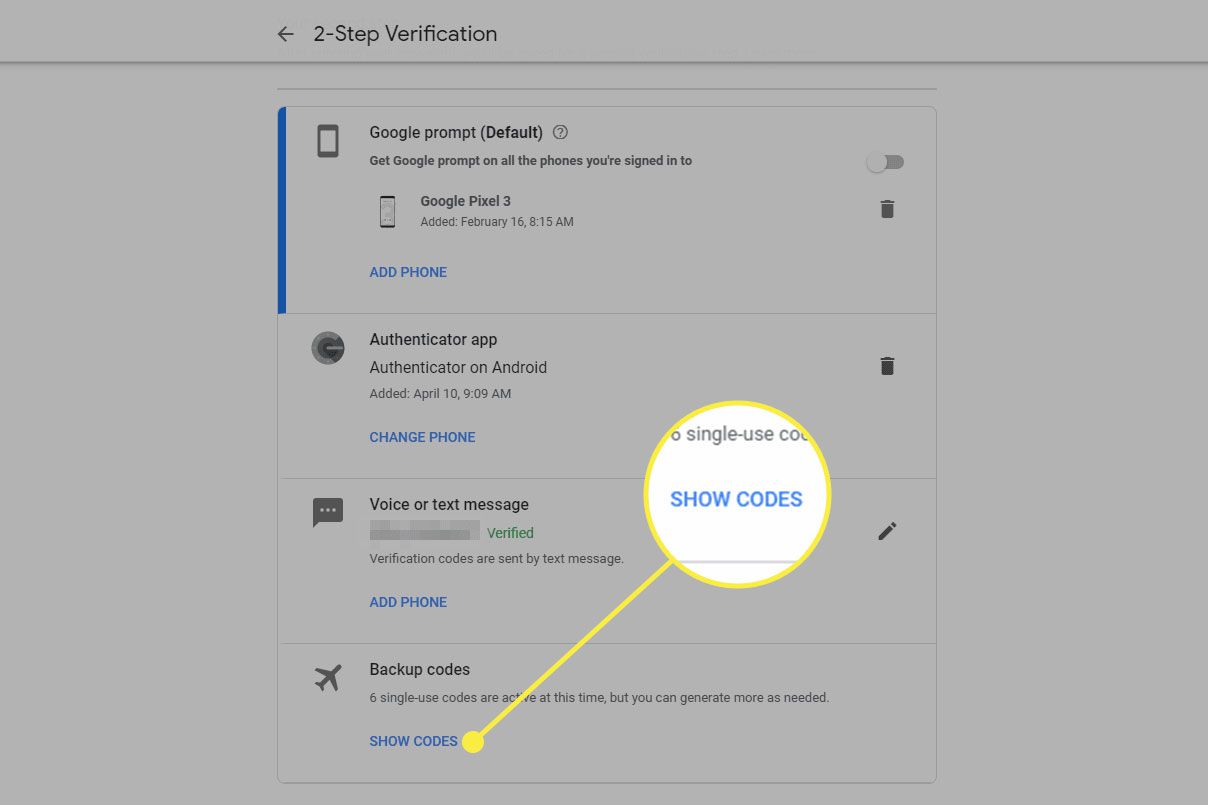
Turning Off 2FA on Google Accounts
Google accounts support various methods of 2FA, including SMS codes and authenticator apps. Here’s how you can turn it off:
- Log In with 2FA: Start by logging in with your current 2FA setup.
- Go to Security Settings: After logging in, go to your Google account settings and navigate to the security section.
- Select 2-Step Verification: Find the option for 2-step verification and click on it.
- Turn Off 2-Step Verification: Select the option to turn off 2-step verification.
- Confirm Disabling: You may be prompted to confirm that you want to disable 2-step verification. Make sure you understand the implications before proceeding.
Turning Off 2FA on Other Platforms
The process of turning off 2FA can vary depending on the platform or service you are using. Here are some general steps that might apply:
- Log In with 2FA: First, ensure you are logged in with your current 2FA setup.
- Navigate to Security Settings: Look for a section related to security or account settings.
- Find 2FA Option: Locate the option specifically related to two-factor authentication.
- Disable 2FA: Select the option to disable two-factor authentication.
- Confirm Disabling: You may be prompted to confirm that you want to disable 2FA. Understand the implications before proceeding.
Potential Risks of Disabling Two-Factor Authentication
Disabling 2FA can expose your account to potential risks, especially if you are not using a strong password or if you are in a high-risk environment (e.g., public Wi-Fi). Here are some potential risks:
- Increased Vulnerability to Phishing Attacks: Without 2FA, phishing attacks become more effective because hackers only need your password to gain access.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering attacks can trick users into revealing their passwords, and without 2FA, these attacks become more successful.
- Account Compromise: If your password is compromised, disabling 2FA makes it easier for hackers to gain full access to your account.
Read more: How To Turn Off VPN On Chromebook
Best Practices for Managing Two-Factor Authentication
While turning off 2FA might be necessary in certain situations, it's crucial to manage it wisely to maintain account security:
- Use Strong Passwords: Always use strong, unique passwords for each account.
- Keep Devices Updated: Ensure that all devices used for 2FA are updated with the latest software and security patches.
- Backup Recovery Codes: If available, backup recovery codes in a secure location to avoid losing access to your account.
- Regularly Review Settings: Periodically review your account settings to ensure that 2FA is enabled where necessary.
Additional Considerations
- Businesses and Organizations: Businesses like banks often use shared secret information that both sides know to re-authenticate users and reset their 2FA in case they lose access to their authentication device.
- Technical Hurdles: There are technical hurdles such as the lack of a helpdesk for users to report issues with 2FA and no good way to positively identify users who break their 2FA, requiring a reset.
- User Adoption: The potential loss of good admins due to the requirement of using 2FA can outweigh any reduction in security breaches, especially if the system is not well-managed.
By understanding these considerations, you can make informed decisions about when and how to turn off two-factor authentication, ensuring that your online security remains robust while minimizing inconvenience.