Home>Latest News>Technology Trends>Creating Augmented Reality Buildings


Technology Trends
Creating Augmented Reality Buildings
Modified: September 5, 2024
Stay ahead of the curve with the latest technology trends in creating augmented reality buildings. Explore the future of architecture and construction with cutting-edge AR technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- What is Augmented Reality?
- Applications of Augmented Reality in Architecture
- Benefits of Augmented Reality for Architecture
- Tools and Software for Creating Augmented Reality Experiences
- Equipment Needed for AR Experiences
- Case Studies and Examples
- Challenges and Limitations
- Future of Augmented Reality in Architecture
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the real world. Using a camera and software, it recognizes and tracks real-world objects, adding virtual content to the view. This can include text, images, 3D models, and animations. Unlike Virtual Reality, which creates an entirely artificial environment, AR enhances our experience of the real world by adding digital elements.
Read more: Creating DIY Augmented Reality Glasses
Applications of Augmented Reality in Architecture
Visualization
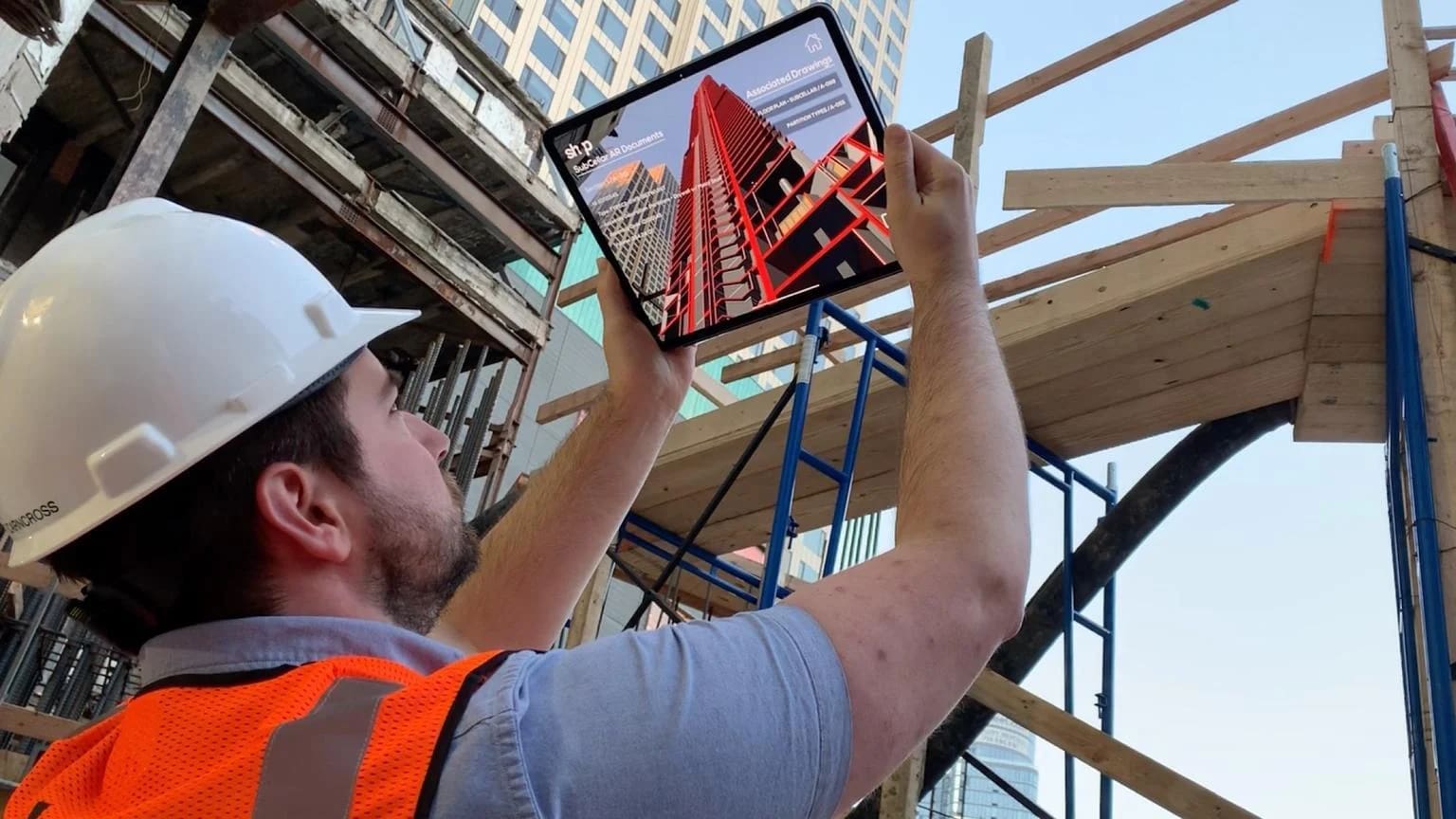
AR helps architects create digital overlays of building models onto the real world. This allows clients and stakeholders to visualize designs in a more immersive way, improving communication and understanding.
Collaboration
AR facilitates collaboration between architects, contractors, and clients. By creating a shared digital environment, all parties can make design decisions and solve problems in real-time, leading to more efficient decision-making.
Design Exploration
Architects can explore different design options quickly using AR. By overlaying various design elements onto the real world, they can better understand how different options will look and feel in the actual space.
Marketing
AR serves as a powerful marketing tool. By creating immersive, interactive experiences, architects can showcase designs to potential clients, giving them a taste of what it would be like to live or work in the building.
Benefits of Augmented Reality for Architecture
-
Better Communication: AR enables architects to communicate designs in a more engaging way, leading to better understanding and buy-in from clients and stakeholders.
-
Improved Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between architects, contractors, and clients, leading to more efficient decision-making and problem-solving.
-
Time and Cost Savings: Allows architects to explore different design options quickly, helping save time and reduce design process costs.
-
Improved Design Quality: Provides a more immersive and realistic view of the design, helping architects create better, more impactful designs.
Tools and Software for Creating Augmented Reality Experiences
3D Modeling Software
Architects use 3D modeling software to create detailed models of buildings. Popular options include SketchUp, Rhino, and Revit. These tools enable the design of complex structures with precision and accuracy, which are then used to create AR experiences.
Read more: The Advantages of Augmented Reality
AR Software
AR software is essential for overlaying digital content onto the real world. Tools like Unity and Unreal Engine are widely used due to their robust features and ease of use. These platforms allow architects to import 3D models from various sources, including CAD files, and integrate them with real-world environments using AR technology.
Tracking Markers
Tracking markers are physical objects, such as QR codes or images, placed in the real world and used by AR software to anchor digital content. They help the AR system understand the spatial relationship between the real world and virtual content, ensuring a seamless and accurate experience.
Equipment Needed for AR Experiences
AR-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or AR headsets, are necessary to experience augmented reality. These devices come equipped with cameras and sensors that allow them to track the real world and overlay digital content on top of it. The choice of device depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as the level of immersion needed and the complexity of the design.
Case Studies and Examples
Read more: Creating an Augmented Reality App
End-User Involved Design Review
A study published in Applied Sciences in 2020 explored the effectiveness of AR in end-user involved design collaboration. The study found that AR significantly improved the quality of visual presentation, user acceptability, and user experience during design reviews. Participants reported higher satisfaction levels with the use of AR, indicating its potential to enhance collaboration and communication in architectural design.
Visualization in Real-World Settings
In another example, architects used AR to visualize a new skyscraper in a bustling city. By overlaying a 3D model of the building onto the real-world environment, they demonstrated how the structure would interact with its surroundings. This immersive experience helped stakeholders understand the design's impact on the urban landscape, leading to more informed decision-making.
Challenges and Limitations
While AR offers numerous benefits, it also comes with some challenges and limitations. One primary concern is the need for high-quality tracking markers to ensure accurate overlaying of digital content. Additionally, the cost of AR-enabled devices and software can be a barrier for some projects, particularly smaller-scale developments. Furthermore, integrating AR technology into existing workflows can be complex, requiring substantial training and support.
Future of Augmented Reality in Architecture
The future of AR in architecture looks promising, with advancements in technology expected to further enhance its capabilities. As AR technology continues to evolve, more sophisticated applications in the field of architecture are anticipated. For instance, the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms will enable more complex and dynamic AR experiences, allowing architects to create even more realistic and immersive designs.